Technologies
IPhone 15 and USB-C: Expect a Cable Mess, but It Might Not Bug You
Commentary: USB-C’s versatility in charging and data transfer brings complications that millions of customers will now get to experience firsthand.

I love USB-C, the data and charging port I first encountered in my 2016 MacBook Pro that’s now spread to almost every device in my life.
I wanted a USB-C iPhone in 2018, back when Apple first added that tech to the iPad Pro. I grew more optimistic in 2021, when Apple spread USB-C to lower-end iPads. And though I’m skeptical that regulation is the best way to direct product development, I’m not displeased that the European Union has now pushed Apple toward USB-C. Charging everything with USB-C is great for me.
So I’m psyched the iPhone 15 models all get USB-C ports. But here’s the bad news Apple didn’t share at its iPhone launch event Tuesday: Millions of people entering the USB-C ecosystem will encounter the technology’s ugly side, too.
The utility and flexibility of USB-C are tainted by confusion over just what the heck comes along with that USB-C port on the side of a device and the cable you plug into it. In short, it’s not always obvious whether your device or cable supports high-speed data transfer, high electrical power for fast charging, both, or neither.
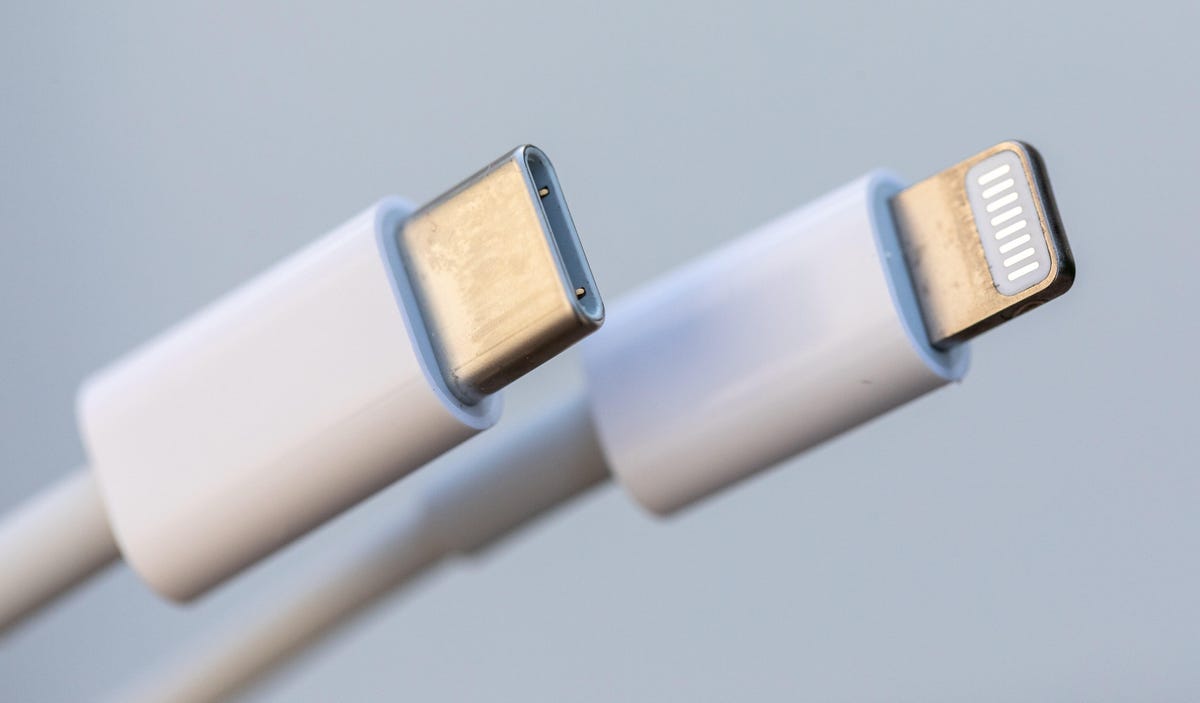
As the rumors predicted, the iPhone 15 will ship with a USB-C port and charging cable that’ll give customers a taste of the trouble. That cable reportedly will be fine for charging but will transfer data at a mere 480 megabytes per second, the poky speed that arrived with the USB 2.0 standard from 2000.
During its launch event, Apple conspicuously avoided saying anything about how fast the iPhone 15 USB-C port is, but the spec sheet says it’s only slow USB 2.0. The iPhone 15 Pro models will work at the more useful 10Gpbs speed of USB 3.
More from the Apple event
For most folks, the problem is likely to be merely an inconvenience. But it reflects the difficulties of the vast USB ecosystem, where the pressure to keep costs low is fierce and certification isn’t required. USB-C is a much faster, more useful connection technology than the Apple Lightning port iPhone users have had since 2012, but Apple customers will have to endure some pain leaving the cozy Lightning world.
Apple didn’t respond to a request for comment for this article. But it did tout this major change on what’s arguably the single most important gadget on the planet. For one thing, USB-C means a single charging cable is all you need for many Apple devices. For another, you’ll be able to use your iPhone to charge your AirPods. And on iPhone 15 Pro phones, you’ll be able to record data-intensive 4K 60fps ProRes video to an external storage device.
The triple whammy USB mess
Part of the problem with USB is that the term actually refers to three separate standards. Let me explain.
The original standard, Universal Serial Bus, governs how devices identify themselves and send data across a connection. USB arrived in 1996 with a top speed of 12Mbps, but USB 2.0 was much more useful at 480Mbps, enough for printers and thumb drives. The first big speed jump after that was USB 3.0 in 2008 at 5 gigabits per second, better for external hard drives. Successors hit 10Gbps, 20Gbps, and most recently 40Gbps with USB 4. The upcoming USB 4 version 2 should reach 80Gbps. That’s good for high-performance storage systems, fast networks, and big, high-resolution monitors.
The next standard is USB-C, which refers only to the oval-shaped connector technology. Earlier in USB-C’s history, it was common for Android phones to support only slow USB 2.0 data transfer speeds, though that problem has faded with newer models. The newest USB standard, USB 4.0, requires USB-C ports, so as time goes by, it’ll be fairer to equate USB-C with high speed.
Last is USB PD, short for Power Delivery, which governs how USB is used for charging at rates up to 240W. Most devices don’t require that much power, but they do need to know how to negotiate electrical matters — for example, whether a portable battery should charge your laptop or vice versa.

Having three standards — USB, USB-C and USB PD — makes it harder to understand the abilities of all your devices and cables.
Worse, plenty of device manufacturers trying to cut costs and quickly ship products skip the certification process that the USB Implementers Forum offers. Unlike with Intel’s Thunderbolt, which developed the fast data transfer approach in modern USB, there’s no requirement to pass tests.
Low costs fuel USB-C’s problems
Nobody wants to spend $60 instead of $15 for a USB cable. But be careful: You get what you pay for, roughly. It’s more expensive to build cables that support high-speed data or high-power charging. One rule of thumb: Cables billed as «charging cables» in my experience don’t bother with the extra cost of high-speed data support. That includes the USB-C cables Apple itself shipped with MacBooks for several years.
One affordable cable I saw billed itself as a USB 4 product, but on deeper inspection, it turned out to support only USB 2.0 data transfer. Either the manufacturer was confused, lying, or trying to argue that the cable would work in a USB 4 port even if it only supported slow data rates. (USB’s good backward compatibility means slower, older products generally still work fine when attached to newer ones.)
I haven’t struggled too much with the slow cable problem. Mostly I use USB-C for charging, and my devices that need fast connections stay attached to their own fast cables.
But problems can happen. A couple of months ago, when I got a new Canon mirrorless camera, I was caught on a trip with slow cables that really bogged down the process of transferring photos to my laptop.
When USB-C is a problem and when it’s not
The good news for future iPhone owners is that most of them won’t have to care much about whether they have a slow cable. Indeed, iPhone 15 non-Pro phone owners won’t be able to benefit from the speeds of a fast cable even if they have one.
Data rates were more important in the olden days when we used iTunes to sync music and photos between laptops and iPhones. Even as photo and video files have exploded in size with 50-megapixel phone cameras and 4K video, most of us get that data off our phones with mobile networks, Wi-Fi and AirDrop, not with cables.
That’s the big reason Apple could mostly justify shipping an iPhone 15 with a USB 2.0 cable.
Now, for serious data hogs, the kind of person who’s shooting many gigabytes of 4K ProRes video, a faster cable is useful. It’s one reason I’ve been annoyed with the Lightning port on my iPhone. Those customers will, I hope, generally be discriminating enough to find a high-quality cable for their needs — or, if rumors are correct, just use the faster cable that Apple will ship with iPhone 15 Pro models. (Apple hasn’t yet revealed what’s ships with the new phones.)
I prefer buying USB-C products that have passed USB-IF’s compliance testing. I look for the USB-IF certifications, and I love it when companies like Plugable attach clear descriptive labels so we don’t have to decode USB-IF icons. (And most products don’t even have icons.)
But if you’re nervous about doing the product comparisons yourself, you can always let Apple sales staff steer you to higher-end Apple USB-C accessories that generally work well together even if they’re often more expensive than third-party products.
USB-C transition less painful than Lightning
There was plenty of kvetching when Apple switched to the Lightning port, even though it was clear Lightning was superior to the bulky, fragile 30-pin connector that preceded it. I’m expecting more complaints with the iPhone’s USB-C switch as people discover that all those cables they have stashed in glove boxes, office desks, school backpacks and bedside tables have become obsolete.
But the good news is that USB-C is already very well established, and not just on MacBooks and many iPads. The oval-shaped connector is on modern Android phones, Windows laptops, Nintendo Switch gaming consoles, iPad Pro and Air tablets, Sony noise-canceling headphones and countless other devices. There’s a good chance a lot of us already have some spare USB-C cables lying around.
When I talk to USB-IF executives about the USB-C’s labeling problems, they assure me that most people don’t notice any sort of bother, and that the gradually maturing technology will mean incompatibilities and product shortcomings eventually will slip into the back of our collective junk drawers.
I hope so. For me, the flexibility and power of USB-C is well worth the pain. But I do wish there wasn’t so much pain.
Technologies
SXSW 2026 Updates: What We Expect on Tech and Culture From Austin
Technologies
Uber May Soon Let You Book a Zoox Robotaxi in Las Vegas and LA
Amazon-owned Zoox hopes to start offering paid robotaxi rides to regular riders sometime this year. Right now, the rides are free.
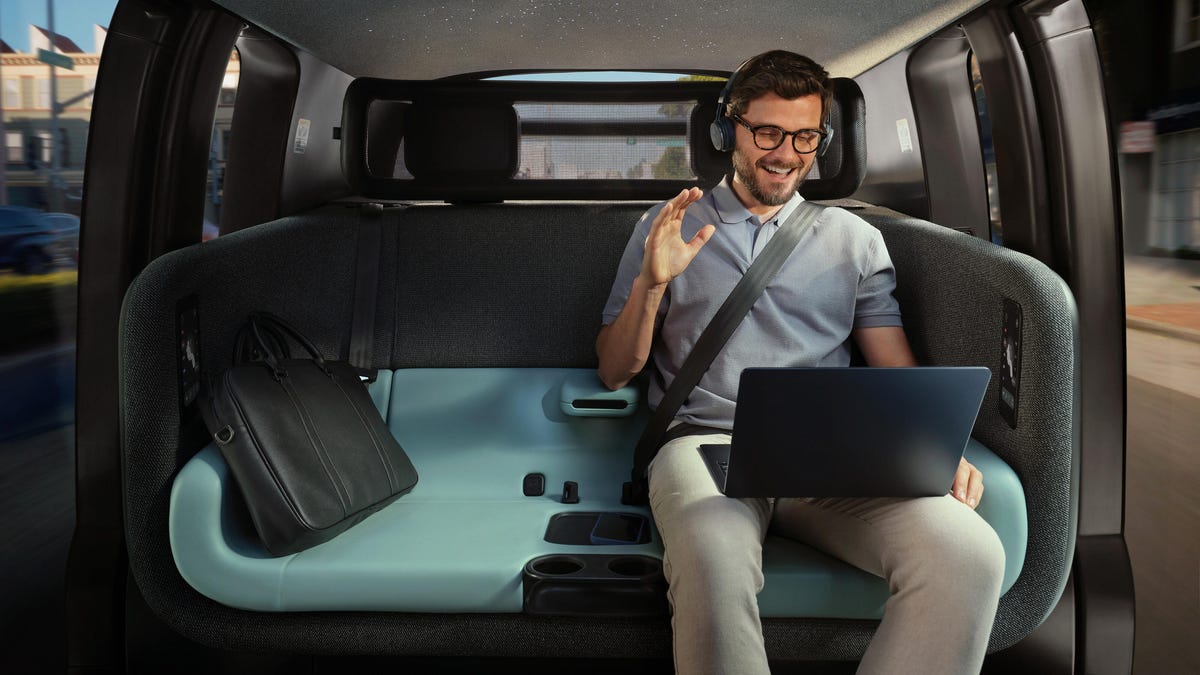

No steering wheel, no pedals, no problem. Zoox announced Wednesday that it’s partnering with Uber to make its robotaxis available on the ride-hailing company’s app in Las Vegas and Los Angeles, pending US government approval.
The multiyear partnership, announced by Zoox and Uber on Wednesday, would enable Uber customers to get rides on Zoox robotaxis in Vegas this summer and in LA in 2027. After the partnership launches, the app will match riders with robotaxis on eligible trips, Uber said in a statement. Zoox will also offer rides on its robotaxis through its own app, so customers can use either the Uber or Zoox app to ride in the vehicles.
Uber CEO Dara Khosrowshahi called Zoox an «ideal partner» in a statement.
«The Zoox robotaxi is unlike any othervehicle on the planet — it was purpose-built from the ground up to deliveran extraordinary experience,» Khosrowshahi said. «Zoox’scommitment to safety and their advanced autonomous driving technology makethem an ideal partner. We’re thrilled to work together to introduce moreriders to the future of mobility.»
Zoox, founded in 2014 and acquired by Amazon in 2020, currently offers free rides in Las Vegas and San Francisco during its demonstration phase of service. The company said its robotaxis have logged more than 1 million miles for more than 300,000 riders.
Zoox is also conducting tests in six other cities — Seattle, Miami, Los Angeles, Atlanta, Washington, DC, and Austin, Texas — and announced earlier this week that Dallas and Phoenix are next. Only people in San Francisco and Las Vegas can currently get test rides through the Zoox app.
«We’re taking a measured, step-by-step approach by starting small, learning quickly, and scaling responsibly,» Zoox said in its announcement Wednesday. «This partnership with Uber will mirror that approach, beginning with a controlled deployment with the potential to expand as we refine our operations, technology, and customer experience.»
No steering wheel
The Zoox is a fully autonomous vehicle that can carry up to four passengers (PDF). It has no steering wheel, no accelerator or brake pedals, and is bidirectional, meaning it can go forward and reverse by simply switching which end of the car is considered the front. There are touchscreens and emergency call buttons. Zoox had early issues with erratic braking that caused injuries and a crash, but addressed the issue through software updates during the ensuing investigation by the National Highway Traffic Safety Administration.
CNET’s Abrar Al-Heeti caught a ride in a Zoox in Las Vegas. She said she felt «oddly at ease as I watch a stream of cars, chain restaurants and desert landscape flash past the windows.»
Before it can start making money on its robotaxi rides, Zoox must get an exemption from the Federal Motor Vehicle Safety Standards. NHTSA is now accepting public comments on Zoox’s application for the exemption — you can post a comment here until April 10.
Zoox is seeking eight federal vehicle safety exemptions, including from rules requiring windshield wipers and windshield defrosting systems, TechCrunch reported.
Waymo is currently the main player in the US robotaxi market, with fully autonomous service in 10 US cities. But several other companies are looking to ramp up their self-driving presence this year, including Zoox, Tesla and Uber. That market expansion aligns with a Goldman Sachs forecast that more than 35,000 robotaxis will operate in the US in 2030, up from 1,500 currently. That would represent 8% of the rideshare market, with traditional human-driven rideshare comprising the other 92%.
Uber has partnerships with 25 other robotaxi services around the world, primarily Waymo — you can use the Uber app to get Waymo rides in Atlanta and Austin — and China’s Baidu, which will be testing self-driving rides in London this year.
Technologies
Today’s NYT Connections Hints, Answers and Help for March 12, #1005
Here are some hints and the answers for the NYT Connections puzzle for March 12 No.1,005.

Looking for the most recent Connections answers? Click here for today’s Connections hints, as well as our daily answers and hints for The New York Times Mini Crossword, Wordle, Connections: Sports Edition and Strands puzzles.
I spotted a couple of the categories in today’s NYT Connections puzzle, but the fact that I don’t take a lot of gym classes hurt my knowledge. You avid exercisers will have an advantage today. Read on for clues and today’s Connections answers.
The Times has a Connections Bot, like the one for Wordle. Go there after you play to receive a numeric score and to have the program analyze your answers. Players who are registered with the Times Games section can now nerd out by following their progress, including the number of puzzles completed, win rate, number of times they nabbed a perfect score and their win streak.
Read more: Hints, Tips and Strategies to Help You Win at NYT Connections Every Time
Hints for today’s Connections groups
Here are four hints for the groupings in today’s Connections puzzle, ranked from the easiest yellow group to the tough (and sometimes bizarre) purple group.
Yellow group hint: Beach time.
Green group hint: This way, then that way.
Blue group hint: Workout time.
Purple group hint: Chirp!
Answers for today’s Connections groups
Yellow group: Places to find sand.
Green group: Things that move back and forth.
Blue group: Apparatus-based exercise classes.
Purple group: Featuring birds.
Read more: Wordle Cheat Sheet: Here Are the Most Popular Letters Used in English Words
What are today’s Connections answers?
The yellow words in today’s Connections
The theme is places to find sand. The four answers are bunker, desert, hourglass and sandbox.
The green words in today’s Connections
The theme is things that move back and forth. The four answers are metronome, pendulum, swing and windshield wiper.
The blue words in today’s Connections
The theme is apparatus-based exercise classes. The four answers are barre, reformer, spin and step.
The purple words in today’s Connections
The theme is featuring birds. The four answers are cuckoo clock, Froot Loops, Mexican flag and weather vane.
-

 Technologies3 года ago
Technologies3 года agoTech Companies Need to Be Held Accountable for Security, Experts Say
-

 Technologies3 года ago
Technologies3 года agoBest Handheld Game Console in 2023
-

 Technologies3 года ago
Technologies3 года agoTighten Up Your VR Game With the Best Head Straps for Quest 2
-

 Technologies4 года ago
Technologies4 года agoBlack Friday 2021: The best deals on TVs, headphones, kitchenware, and more
-

 Technologies5 лет ago
Technologies5 лет agoGoogle to require vaccinations as Silicon Valley rethinks return-to-office policies
-

 Technologies5 лет ago
Technologies5 лет agoVerum, Wickr and Threema: next generation secured messengers
-

 Technologies4 года ago
Technologies4 года agoOlivia Harlan Dekker for Verum Messenger
-

 Technologies4 года ago
Technologies4 года agoiPhone 13 event: How to watch Apple’s big announcement tomorrow
