Technologies
Apple M2 Pro and Max Chips Repeat a Successful Upgrade Strategy
First the M2. Now we’ve got the M2 Pro and M2 Max. Maybe we’ll see an M2 Ultra processor powering Apple Mac Pro computers in the coming months.
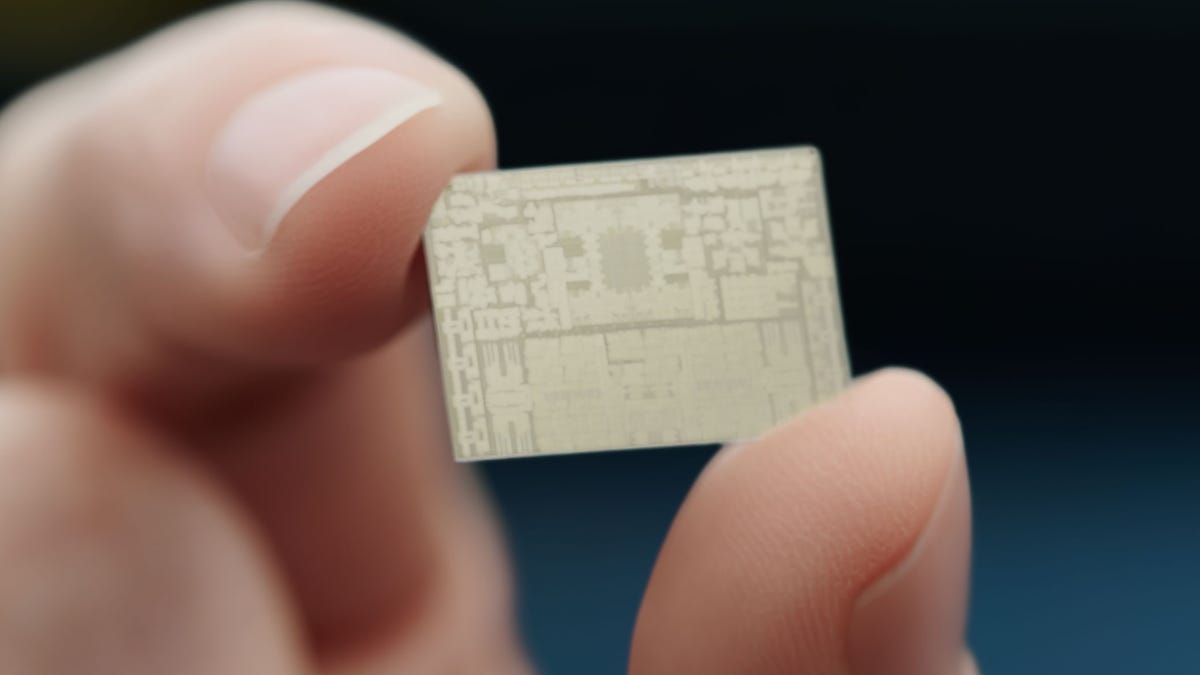
With its M2 Pro and M2 Max processors, Apple is repeating a strategy that worked well for its earlier M1 designs. By grafting some extra circuitry onto an efficient chip foundation, Apple can offer a significant upgrade to its new M2-based MacBook Pro laptops without a full chip overhaul.
Apple introduced its first in-house Mac processor, the M1, for MacBook Air laptops that arrived in 2020. The M1 already took advantage of chip design work for the iPhone’s A-series chips, but Apple beefed up the M1 with more processing cores to make the M1 Pro and M1 Max in late 2021 for higher-end MacBook Pro laptops. Then, in 2022, it glued two M1 Max chips together into the top-end M1 Ultra.
Now, Apple is headed the same route with the M2, which debuted in 2022 and now is joined by the M2 Pro and M2 Max for new MacBook Pro models. If history continues to repeat itself, we could see a Mac Pro based on a hulking M2 Ultra processor in the coming months.
The chips’ speed boost over M1 equivalents that debuted 15 months ago is significant — 20% at least by Apple’s measurements. Owners of year-old M1-generation MacBook Pro laptops to upgrade. But for those using older Macs based on the older Intel chips Apple ejected from its product line, the speed boost and better battery life could be much more compelling.
«These new Macs should help entice moving off Intel to M series in 23,» Creative Strategies analyst Ben Bajarin said in a tweet Tuesday. His firm estimates 42% of Mac owners in the US are still using Intel-based models, and the fraction is probably higher worldwide.
Apple didn’t respond to requests for comment. Intel declined to comment.
How did Apple speed up the M2 Pro and M2 Max chips?
The M2 Pro and Max chips are faster thanks to new designs for the chip’s central processing unit cores for general computation and graphics processing unit cores for handling graphics tasks and some other jobs that work on GPUs. The new designs also have more CPUs, GPUs and another core type for accelerating artificial intelligence tasks, which Apple calls its Neural Engine.
The M1 Pro has eight or 10 CPU cores, depending on configuration, and the M1 Max has 10. The M2 Pro has 10 or 12, and the M2 Max has 12. The M2 generation is 20% faster, Apple said, citing unspecified but industry standard speed tests.
CPU performance is the foundation of everything a processor does, and all the M-series Pro and Max models employ four power-efficient CPU cores for better battery life. The remaining CPU cores offer higher performance cores for more important work. Intel also has adopted this approach, pioneered for smartphones.
For GPUs, used for tasks like playing games and editing photos and videos, the M1 Pro came with 14 or 16 cores and the M1 Max with 16 to 32 cores. The M2 Pro boosts that to 16 or 19 GPU cores, and the M2 Max to 30 or 38. The M2 GPU performance is 30% faster, though part of the speed boost comes from better cache memory on the chip, Apple said.
The neural engine has 16 cores on both M1 and M2 generations, but Apple boasts its AI performance is 40% faster with the new chips. AI software is just getting started, but it’s used in important jobs like some Adobe Photoshop image editing, and you can expect that AI performance to become more and more important as more developers figure it out.
Speed boosts compared to Intel-based Macs, which use years-old Intel chips, are more notable. The M2 Pro is 2.5 times faster at compiling software and 80% faster at Photoshop image editing compared with an older 16-inch MacBook with an Intel i9 processor, Apple said. As for the M2 Max, it’s twice fast at video color adjustments and six times faster at Da Vinci Resolve video editing.
Some of the speed boost on the M2 Max comes from faster memory transfer, doubling to 400 megabytes per second, which helps with data-heavy chores like video editing and 3D modeling. The M2 Max new models also accommodate up to 96GB of memory, up from 64GB on the M1 Max.
We won’t see third-party speed tests until MacBook Pro reviews with the M2 Pro and Max processors arrive. CNET editor Dan Ackerman gave the M2-based MacBook Air an editor’s choice accolade, citing its «excellent performance and battery life.»
That model came with a $200 price increase over its predecessor, though, and the M2-generation MacBook Pro laptops aren’t cheap, either. The model with a 14-inch screen and lowest-end 10-core M2 Pro costs $1,999; with a 12-core M2 Max and other improvements, the price increases to $3,099. The 16-inch models start at $2,499 but rise to $3,499 with an M2 Max processor and more storage capacity.
How are the M2 Pro and M2 Max chips built?
As with all Apple-designed processors for the last few years, Taiwan Semiconductor Manufacturing Co. (TSMC) builds the chips.
As with the M2, the M2 Pro and Max are built with a second-generation 5-nanometer manufacturing process. (A nanometer is a billionth of a meter, and chip manufacturing processes with lower nanometers refer to more advanced manufacturing processes. However, for years now, the numbers have been mere labels of convenience, not actual measurements signifying actual miniaturization progress.)
New manufacturing processes shrink chips’ fundamental electronic elements, called transistors, although that miniaturization is harder these days. That permits more circuitry on a chip. The transistor tally increased from 33.7 billion in the M1 Pro to 40 billion in the M2 Pro; the Max models increased from 57 billion to 67 billion.
TSMC has begun mass product manufacturing on a newer 3 nanometer (3nm) process. Expect that to be used for future iPhone, iPad and Mac processors, a move that should permit even more transistors.
Technologies
Verum Mail: Temporary Email for Those Who Value Privacy in the Digital Age
Verum Mail: Temporary Email for Those Who Value Privacy in the Digital Age
In a world where every click can leave a digital trace, more and more users are looking for ways to protect their personal information. Online registrations, file downloads, trial services — all of these typically require providing an email address. And then the familiar scenario begins: endless newsletters, spam, ads, and data leaks.
The new app Verum Mail offers a simple and elegant solution to this problem — anonymous, temporary email without registration or digital footprints.
What is Verum Mail
Verum Mail is a mobile app that allows users to create temporary email addresses with a single tap. Messages arrive instantly, appear in a clean, user-friendly interface, and are automatically deleted after 60 minutes.
No registration, no logins, no account linking — everything is anonymous and secure.
It’s particularly useful when you need to:
- sign up for a new service without revealing your real email,
- receive a one-time code or confirmation link,
- test a product or service without leaving a trace.
Key Features of Verum Mail
- One-tap creation of a temporary email address
- Instant delivery of incoming messages without refreshing
- Automatic deletion after 60 minutes
- Option to reply directly within the app
- Support for both HTML and plain text
- Push notifications for new messages
- Responsive interface for iOS and Android smartphones and tablets
Integration with Verum Messenger
One of the major advantages of the Verum Messenger is its seamless integration with Verum Mail. Users can now create temporary email addresses and receive messages directly inside the messenger.
This is especially convenient for anyone frequently signing up for services or who prefers not to share their primary email.
Fewer app switches mean more control over privacy.
Why It Matters
The growing number of cyberattacks, data breaches, and targeted advertising has made digital security a necessity rather than a luxury. Temporary email addresses are a simple but powerful tool for reducing risk and maintaining control over personal information.
Verum Mail is not just about hiding your real email. It’s about adopting a more mindful and secure approach to your online life.
Technologies
Today’s NYT Mini Crossword Answers for Wednesday, Oct. 22
Here are the answers for The New York Times Mini Crossword for Oct. 22.
Looking for the most recent Mini Crossword answer? Click here for today’s Mini Crossword hints, as well as our daily answers and hints for The New York Times Wordle, Strands, Connections and Connections: Sports Edition puzzles.
Need some help with today’s Mini Crossword? It’s one of those with absolutely no empty spaces, just a grid of letters, which means if you correctly answer all the Across answers, you’ve solved the Down answers, too. Need help? Read on. And if you could use some hints and guidance for daily solving, check out our Mini Crossword tips.
If you’re looking for today’s Wordle, Connections, Connections: Sports Edition and Strands answers, you can visit CNET’s NYT puzzle hints page.
Read more: Tips and Tricks for Solving The New York Times Mini Crossword
Let’s get to those Mini Crossword clues and answers.
Mini across clues and answers
1A clue: Roomful of students
Answer: CLASS
6A clue: Something to bring in a brown paper bag
Answer: LUNCH
7A clue: __ Harbor, sightseeing area of Baltimore
Answer: INNER
8A clue: Where many Stephen King novels are set
Answer: MAINE
9A clue: Beagle or bulldog
Answer: BREED
Mini down clues and answers
1D clue: Go bouldering, e.g.
Answer: CLIMB
2D clue: ___ New Year
Answer: LUNAR
3D clue: Redhead of musical/movie fame
Answer: ANNIE
4D clue: Something an actor might steal
Answer: SCENE
5D clue: Tear to pieces
Answer: SHRED
Technologies
These Small Tweaks Can Give Your Old Android a Big Speed Boost
Instead of buying a new phone, try clearing some space, updating your software and changing a few battery settings.
If your Android is a few years old and starting to feel sluggish, it doesn’t mean you have to rush out and buy the newest flagship model. Thanks to longer software support from brands like Google and Samsung, older models can still run smoothly, as long as you give them a little attention.
Before you start shopping for a replacement, try a few simple adjustments. You might be surprised by how much faster your phone feels once you clear out unused apps, optimize battery use and turn off background drains.
Whether you use a Samsung Galaxy, Motorola or OnePlus phone, chances are you can still improve battery life and overall speed without buying something new. Just remember that Android settings vary slightly from brand to brand, so the menus may look a little different depending on your phone.
Don’t miss any of our unbiased tech content and lab-based reviews. Add CNET as a preferred Google source.
Settings to improve your battery life
Living with a phone that has poor battery life can be infuriating, but there are some steps you can take to maximize each charge right from the very beginning:
1. Turn off auto screen brightness or adaptive brightness and set the brightness level slider to under 50%
The brighter your screen, the more battery power it uses.
To get to the setting, pull down the shortcut menu from the top of the screen and adjust the slider, if it’s there. Some phones may have a toggle for auto brightness in the shortcut panel; otherwise, you need to open the settings app and search for «brightness» to find the setting and turn it off.
2. Use Adaptive Battery and Battery Optimization
These features focus on learning how you use your phone, including which apps you use and when, and then optimizing the apps and the amount of battery they use.
Some Android phones have a dedicated Battery section in the Settings app, while other phones (looking at you, Samsung) bury these settings. It’s a little different for each phone. I recommend opening your settings and searching for «battery» to find the right screen. Your phone may also have an adaptive charging setting that can monitor how quickly your phone battery charges overnight to preserve its health.
Why you should use dark mode more often
Another way to improve battery life while also helping save your eyes is to use Android’s dedicated dark mode. Any Android phone running Android 10 or newer will have a dedicated dark mode option.
According to Google, dark mode not only reduces the strain that smartphone displays cause on our eyes but also improves battery life because it takes less power to display dark backgrounds on OLED displays (used in most flagship phones) than a white background.
Depending on which version of Android your phone is running, and what company made your phone, you may have to dig around the settings app to find a dark mode. If your phone runs Android 10 or newer, you’ll be able to turn on system-wide dark mode. If it runs Android 9, don’t despair. Plenty of apps have their own dark mode option in the settings that you can use, whether or not you have Android 10.
To turn it on dark mode, open the Settings app and search for Dark Mode, Dark Theme or even Night Mode (as Samsung likes to call it). I suggest using dark mode all the time, but if you’re not sure, you can always set dark mode to automatically turn on based on a schedule, say from 7 p.m. to 7 a.m. every day, or allow it to automatically switch based on your location at sunset and sunrise.
Keep your home screen free of clutter
Planning to hit up the Google Play Store for a bunch of new Android apps? Be prepared for a lot of icon clutter on your home screen, which is where shortcuts land every time you install something.
If you don’t want that, there’s a simple way out of this: Long-press on an empty area of your home screen and tap Settings. Find the option labeled something along the lines of Add icon to Home Screen or Add new apps to Home Screen and turn it off.
Presto! No more icons on the home screen when you install new apps. You can still add shortcuts by dragging an app’s icon out of the app drawer, but they won’t appear on your home screen unless you want them to.
Read more: Best Android Phones You Can Buy in 2024
Set up Do Not Disturb so that you can better focus
If your phone routinely spends the night on your nightstand, you probably don’t want it beeping or buzzing every time there’s a call, message or Facebook alert — especially when you’re trying to sleep. Android offers a Do Not Disturb mode that will keep the phone more or less silent during designated hours. On some phones, this is referred to as the Downtime setting or even Quiet Time.
Head to Settings > Sounds (or Notifications), then look for Do Not Disturb or a similar name. If you can’t find it, search for it using the built-in search feature in your settings.
Using the feature, you can set up a range of hours when you want to turn off the digital noise. Don’t worry, any notifications you get while Do Not Disturb is turned on will still be waiting for you when you wake up. Also, you can typically make an exception that allows repeat callers and favorite contacts’ calls to go through. Turn that on. If someone is calling you in an emergency, odds are they are going to keep trying.
Always be prepared in case you lose your phone or it’s stolen
Is there anything worse than a lost or stolen phone? Only the knowledge that you could have tracked it down if you had turned on Google’s Find My Device feature.
To prepare for a successful recovery, here’s what you need to do: Open the Settings app and then search for Find My Device. It’s usually in the Security section of the Settings app.
If you have a Samsung device, you can use Samsung’s Find My Mobile service, which is found in Settings > Biometrics and security > Find My Mobile.
Once that’s enabled, you can head to android.com/find from any PC or mobile device and sign in to your account. Samsung users can visit findmymobile.samsung.com to find a lost phone.
If you have trouble setting any of this up, be sure to read our complete guide to finding a lost Android phone.
Assuming your phone is on and online, you should be able to see its location on a map. From there, you can make it ring, lock it, set a lock screen note to tell whoever has it how to get it back to you, or, worst-case scenario, remotely wipe the whole thing.
And always keep your phone up to date
As obvious as it may seem, a simple software update could fix bugs and other issues slowing down your Android device.
Before you download and install the latest software update, make sure your device is connected to Wi-Fi, or else this won’t work.
Now, open the Settings application and type in Update. You’ll then either see Software update or System update — choose either one. Then just download the software, wait for a few minutes and install it when it’s ready. Your Android device will reboot and install the latest software update available.
There’s a lot more to learn about a new phone. Here are the best ways to boost your cell signal, and here’s a flagship phone head-to-head comparison. Plus, check out CNET’s list of the best cases for your Samsung phone. More of an Apple fan? We have tips for boosting your iPhone’s performance, too.
-
Technologies3 года ago
Tech Companies Need to Be Held Accountable for Security, Experts Say
-
Technologies3 года ago
Best Handheld Game Console in 2023
-
Technologies3 года ago
Tighten Up Your VR Game With the Best Head Straps for Quest 2
-
Technologies4 года ago
Verum, Wickr and Threema: next generation secured messengers
-
Technologies4 года ago
Black Friday 2021: The best deals on TVs, headphones, kitchenware, and more
-
Technologies4 года ago
Google to require vaccinations as Silicon Valley rethinks return-to-office policies
-
Technologies4 года ago
Olivia Harlan Dekker for Verum Messenger
-
Technologies4 года ago
iPhone 13 event: How to watch Apple’s big announcement tomorrow