Technologies
Android 14 Beta 3 Is Available for Download on Your Phone Right Now
You can install the latest Android beta release on your compatible Pixel device.

Google dropped Android 14 Beta 3 in a blog post today. The prerelease software, which mostly fixes bugs, is available to download and install on the Pixel 4A 5G and later. There is only one more Android 14 beta release, slated for July, before the public Android 14 update comes out in the fall.
Android 14 in general will bring tweaks and revamps, including updates to the Android system UI and improvements to privacy and security.
Android 14 Beta 3 is the latest preview of Google’s mobile system, which first went to developers with the Android 14 developer preview, to test before the general release.
Read more: Second Android 14 Developer Preview Adds More App Customization
Prior to the beta releases of Android 14, the process of installing Android developer previews wasn’t super easy. It involved unlocking developer options, downloading a sizable file, factory resetting your device and more. Now, it’s much more simple to download and install the latest Android 14 beta.
The final version of Android 14 will eventually be the most accessible way to get it, but that’s not expected until later this year. If you really want an early look at what’s coming, and you have a supported Android device, such as the Pixel 7 or Pixel 7 Pro, you can begin testing Android 14 beta 3 right now. Here’s how.
While you’re here, check out the best Android phones you can buy in 2023 and how the Galaxy S22 and S23 stack up against each other.
A console-level control for your Android that’s compatible with popular cloud gaming services like Xbox Game Pass Ultimate, Steam Link and GeForce Now, as well as hundreds of mobile games like Minecraft, Fortnite and Roblox.
Is the Android 14 beta safe to download?
Although the Android 14 beta is more refined and solid than the Android 14 developer preview, you should still expect bugs with this release that may make your phone more difficult to use. Only download the Android 14 beta if you’re willing to deal with these issues or if your device is a backup from your daily phone. Also, make sure to back up your device before downloading the Android 14 beta, in case something goes wrong or you decide to leave the program later.
Note: Some of the new features that are in development might not end up in the final version of Android 14, so anything you do use should be considered an early preview and not necessarily final.
Which Android devices are compatible with the Android 14 beta?
For now, only a select number of Pixel smartphones support Android 14:
You can check out if your device is compatible with Android 14 Beta here. We’ll add more devices to this list as they become supported. While not listed, the just-released Pixel 7A may also be able to run the beta.
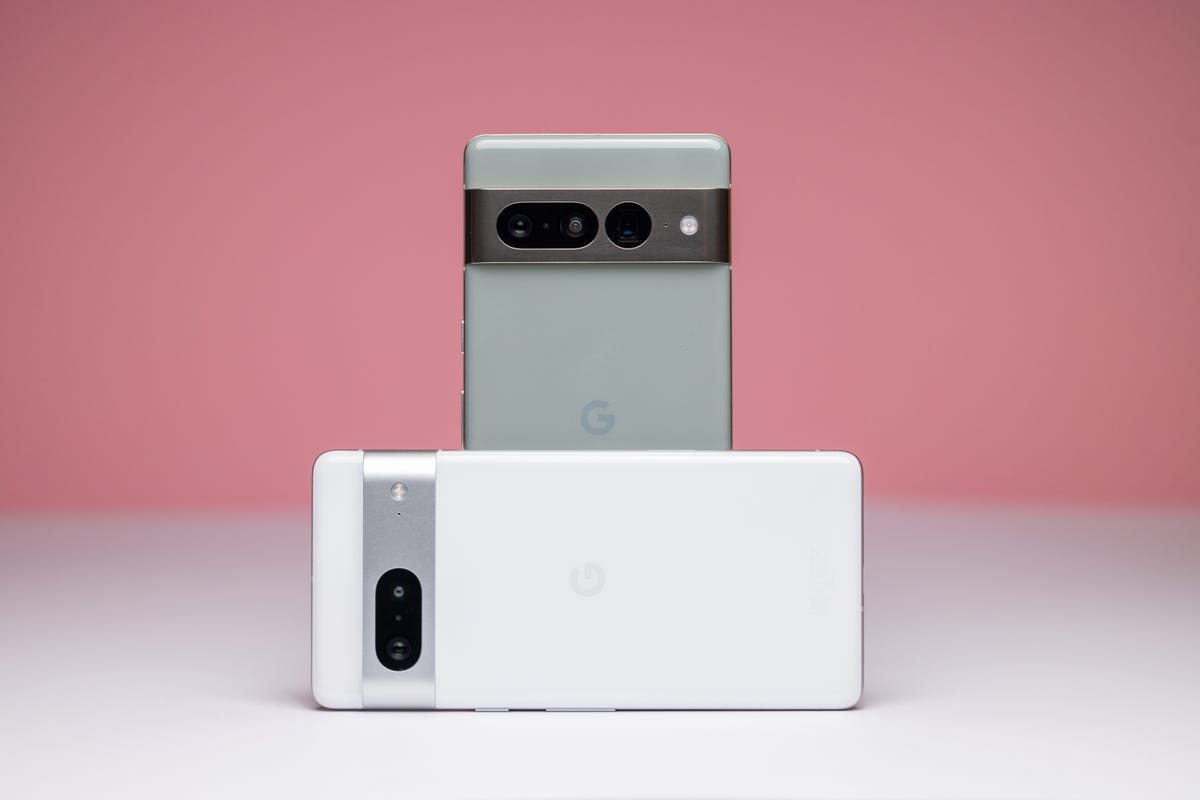

The Pixel 7 and Pixel 7 Pro are two of the currently supported devices that can currently run Android 14 beta.
How to download Android 14 Beta 3 on your supported device
The easiest way to download Android 14 Beta 3 on your phone is to go to the Android Beta for Pixel page on your computer, check if your device is supported and then enroll in the Android 14 program.
Under the Your eligible devices option, you should see your phone if it is supported (make sure your phone is charged over 10% or else it may not appear).
As long as you haven’t signed up for the Android 13 beta or Android 14 developer preview, you will see the option to opt in. If you’ve already signed up for the aforementioned prereleases, you don’t need to do anything to get Android 14 Beta 3. You should automatically receive an over-the-air update on your phone.
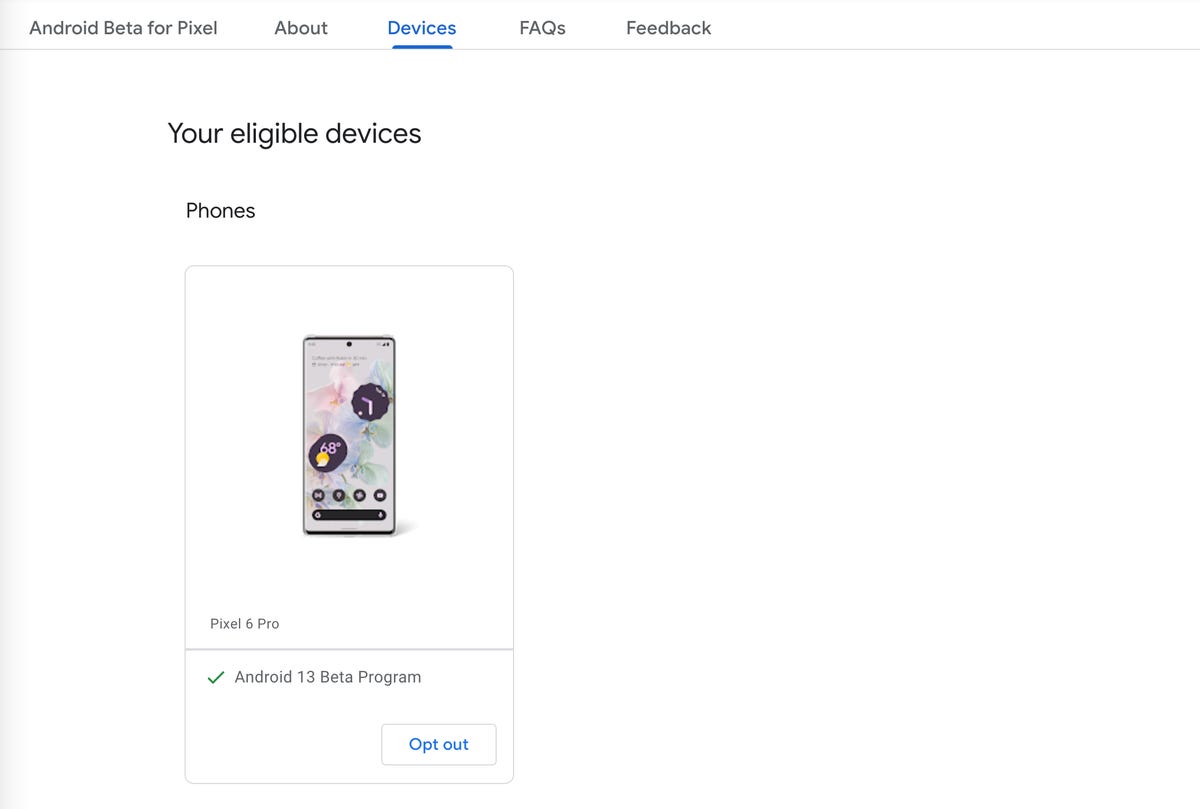
If your device supports Android 14 beta, it will appear under «Your eligible devices.»
To enroll in the Android 14 beta, click Opt in and then click Confirm and enroll after reading the terms and conditions. You should see a notification that says your device is now part of the Android 14 beta program.
You will then receive an over-the-air update on your phone. If you don’t get a notification on your phone, go to Settings > System > System update to view your Android 14 update. It may take up to 24 hours to receive the OTA update.
How long will the Android 14 beta last for?
You should expect updates up until the public release of Android 14, which will likely launch sometime in the fall of this year. According to Google, you should receive an update a month in May and June, with two in July.
Also, the Android 14 beta program as a whole will continue until next year, which means that you’ll continuously receive beta updates up until the next beta release, unless you opt out.
How do I opt out of the Android 14 beta?
To opt out of the Android 14 beta program, go back to the Android Beta for Pixel page, but this time click Opt out. Within 24 hours, you should receive an OTA update on your phone that will wipe out all your locally saved data and provide you with whatever the latest public version of Android is at the time. As mentioned before, this is why you need to back up your device before enrolling in the Android 14 beta program.
Technologies
The Most Exciting Video Game Rumors and Leaks Ahead of 2026
Technologies
Today’s NYT Mini Crossword Answers for Wednesday, Dec. 17
Here are the answers for The New York Times Mini Crossword for Dec. 17.

Looking for the most recent Mini Crossword answer? Click here for today’s Mini Crossword hints, as well as our daily answers and hints for The New York Times Wordle, Strands, Connections and Connections: Sports Edition puzzles.
Need some help with today’s Mini Crossword? Read on. And if you could use some hints and guidance for daily solving, check out our Mini Crossword tips.
If you’re looking for today’s Wordle, Connections, Connections: Sports Edition and Strands answers, you can visit CNET’s NYT puzzle hints page.
Read more: Tips and Tricks for Solving The New York Times Mini Crossword
Let’s get to those Mini Crossword clues and answers.
Mini across clues and answers
1A clue: Nod (off)
Answer: DOZE
5A clue: Naval submarine in W.W. II
Answer: UBOAT
7A clue: Tricky thing to do on a busy highway
Answer: MERGE
8A clue: Heat-resistant glassware for cooking
Answer: PYREX
9A clue: Put into groups
Answer: SORT
Mini down clues and answers
1D clue: Break up with
Answer: DUMP
2D clue: Falls in line, so to speak
Answer: OBEYS
3D clue: Legendary vigilante who cuts a «Z» with his sword
Answer: ZORRO
4D clue: Rarin’ to go
Answer: EAGER
6D clue: Common reminder for an upcoming appointment
Answer: TEXT
Don’t miss any of our unbiased tech content and lab-based reviews. Add CNET as a preferred Google source.
Technologies
You Can Watch an Exclusive Avatar: Fire and Ash Scene on TikTok Right Now
Disney and TikTok partner on an immersive content hub for James Cameron’s latest movie about the alien Na’vi.
If you’re not quite ready to head to the theater to watch Avatar: Fire and Ash, an exclusive scene preview might sell you on the visual spectacle. As part of a new collaboration with the social media giant, Disney is posting snippets of its new movie to its TikTok account.
This scene isn’t part of any trailer and won’t be posted to other social media accounts, making TikTok the only place you can view it — unless you buy a movie ticket. A first look at the new movie’s scenes isn’t the only Avatar-related bonus on the social media platform right now, either. TikTok has partnered with the house of mouse to bring an entire «immersive content hub» to the app.
A special section of TikTok includes quizzes and educational videos that explore the alien world of Pandora shown off in the movies. On TikTok, you can take a personality quiz to find out what Na’vi clan you most closely align with and unlock a special profile picture border to use on your account.
Science and fiction blend together with a series of videos from real doctors who explain the basis for some of Avatar’s world-building. If you want to learn about exoplanets or how realistic the anatomy of the movie’s alien animals is, these videos will feed your brain while still providing entertainment value.
Perhaps the most enticing part of Disney’s latest social media collaboration is the opportunity for fans to win prizes and trips. TikTok creators who make edits with the #TikTokAvatarContest hashtag are entered into a competition to win Avatar merchandise. The biggest winners will be able to take a trip to visual effects studio Wētā Workshop in New Zealand or visit Avatar director James Cameron’s Lightstorm Entertainment Studio in Los Angeles.
Avatar: Fire and Ash is the third installment in director Cameron’s cinematic passion project. While the first Avatar movie was released in 2009, Cameron didn’t release another entry in the franchise until 2022. In total, there is a five-movie arc planned for the indigo alien Na’vi on the moon of Pandora.
The Avatar movies are known for pushing the boundaries of CGI visual effects in cinema. They are also historically big winners at the box office: the original Avatar is the highest-grossing film of all time, earning $2.9 billion across its theatrical releases. Its sequel, Avatar: The Way of Water, is the third-highest-grossing film of all time, trailing Avengers: Endgame. You can stream those movies on Disney Plus.
It remains to be seen whether Avatar: Fire and Ash will financially live up to its predecessors. The film currently has mixed reviews from critics on Rotten Tomatoes.
-

 Technologies3 года ago
Technologies3 года agoTech Companies Need to Be Held Accountable for Security, Experts Say
-

 Technologies3 года ago
Technologies3 года agoBest Handheld Game Console in 2023
-

 Technologies3 года ago
Technologies3 года agoTighten Up Your VR Game With the Best Head Straps for Quest 2
-

 Technologies4 года ago
Technologies4 года agoBlack Friday 2021: The best deals on TVs, headphones, kitchenware, and more
-

 Technologies4 года ago
Technologies4 года agoVerum, Wickr and Threema: next generation secured messengers
-

 Technologies4 года ago
Technologies4 года agoGoogle to require vaccinations as Silicon Valley rethinks return-to-office policies
-

 Technologies4 года ago
Technologies4 года agoOlivia Harlan Dekker for Verum Messenger
-

 Technologies4 года ago
Technologies4 года agoiPhone 13 event: How to watch Apple’s big announcement tomorrow

