Technologies
Twitter Is Ending Free SMS 2FA, but There’s a Better Option on Your iPhone
Don’t pay for Twitter Blue. Your iPhone has a two-factor authentication feature that’s more secure than text message.
Twitter announced earlier this month that it will no longer support text message two-factor authentication. As a Twitter user, the only way you can continue using SMS 2FA is if you sign up for the Twitter Blue service, which requires a monthly payment. If you’re an iPhone owner, there is a more secure 2FA alternative for Twitter that’s already built into your iPhone anyway — and it’s free to use.
According to Twitter, 74% of Twitter users with two-factor authentication enabled use the text message option. While it’s unfortunate that you’ll no longer have that available to you unless you pay, you’re better off without SMS 2FA anyway. Authentication apps such as Google Authenticator are superior because they’re more secure than the text message method — it’s easier for attackers to spoof your texts remotely, especially with SIM swapping.


And if you use an iPhone, you don’t have to download any third-party apps to get better two-factor authentication protection on your device. Apple has an authenticator hidden in your settings that you can use to help better secure your accounts and data.
Here’s how to set it up with Twitter, as well as with other apps and websites.
And if you’re interested in other ways of protecting your accounts, check out the best password managers to use for 2023 and how to transfer your Google Authenticator accounts if you’ve bought a new phone.
How to set up your iPhone’s built-in 2FA with Twitter
If you want to use your iPhone’s built-in two-factor authenticator specifically with Twitter, here’s what you need to do.
In the Twitter app, tap on your profile icon in the top-left and then go to Settings and Support > Settings and privacy > Security and and account access > Security > Two-factor authentication. If you’re asked to enter your Twitter password at any time, do so to continue.
Now, toggle on the Authentication app option, enter your account password, tap Get Started and hit the Link app button. You’ll be redirected to your saved Twitter passwords in your settings — choose the correct one for your account. Next, copy the verification code to your clipboard and enter it into Twitter. Finally, hit Confirm and your Twitter account should now be protected by your iPhone’s two-factor authenticator.
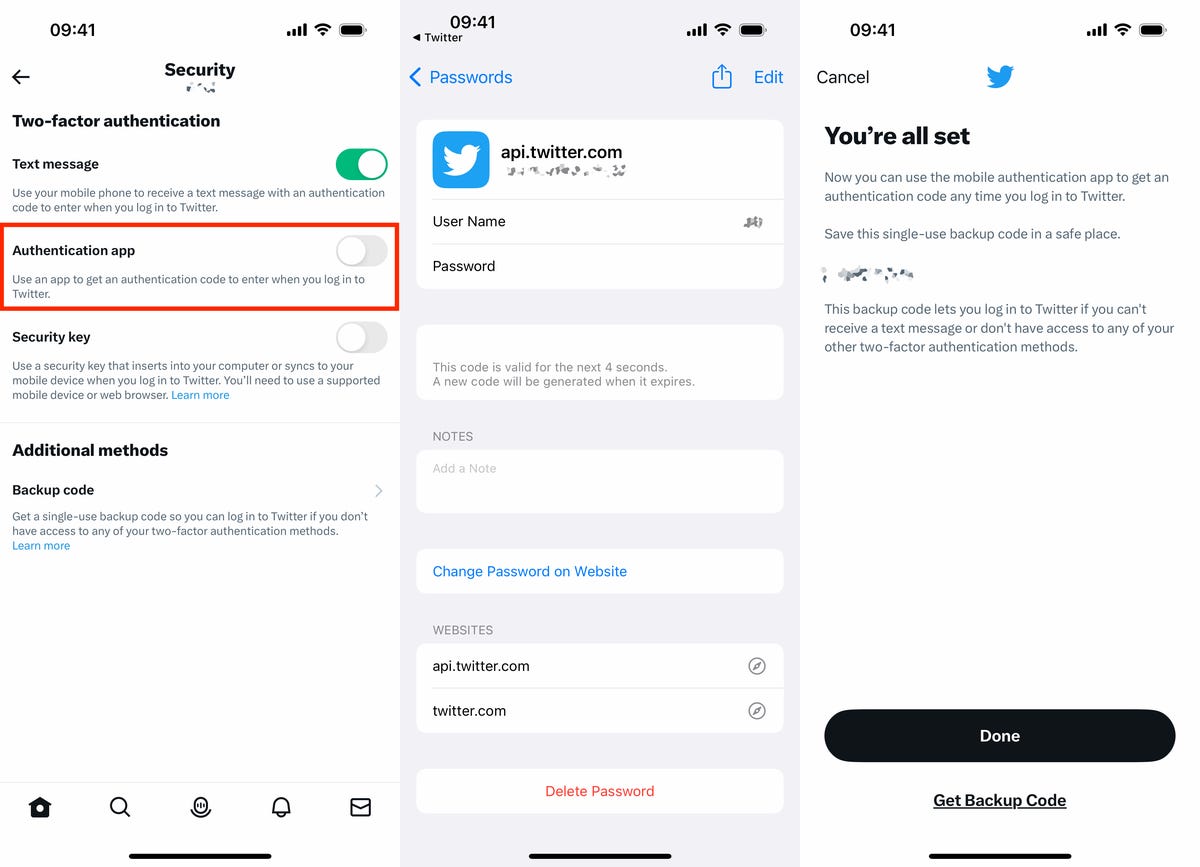

Enter your confirmation code quickly. You only have a a few seconds before a new one is generated.
Nelson Aguilar/CNETBefore you continue, make sure to write down the single-use backup code that appears. This will help you log back into Twitter if you have trouble accessing your iPhone’s two-factor authentication method. Also, you can toggle off text message 2FA now or wait until Twitter automatically disables it for you.
You can also set up iOS’s built-in 2FA with other apps and websites
For every other service that’s not Twitter, launch the Settings application on your iPhone and go into Passwords. Use Face or Touch ID to access your passwords and then tap on whatever account it is you want to set up 2FA for.
Note: This method of two-factor authentication does not work with every website or app.
Next, tap Set Up Verification Code and a menu will appear with two options:
- Enter Setup Key
- Scan QR Code
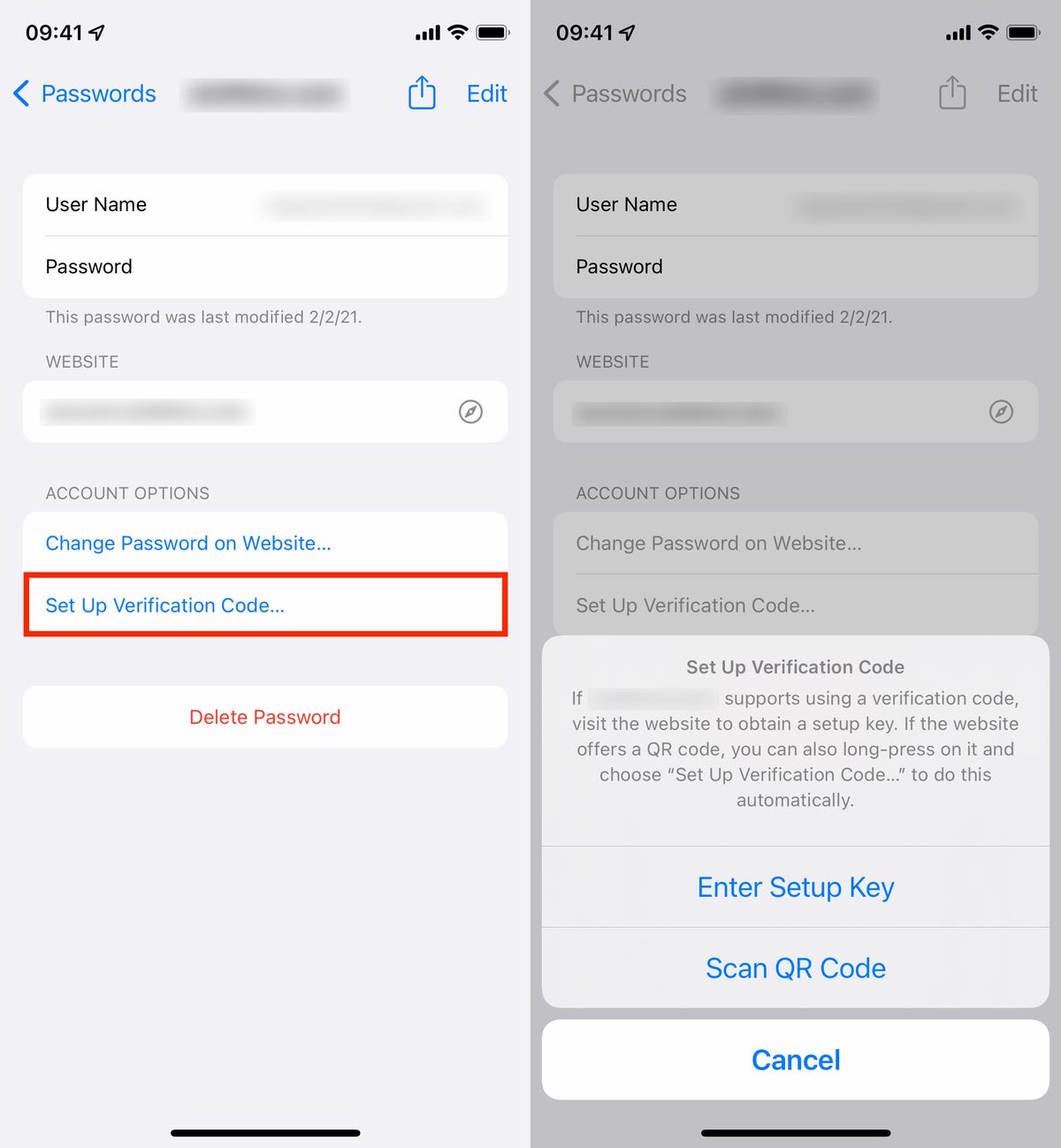

Go to Settings -> Passwords -> Set Up Verification Code to set up 2FA.
Nelson Aguilar/CNETThese are your two options to set up 2FA, which you can find on the website of whichever account you’re attempting to secure. To continue, go to the website, use your credentials to log in and then go into the website’s account settings. There is no single place where you’ll find the setup key or QR code for 2FA, but generally you should find them in «passwords» or «two-factor authentication.»
For this example, we’ll be using the setup key found in the account settings on Mega’s website. If you see a setup key, simply copy it to your clipboard, and then go back to the Settings app on your iPhone and choose the Enter Setup Key option. Next, paste in the setup key and then hit OK. Once you do, a verification code will appear.
Go back to the website you grabbed the setup key from and enter the verification code to enable 2FA. You don’t have to manually enter the setup key, as it should appear at the top of your keyboard, so you can just tap there to enter it. However, you must be quick to enter the setup key because it’ll change every 30 seconds.
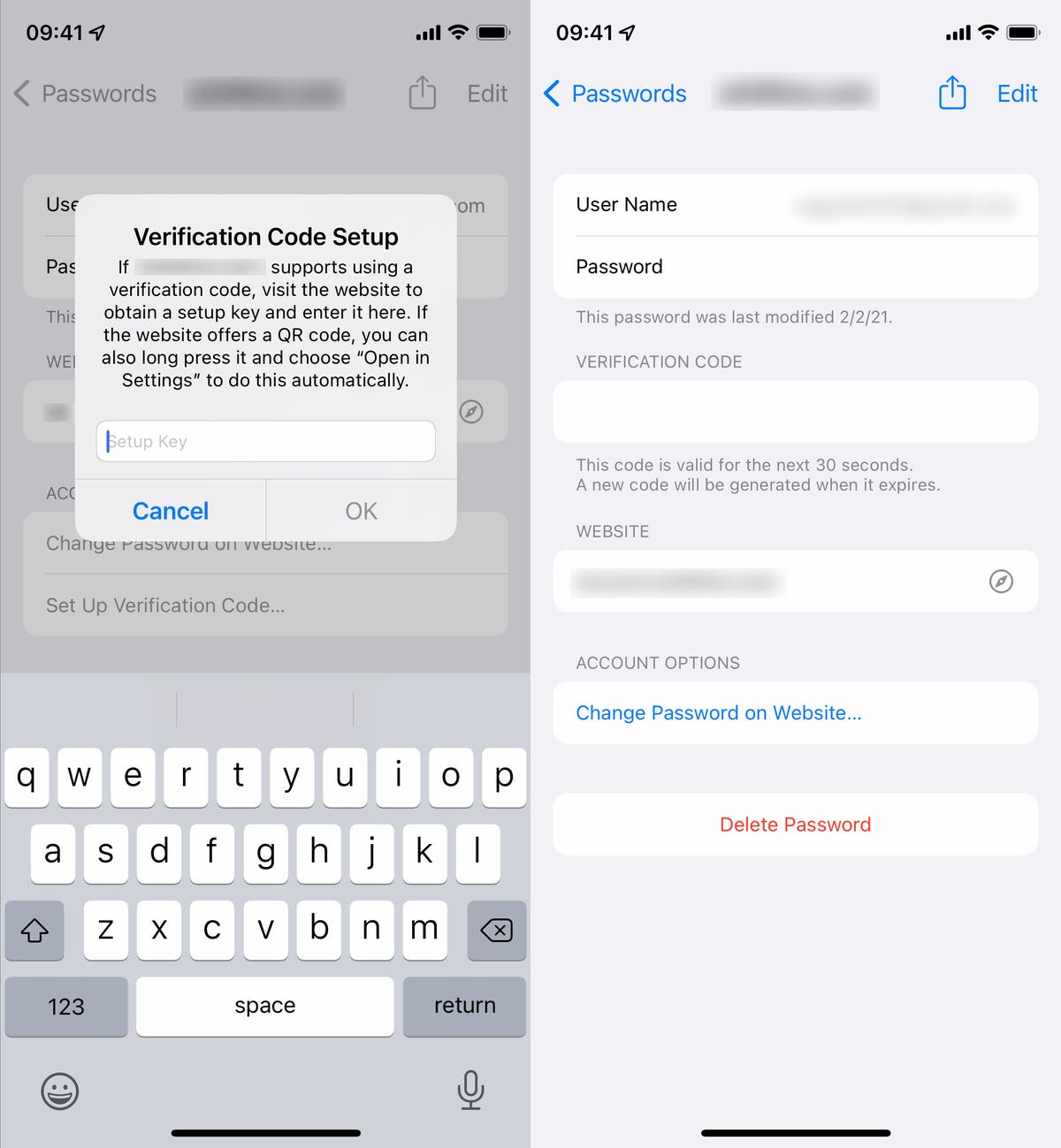

If using the setup key option, paste it into Settings when prompted and then enter the verification code on the website.
Nelson Aguilar/CNETIf you use the Scan QR Code option, the process will pretty much be the same, but instead of entering the setup key manually, you’ll simply scan the QR code with your smartphone’s camera. However, this option may not be ideal if you’re doing everything on your smartphone, so really only use this if you’re accessing the website on another device.
Once you’re finished, two-factor authentication should be enabled for that website. Anytime you log in to that website in the future, you’ll be asked to enter a verification code as well, which will be generated by the built-in feature.
Technologies
On Expands Robot Factories to Manufacture Its Cloud-Like Sneakers
This is the second factory the Swiss brand is banking on to produce its shoes.
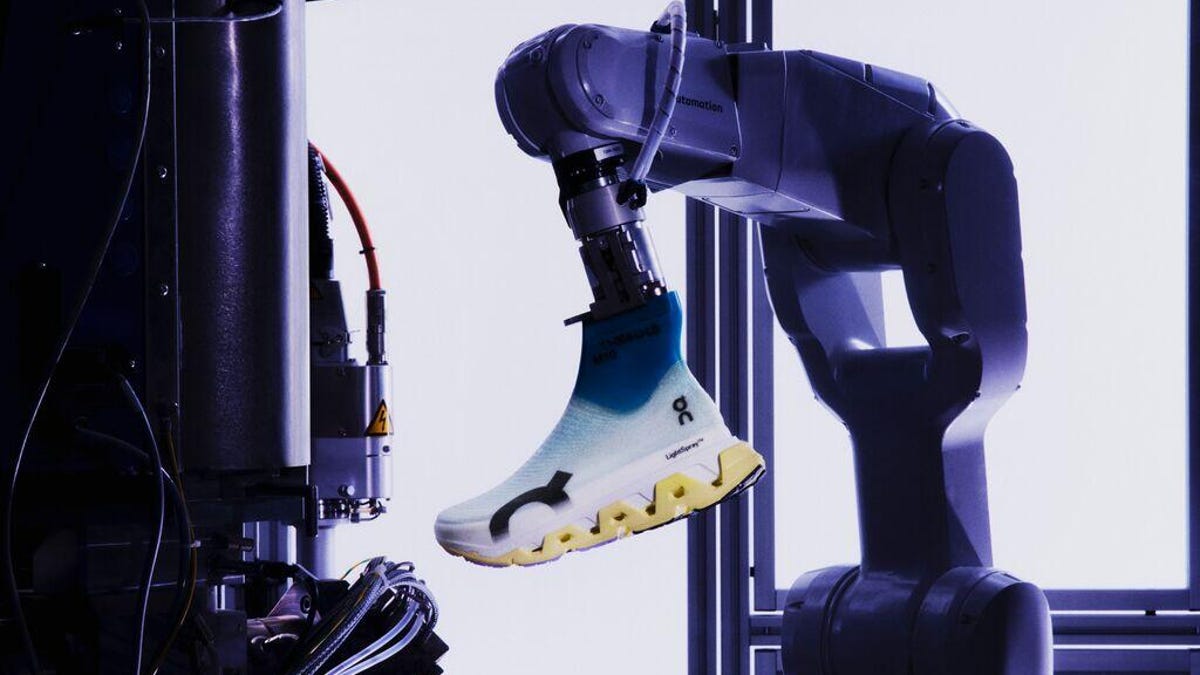

Popular sneaker brand On announced on Wednesday that it’s expanding its robotic production facility and opening up a new location in South Korea.
The Swiss brand is most known for developing running, training and lifestyle sneakers with a heavily cushioned, cloud-like sole. On opened its first robotic factory in Zurich in July 2025, after four years of development, and began production with four robots to make its first laceless LightSpray Cloudboom Strike LS shoe.
A representative for On did not immediately respond to a request for comment.
The process involves a robotic arm that sprays On’s signature LightSpray material onto the shoe, creating a light, one-piece upper in just a few minutes. With the new location, the company plans to increase production by using 32 more automated robots.
As robots and AI continue to move more deeply into companies, there’s controversy about what this could mean for human workers. As recently as this year’s CES event, it’s evident that robots are here to stay, with Hyundai unveiling its Boston Dynamics Atlas humanoid robot among other robot demos. Robot manufacturing companies are also expanding by using humanoid robots to take over specific tasks, and possibly for home use; however, the technology has not yet advanced enough to rely on them completely.
Supporters say robots could help in certain instances, such as social robots assisting kids to build confidence when reading aloud. In other cases, it could increase efficiency in a warehouse or factory setting and help around the home. But critics say automation could lead to more job loss, and even eliminate entry-level jobs.
In addition to the location announcement, On is launching the LightSpray Cloudmonster 3 Hyper, which is the first shoe upper designed at the new factory. According to On, the shoe is an ultimate super trainer for long runs and tempo runs, which are specific training runs where you’re running at a moderate-to-hard pace. The new shoe will be available first in North America on March 5, and then globally on April 16.
On says using robots to manufacture its latest shoes reduces waste and carbon emissions, plus cuts the time it takes to design an upper compared to handcrafted shoes.
«The beauty of LightSpray is that we can precisely program each robot, whether in Zurich or Busan, to execute precisely choreographed movements to craft each shoe’s unique look and feel,» said On’s chief innovation officer, Scott McGuire, in a statement.
On chose South Korea for its second factory location because of the country’s advancements in automation and robotics, and hopes to continue expanding its factories globally over the next few years. The company aims to eventually start production in the Americas and increase production in Europe.
Technologies
Today’s NYT Connections Hints, Answers and Help for Feb. 26, #991
Here are some hints and the answers for the NYT Connections puzzle for Feb. 26 #991.

Looking for the most recent Connections answers? Click here for today’s Connections hints, as well as our daily answers and hints for The New York Times Mini Crossword, Wordle, Connections: Sports Edition and Strands puzzles.
Today’s NYT Connections puzzle is a fun one. One of the groups matches up with the color of its category, which you might spot right away. Read on for clues and today’s Connections answers.
The Times has a Connections Bot, like the one for Wordle. Go there after you play to receive a numeric score and to have the program analyze your answers. Players who are registered with the Times Games section can now nerd out by following their progress, including the number of puzzles completed, win rate, number of times they nabbed a perfect score and their win streak.
Read more: Hints, Tips and Strategies to Help You Win at NYT Connections Every Time
Hints for today’s Connections groups
Here are four hints for the groupings in today’s Connections puzzle, ranked from the easiest yellow group to the tough (and sometimes bizarre) purple group.
Yellow group hint: Iconic moment.
Green group hint: Color of this group.
Blue group hint: Try the fish, I’m here all week.
Purple group hint: Polite request.
Answers for today’s Connections groups
Yellow group: Pivotal point.
Green group: Green things.
Blue group: Elements of joke-telling.
Purple group: «____ please.»
Read more: Wordle Cheat Sheet: Here Are the Most Popular Letters Used in English Words
What are today’s Connections answers?
The yellow words in today’s Connections
The theme is pivotal point. The four answers are crossroads, landmark, milestone and watershed.
The green words in today’s Connections
The theme is green things. The four answers are grasshopper, shamrock, Statue of Liberty and wasabi.
The blue words in today’s Connections
The theme is elements of joke-telling. The four answers are callback, punchline, setup and timing.
The purple words in today’s Connections
The theme is «____ please.» The four answers are attention, check, drumroll and pretty.
Technologies
The Top 25 Best Pokemon Games of All Time, Ranked
Whether you’re a new fan or a Pokemon master, the famous monster-catcher franchise has a game for everyone. Strap in to catch ’em all, enter a multiplayer online battle arena or solve an engrossing mystery.

There’s a reason your mom knows Pikachu. Over the past three decades, Pokemon has gone from being Satoshi Tajiri’s childhood dream to the highest-grossing entertainment franchise in the world.
The pocket monsters’ legacy includes a wildly popular anime, widely scalped trading cards, a movie starring Ryan Reynolds and many, many games. New entries in the series are dipping into the history of the franchise and dialing up the nostalgia. Pokemon Champions, which is slated to release in 2026, will combine all of the franchise’s battling gimmicks under one unified competitive game.
A Pokemon game exists for nearly every gamer, whether you love exploring new worlds, bonding with cuddly creatures, crawling through dungeons, solving mysteries or battling with other players.
We’ve curated this list of the best Pokemon games you can play, including mainline games and spin-off titles from throughout the franchise’s history.
Read more: Best Pokemon Day Deals: Enjoy Big Savings on Switch Games, TCG, Plushies and More
Best Pokemon games of all time
Recent updates to the list
February 2026: Removed Pokken Tournament DX. Added Pokemon Legends: Z-A, the latest game in Game Freak’s open world Pokemon spin off series.
New Pokemon games coming in 2026
There are multiple new Pokemon games releasing in 2026. Pokemon Champions is a player-versus-player battler that will be released for the Nintendo Switch, Android and iOS allowing players to bring over their favorite monsters from the Pokemon Home app. New set expansions for Pokemon TCG Pocket and new events for Pokemon Scarlet and Violet will also be released throughout the year.
Best Pokemon game FAQs
How we determined CNET’s best Pokemon games
When creating this list of the best Pokemon games, we factored in how unique and enjoyable these games are for most players. We evaluated criteria including graphics quality, innovative gameplay mechanics and compelling narratives. We balanced our picks to include a variety of mainline titles across all nine generations while still representing the wealth of Pokemon spin-offs from other genres. We favored games that hold up well for contemporary gamers and added something new to the iconic franchise. If you’re looking for help choosing your next game, CNET’s top PlayStation 4 list is a good place to start narrowing down your choices.
-

 Technologies3 года ago
Technologies3 года agoTech Companies Need to Be Held Accountable for Security, Experts Say
-

 Technologies3 года ago
Technologies3 года agoBest Handheld Game Console in 2023
-

 Technologies3 года ago
Technologies3 года agoTighten Up Your VR Game With the Best Head Straps for Quest 2
-

 Technologies4 года ago
Technologies4 года agoBlack Friday 2021: The best deals on TVs, headphones, kitchenware, and more
-

 Technologies5 лет ago
Technologies5 лет agoGoogle to require vaccinations as Silicon Valley rethinks return-to-office policies
-

 Technologies5 лет ago
Technologies5 лет agoVerum, Wickr and Threema: next generation secured messengers
-

 Technologies4 года ago
Technologies4 года agoOlivia Harlan Dekker for Verum Messenger
-

 Technologies4 года ago
Technologies4 года agoiPhone 13 event: How to watch Apple’s big announcement tomorrow
