Technologies
When will kids under 5 be eligible for the COVID vaccine?
Vaccines for youngest children are close to approval. What vaccines are available and when will they be ready?
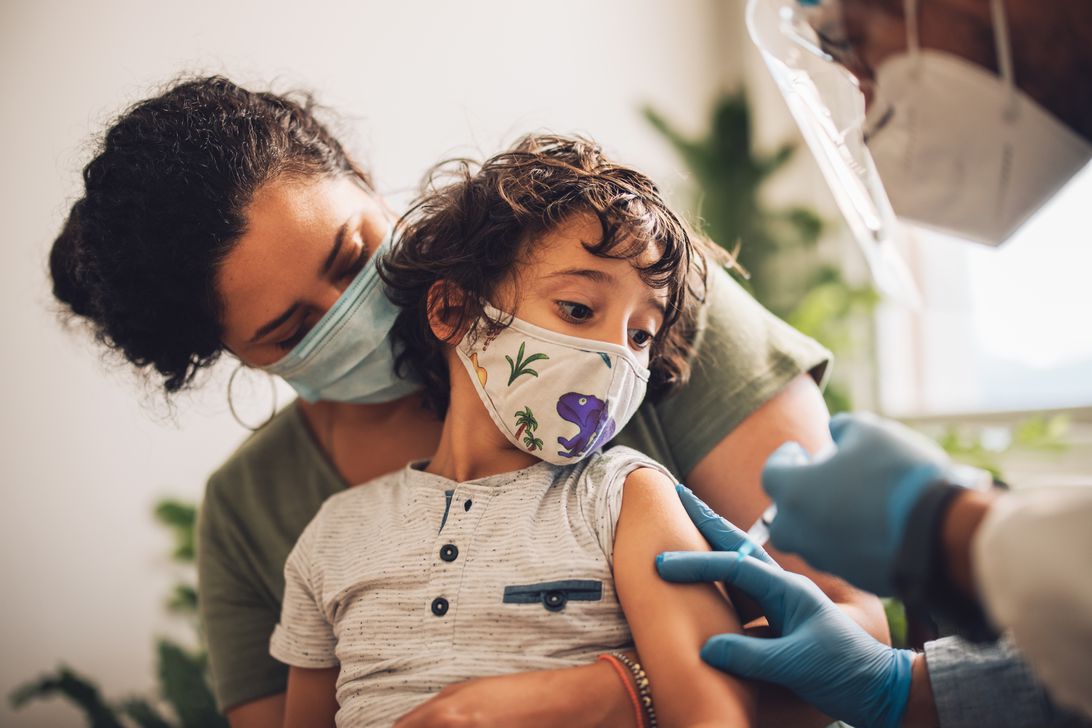
The Food and Drug Administration will meet next week to decide whether or not to authorize the Pfizer/BioNTech vaccine for children age 6 months to 4 years, but government planning for the pediatric vaccine rollout is already underway.
At a Wednesday briefing, Jeff Zients, coordinator for the White House COVID-19 Response Team said, «We’ve secured enough vaccine supply for all kids in this age group — all 18 million. We have enough needles, syringes, and kits. And these are all specially formulated, are made for this age group to send alongside the vaccine.»
Updated Sunday, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention’s «Pediatric COVID-19 Vaccination Operational Planning Guide» indicates that the agency has 10 million vaccine doses ready for dispersal, and that state and local health officials could start receiving doses as early as Feb. 21.
Last week, Pfizer and BioNTech submitted data to the FDA for authorization of their COVID-19 vaccine for children 6 months through 4 years old. While the vaccine for children under 5 is expected to be a three-dose vaccine series (it’s one-tenth the volume of Pfizer’s vaccine for people 12 and up), the FDA asked the companies to submit data on the first two doses as part of a «rolling submission» process.
In December, Pfizer announced that while two doses of the vaccine were effective in children ages 6 months to 2 years, two shots failed to promote a strong enough immune response in children ages 2 through 4 years. This prompted the company to start testing a three-dose version of the vaccine for children under 5.
Kids as young as 5 have been able to be vaccinated against COVID-19 since October 2021. The Kaiser Family Foundation reports that 28.1% of kids 5-11 have received at least one vaccine shot as of Jan. 18. Read on to learn everything you need to know about COVID-19 vaccines for kids under 5.
Also, learn about whether we’ll need a fourth booster shot, the latest on long COVID and the possibility of a vaccine that works against all COVID-19 variants.
When can babies and children under 5 get the vaccine?
Now that Pfizer has submitted data to the FDA, a meeting of experts that gathers to discuss safety and effectiveness data and vote on whether or not the FDA should authorize a vaccine is scheduled for Feb. 15. (The meeting is open to the public and you can tune in here or on the agency’s YouTube channel.)
If the FDA does authorize Pfizer’s vaccine for children as young as 6 months old, the CDC typically goes through the same process: An outside panel of health experts will discuss the benefits and risks of recommending the vaccine to children under 5 years old. If they vote to recommend Pfizer’s vaccine for the younger age group, the CDC’s director will likely accept the panel’s decision and the small doses of Pfizer’s COVID-19 vaccine for kids will become available in pediatricians’ offices or other clinics.
The CDC is expected to move quickly, assuming the FDA does authorize the first two doses of the anticipated three-dose vaccine series. If research finds a third dose is necessary for children under 5, it will be authorized and available after children have already started the vaccine series.
How is Pfizer’s child vaccine for babies and young kids different?
Pfizer and BioNTech’s vaccine for children 6 months through 4 years comes in two doses that are one-tenth the volume of the vaccine for people age 12 and up. A third 3-microgram dose is being researched right now and may be authorized in the near future.
The vaccine for kids 5 to 11 is one-third the dose given to everyone 12 and up, and it’s delivered in two doses. Pfizer’s vaccine for kids can also be stored for up to 10 weeks in a fridge, making it easier to administer, and the cap on the vial is orange instead of purple and gray to avoid mix-ups.
And if it helps to put your kids at ease, the needle used to administer the child’s dose of vaccine is also smaller.
For more information about Pfizer’s vaccine for children ages 5 to 11, check out this fact sheet from the FDA.
Can my child get a COVID booster?
Children as young as 12 can now get a booster dose of Pfizer’s COVID-19 vaccine, given at least five months after their primary vaccination series.
Most kids younger than 12 can’t get a booster, although the CDC recommends a third dose of the Pfizer vaccine for children 5 and up who are immunocompromised. They’re eligible for a third shot 28 days after their second dose.
Where can my kid get a booster shot?
Since Pfizer’s COVID-19 vaccine is the lone vaccine approved for people under 18, it’s generally only available in doctor’s offices and public health clinics, not pharmacies and other mass vaccination sites.
Call your pediatrician or local health clinic for a recommendation on where to go. Parents may also text their ZIP code to 438829 or use this vaccine finder link to find a clinic near them that has the child vaccine available.
Do kids really need a COVID-19 vaccine?
According to a report from the American Academy of Pediatrics, children made up 25% of reported COVID-19 cases for the week ending Feb. 3. (The AAP says the definition of «child» varies by the states reporting.) While pediatric cases were lower than in January, child COVID-19 were «double the peak level of the delta surge in 2021,» the AAP reported.
While it’s true children are much less likely to get severely sick from the virus than adults, some children have died or been hospitalized with the virus. An infection, even a mild case, requires quarantining and potentially sending classmates out of the classroom and back to remote learning. And kids can experience dangerous complications from COVID-19, including long COVID and MIS-C.
There are also racial disparities in the severity of how sick children get from COVID-19: Kids ages 5 to 11 who are Black, Native American or Hispanic are three times more likely to be hospitalized with COVID-19 than white children, according to an FDA advisory panel presentation. Of that group, about 1 in 3 will require admission to an intensive care unit.
Are booster shots safe for children?
In a statement following its authorization of booster doses for kids 12 to 15, the FDA said it reviewed real-world data from more than 6,300 children in Israel, ages 12 to 15, who received a booster shot at least five months after their second dose of Pfizer.
No additional safety concerns were reported to date in those individuals, according to the FDA.
«These additional data enabled the FDA to reassess the benefits and risks of the use of a booster in the younger adolescent population in the setting of the current surge in COVID-19 cases,» the agency said. «The data shows there are no new safety concerns following a booster in this population.»
What are the side effects? Is the COVID vaccine safe for kids?
Vaccine side effects in kids ages 5 to 11 are mostly mild and similar to those adults may experience, according to the CDC, including soreness at the injection site, fever, muscle soreness, nausea and fatigue. In a Dec. 13 report from the agency, the CDC reviewed reports from safety monitoring systems on more than 8 million doses of Pfizer’s vaccine given to kids ages 5 to 11, confirming that children’s immune systems respond well to the vaccine with common mild side effects, and that serious adverse events are rarely reported.
Inflammation of the heart muscle, known as myocarditis, and of the muscle’s outer lining, called pericarditis, are rare and typically mild side effects linked to the Moderna and Pfizer vaccines, mostly in adolescent males and young men ages 12 to 29. (Myocarditis can also occur after infection with COVID-19.)
In one study, the CDC said that 54 recipients out of a million males ages 12 to 17 experienced myocarditis following the second dose of Pfizer-BioNTech’s Comirnaty vaccine. In contrast, kids ages 5 to 11 who catch COVID-19 have a higher risk of multisystem inflammatory syndrome, or MIS-C, a potentially serious complication involving inflammation of the heart, lungs, kidneys, brain, skin, eyes or other organs.
«The bottom line is that getting COVID is much riskier to the heart than anything in this vaccine, no matter what age or sex you are,» Dr. Matthew Oster, a pediatric cardiologist at Children’s Healthcare of Atlanta, told the CDC in November as reported by ABC News.
Do I need to give consent for my young child to get vaccinated?
Yes, parents generally need to consent to their children receiving medical care, including Pfizer’s COVID-19 vaccine. This is especially true for younger children.
However, depending on which state you live in, there may be a legal precedent for teens and other kids to request the vaccine without parental permission: Tennessee’s vaccine director, Michelle Fiscus, was fired in August allegedly in part for sending out a memo detailing Tennessee’s «mature minor doctrine,» which explains how minors may seek medical care without the consent of their parents.
If my child has a serious health condition, can they get a third shot?
The CDC recommended a third dose for children as young as 5 who are «moderately to severely» immunocompromised, 28 days after their second shot. This guidance for immunocompromised children (including kids who’ve had an organ transplant or are taking medications that suppress the immune system) is in line with guidance for adults whose bodies don’t mount a good immune response to the COVID-19 vaccines.
My child has allergies. Can they get the vaccine?
Yes, though you might be asked to stick around the waiting room so health care providers can monitor them for (extremely rare) allergic reactions that can occur after any vaccination.
«If the child has a history of anaphylaxis or other severe allergies, then the observation time after the injection may be 30 minutes instead of 15,» said Dr. Anne Liu, an infectious disease specialist with Stanford Hospital and Clinics and the Lucile Packard Children’s Hospital. Children who have been prescribed an EpiPen for any reason should bring it to their vaccine appointment, Liu added.
As with adults, children with an allergy to an ingredient in Pfizer’s COVID-19 shouldn’t take it. You can find a list of ingredients in Pfizer’s vaccine for kids ages 5 to 11 on the FDA’s fact sheet.
Can my child get the COVID-19 shot at the same time as other vaccines?
According to the CDC, your child may get other vaccines when they go in for their COVID shot without waiting 14 days between appointments. Flu shots can be given to children ages 6 months and older.
The information contained in this article is for educational and informational purposes only and is not intended as health or medical advice. Always consult a physician or other qualified health provider regarding any questions you may have about a medical condition or health objectives.
Technologies
Spotify Launches ‘About the Song’ Beta to Reveal Stories Behind the Music
The stories are told on swipeable cards as you listen to the song.
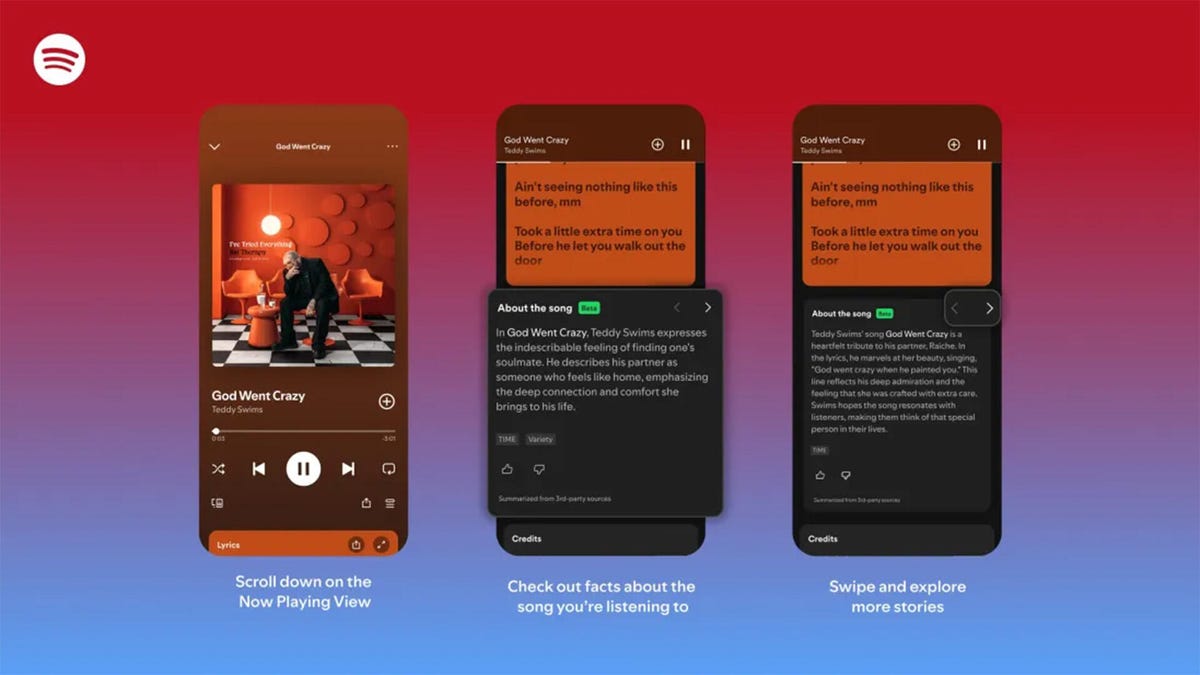
Did you know Chappell Roan drew inspiration for her hit song Pink Pony Club from The Pink Cadillac, the name of a hot-pink strip club in her Missouri hometown? Or that Fountains of Wayne’s song Stacy’s Mom was inspired by a confessed crush a friend had on the late co-founder Adam Schlesinger’s grandmother?
If you’re a fan of knowing juicy little tidbits about popular songs, you might find more trivia in About the Song, a new feature from streaming giant Spotify that’s kind of like the old VH1 show Pop-Up Video.
About the Song is available in the US, UK, New Zealand and Australia, initially for Spotify Premium members only. It’s only on certain songs, but it will likely keep rolling out to more music. Music facts are sourced from a variety of websites and summarized by AI, and appear below the song’s lyrics when you’re playing a particular song.
«Music fans know the feeling: A song stops you in your tracks, and you immediately want to know more. What inspired it, and what’s the meaning behind it? We believe that understanding the craft and context behind a song can deepen your connection to the music you love,» Spotify wrote in a blog post.
While this version of the feature is new, it’s not the first time Spotify has featured fun facts about the music it plays. The streaming giant partnered with Genius a decade ago for Behind the Lyrics, which included themed playlists with factoids and trivia about each song. Spotify kept this up for a few years before canceling due to multiple controversies, including Paramore’s Hayley Williams blasting Genius for using inaccurate and outdated information.
Spotify soon started testing its Storyline feature, which featured fun facts about songs in a limited capacity for some users, but was never released as a central feature.
About the Song is the latest in a long string of announcements from Spotify, including a Page Match feature that lets you seamlessly switch to an audiobook from a physical book, and an AI tool that creates playlists for you. Spotify also recently announced that it’ll start selling physical books.
How to use About the Song
If you’re a Spotify Premium user, the feature should be available the next time you listen to music on the app.
- Start listening to any supported song.
- Scroll down past the lyrics preview box to the About the Song box.
- Swipe left and right to see more facts about the song.
I tried this with a few tracks, and was pleased to learn that it doesn’t just work for the most recent hits. Spotify’s card for Metallica’s 1986 song Master of Puppets notes the song’s surge in popularity after its cameo in a 2022 episode of Stranger Things. The second card discusses the band’s album art for Master of Puppets and how it was conceptualized.
To see how far support for the feature really went, I looked up a few tracks from off the beaten path, like NoFX’s The Decline and Ice Nine Kills’ Thank God It’s Friday. Spotify supported every track I personally checked.
There does appear to be a limit to the depth of the fun facts, which makes sense since not every song has a complicated story. For those songs, Spotify defaults to trivia about the album that features the music or an AI summary of the lyrics and what they might mean.
Technologies
Today’s NYT Connections: Sports Edition Hints and Answers for Feb. 7, #502
Here are hints and the answers for the NYT Connections: Sports Edition puzzle for Feb. 7, No. 502.

Looking for the most recent regular Connections answers? Click here for today’s Connections hints, as well as our daily answers and hints for The New York Times Mini Crossword, Wordle and Strands puzzles.
Today’s Connections: Sports Edition features a fun batch of categories. The purple one requires you to find hidden words inside some of the grid words, but they’re not too obscure. If you’re struggling with today’s puzzle but still want to solve it, read on for hints and the answers.
Connections: Sports Edition is published by The Athletic, the subscription-based sports journalism site owned by The Times. It doesn’t appear in the NYT Games app, but it does in The Athletic’s own app. Or you can play it for free online.
Read more: NYT Connections: Sports Edition Puzzle Comes Out of Beta
Hints for today’s Connections: Sports Edition groups
Here are four hints for the groupings in today’s Connections: Sports Edition puzzle, ranked from the easiest yellow group to the tough (and sometimes bizarre) purple group.
Yellow group hint: Golden Gate.
Green group hint: It’s «Shotime!»
Blue group hint: Same first name.
Purple group hint: Tweak a team name.
Answers for today’s Connections: Sports Edition groups
Yellow group: Bay Area teams.
Green group: Associated with Shohei Ohtani.
Blue group: Coaching Mikes.
Purple group: MLB teams, with the last letter changed.
Read more: Wordle Cheat Sheet: Here Are the Most Popular Letters Used in English Words
What are today’s Connections: Sports Edition answers?
The yellow words in today’s Connections
The theme is Bay Area teams. The four answers are 49ers, Giants, Sharks and Valkyries.
The green words in today’s Connections
The theme is associated with Shohei Ohtani. The four answers are Decoy, Dodgers, Japan and two-way.
The blue words in today’s Connections
The theme is coaching Mikes. The four answers are Macdonald, McCarthy, Tomlin and Vrabel.
The purple words in today’s Connections
The theme is MLB teams, with the last letter changed. The four answers are Angelo (Angels), Cuba (Cubs), redo (Reds) and twine (Twins).
Technologies
Today’s NYT Mini Crossword Answers for Saturday, Feb. 7
Here are the answers for The New York Times Mini Crossword for Feb. 7

Looking for the most recent Mini Crossword answer? Click here for today’s Mini Crossword hints, as well as our daily answers and hints for The New York Times Wordle, Strands, Connections and Connections: Sports Edition puzzles.
Need some help with today’s Mini Crossword? It’s Saturday, so it’s a long one, and a few of the clues are tricky. Read on for all the answers. And if you could use some hints and guidance for daily solving, check out our Mini Crossword tips.
If you’re looking for today’s Wordle, Connections, Connections: Sports Edition and Strands answers, you can visit CNET’s NYT puzzle hints page.
Read more: Tips and Tricks for Solving The New York Times Mini Crossword
Let’s get to those Mini Crossword clues and answers.
Mini across clues and answers
1A clue: Lock lips
Answer: KISS
5A clue: Italian author of «Inferno,» «Purgatorio» and «Paradiso»
Answer: DANTE
6A clue: Cerebral ___ (part of the brain)
Answer: CORTEX
7A clue: Leave home with a stuffed pillowcase as luggage, perhaps
Answer: RUNAWAY
8A clue: No more for me, thanks»
Answer: IMGOOD
9A clue: Fancy fabrics
Answer: SILKS
10A clue: Leg joint
Answer: KNEE
Mini down clues and answers
1D clue: Bars sung in a bar
Answer: KARAOKE
2D clue: How the animals boarded Noah’s Ark
Answer: INTWOS
3D clue: Stand in good ___
Answer: STEAD
4D clue: Smokin’ hot
Answer: SEXY
5D clue: Computer attachment
Answer: DONGLE
6D clue: Yotam Ottolenghi called it «the one spice I could never give up»
Answer: CUMIN
7D clue: Hazard
Answer: RISK
-

 Technologies3 года ago
Technologies3 года agoTech Companies Need to Be Held Accountable for Security, Experts Say
-

 Technologies3 года ago
Technologies3 года agoBest Handheld Game Console in 2023
-

 Technologies3 года ago
Technologies3 года agoTighten Up Your VR Game With the Best Head Straps for Quest 2
-

 Technologies4 года ago
Technologies4 года agoBlack Friday 2021: The best deals on TVs, headphones, kitchenware, and more
-

 Technologies5 лет ago
Technologies5 лет agoGoogle to require vaccinations as Silicon Valley rethinks return-to-office policies
-

 Technologies5 лет ago
Technologies5 лет agoVerum, Wickr and Threema: next generation secured messengers
-

 Technologies4 года ago
Technologies4 года agoOlivia Harlan Dekker for Verum Messenger
-

 Technologies4 года ago
Technologies4 года agoiPhone 13 event: How to watch Apple’s big announcement tomorrow
