Technologies
First ‘true’ millipede with over 1,000 legs discovered deep below Earth’s surface
Emerging from a drill hole in Western Australia, a new record holder for leggiest animal on the planet.
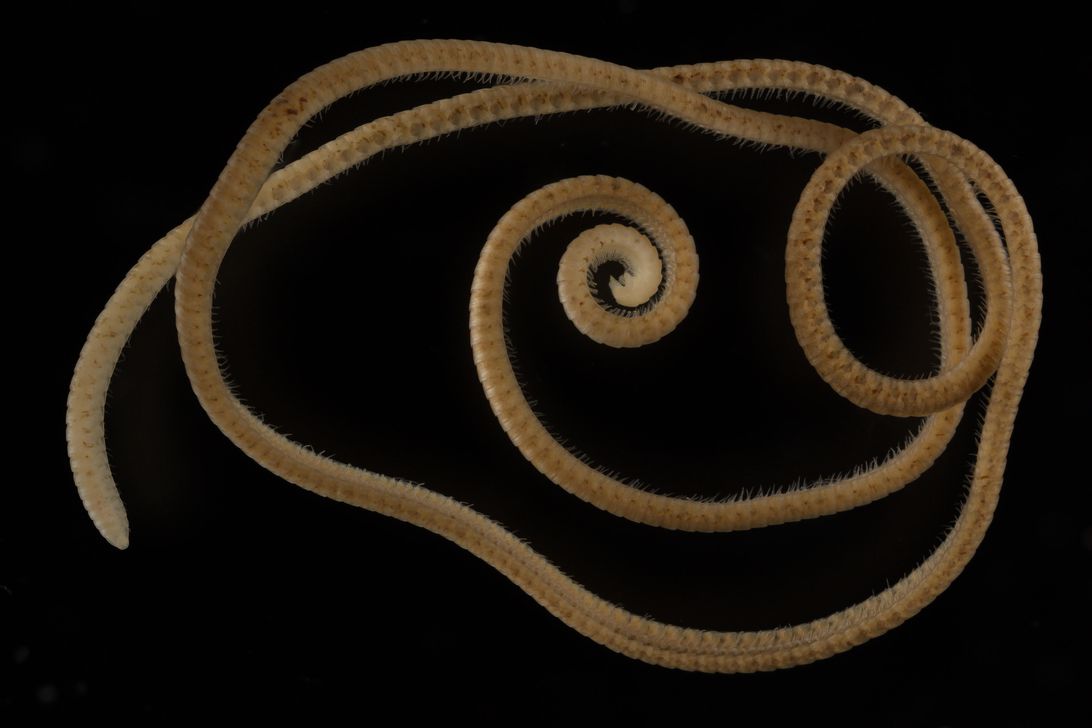

Around the world, more than 7,000 species of millipede crawl across forest floors and garden beds, pairs of legs pumping as they move through soil in search of food. The limbs can number in the dozens to the hundreds, and while the term «millipede» translates to «a thousand feet,» the record number of millipede movers has stood at around 750 legs since the description of a Californian species back in 2006.
«Millipede» has been a misnomer. A thousand feet? A myth. Until today.
«All of the introductory textbooks will have to be rewritten because there is a true millipede now,» says Dennis Black, a millipede expert and adjunct research fellow at LaTrobe University in Australia.
The «true» millipede has been dubbed Eumillipes persephone. The new species was discovered in a borehole, drilled as part of a Western Australian mining operation, almost 200 feet (60 meters) below the Earth’s surface. It’s the first millipede to live up to its multi-legged moniker with a staggering 1,306 legs.
«That’s just an amazing number,» says Paul Marek, an entomologist at Virginia Tech and lead author of a paper documenting the find, published Thursday in the journal Scientific Reports. «I’m still in disbelief.»
Named for Persephone, the Greek goddess of the underworld, the spindly, brown crawler is just over 3.7 inches long and about as thin as a USB cable. The millipede also lives much deeper in the soil than any previously known species, and the story of its discovery makes for a tale of great luck and incredible irony.
Portal to the underworld
The first person to set eyes on the Persephone millipede was Bruno Buzatto, principal biologist at Bennelongia Environmental Consultants in Western Australia. The group specializes in subterranean surveys of animal life and is often contracted by mining companies looking to perform environmental assessments as they search for resources. The mining companies drill the holes that, Buzatto says, are like «portals» into the subterranean world.
To assess what life lurks in the underworld beneath our feet, Buzatto sends «traps» through the portals. He takes a plastic tube with a few holes in the side and fills it with leaf litter. He then drops it down one of the drill holes and leaves it there. Life in the soil is attracted to the litter, hoping to fill its stomach. When Buzatto pulls the trap out a month or two later, it’s often teeming with life.
Buzatto says these traps routinely catch new creatures, some of which have never been seen before. «About 80 to 90% of what we pull up is undescribed species,» he says. So it was no surprise to him when, in August 2020, he laid eyes on an unusual animal he’d never seen before. In a haul plucked from a hole in the Eastern Goldfields Province of Western Australia, Buzatto found an extremely long millipede. «I realized it was a very special animal,» he says.
A few years earlier, Buzatto had been flicking through a research paper about Illacme plenipes, a Californian species of millipede with the record for most number of legs. The lead author of that study was Paul Marek, an entomologist at Virginia Tech. Buzatto shot him an email, attaching a picture of his find.
«I did a quick count and it had 818 legs,» Marek says. «I was pretty pumped about that.»
To make it official, Marek needed to see the specimens, place them under a powerful microscope and analyze their DNA. Buzatto, in collaboration with the Western Australian Museum, shipped specimens to Marek’s lab in the US. In total, the team was able to find and analyze five millipedes, with one female taking out the legs record (1,306) and a male falling just short of the mythic 1,000-leg mark at 998.
Why so many legs?
The Persephone millipede lives in a world with no light and, likely, limited food. Evolution has built it for this world with unique characteristics – similar to, but distinct from, Illacma plenipes.
When Marek was able to look at the Persephone under the microscope, he noticed many similarities to the Illacme plenipes, a millipede that lives halfway across the world, separated by the Pacific Ocean. However, it also had some bizarre features. «It was nothing like other members of the family,» Marek says.
For one, it had no eyes, which is unique in this order of animals. Two, it was unpigmented.
Both changes make sense. Living in the underworld, eyes aren’t all that important. You don’t need to detect changes in the light. Instead, the Persephone has huge antennae. Pigmentation loss occurs in a wide variety of animals that live in places without light, such as caves, but the evolutionary pressures underlying pigmentation loss are still being fully elucidated.
All of the characteristics helped Marek and the team place the species in the order Polyzoniida, distant relatives of the previous leggiest record holder, and suggested the Persephone and Illacma plenipes are an example of convergent evolution – where two distantly related species evolve similar physiological traits to adapt to their niches.
But why does a creature need so many legs?
The answer isn’t all that surprising. Legs are for locomotion. They allow you to move around the world. The researchers haven’t seen live specimens moving around in their home underworld, but they can draw on insights from similar species in nature. Based on earlier studies, Marek and the team suggest the super-elongation and short legs help to burrow through the underworld, providing additional propulsive force as it moves in a telescoping motion.
«The combination of these characteristics really speaks to the importance of being able to traverse deep underground, probably as a result of a limited set of nutrients in the place that it lives,» Marek said.
Minefield
There is a great irony to the discovery, one that several of the authors have wrestled with.
Collecting and describing new species from deep within the soil hasn’t been done to a great extent in Western Australia. There could be dozens of species living underneath our feet that we have never seen before. Before August 2020, no one had ever seen the Persephone millipede. No one knew it existed. And it would have remained that way, if not for Buzatto’s drill hole trap.
«I don’t think we would have ever known about this had it not been for the mineral exploration that’s occurring,» says Dennis Black, the millipede expert from LaTrobe and a co-author on the study. Buzatto notes the mining company, in this instance, paid for the surveys.
At the same time, the main threat to the survival of the species, at least as far as we know right now, would be those same mining operations. If a rich resource was discovered in the same mining exploration what would win out? The millipede? Fortunately for the Persephone, Buzatto notes the area it was discovered in isn’t one in which the mining company is looking to target.
But it raises interesting questions about how to protect species like the Persephone we don’t even know about, so-called «cryptic» organisms contributing to ecosystems we know nothing about. These ecosystems, Persephone shows, are yielding incredible discoveries and preventing further loss of biodiversity. To prevent an anonymous extinction, scientists need to know what’s out there, including deep beneath the surface of the Western Australian desert.
«There couldn be a heck of a lot living over that vast area,» Black says. «We simply don’t have a clue.»
If we did, there’s a chance the Persephone too will be dethroned. Marek says there’s «some correlation» between the depth at which these creatures are found and the number of legs they have. Exploring even deeper below the surface might mean running into another god of the underworld, leggier than we’d ever imagined.
«It’s possible there are longer ones down there,» Black says. «What I want to do is win the lotto, buy some drilling equipment and spend my retirement drilling holes.»
Technologies
Apple Gave Us the Neo, Now It Might Be Planning a High-End MacBook Ultra
The company might launch its most sophisticated MacBook ever, with its first OLED screen.

Apple went budget with the MacBook Neo. Now reportedly the company is preparing to go high end, and high price.
Apple is gearing up to launch a MacBook «Ultra» in the fall, outfitted with the first OLED display in MacBook history, according to a report from Bloomberg’s Mark Gurman.
Gurman says the new laptop will have a touchscreen and new M6 chips. Last month, Bloomberg reported that Apple could be launching its first touchscreen MacBook — with a Dynamic Island. The Dynamic Island is a feature on more recent iPhone models — iPhone 14 and later — that’s shaped like a long horizontal pill atop the screen and shows alerts, notifications, timers and music.
It if happens, the Ultra would be at the opposite end of the cost spectrum from the Neo, which Apple launched earlier this month for $599 as a rival to Chromebooks and Windows laptops in the same price range. Gurman says the MacBook Ultra could cost 20 percent more than the new MacBook Pro (M5 series), which Apple lists at $1,699.
If you want to read more about the new Neo, CNET has been all over it: Here’s why students might love it, the colors we liked and didn’t like and why the Neo is a really is a game-changer.
Gurman suggested that Apple might keep selling the M5 series MacBook Pro even after the Ultra launches. That would give the company a wider range of MacBooks at various costs — the Neo ($599), the Air (starting at $1,099), the Pro ($1,699) and the Ultra.
Tech analyst Paolo Pescatore said adding the premium MacBook Ultra would «signal a clear shift in strategy» for Apple.
«If this turns out to be the case, then Apple appears to be stretching the Mac further upmarket,» Pescatore told CNET. «The opportunity is to drive higher spending and keep premium users firmly within Apple’s ecosystem. The challenge will be avoiding confusion, especially if the lines between MacBook Pro and iPad Pro become even more blurred.»
Gurman also said that Apple’s first foldable iPhone, rumored to be launched later this year, might be called the «iPhone Ultra.»
Technologies
AI Is One of the Least-Liked Things in America, According to New NBC Poll
The poll finds that AI is viewed less positively than ICE and President Donald Trump, and only more positively than Iran and the Democratic Party.
Artificial intelligence has rapidly become embedded in everything from phones to schoolwork to war plans. And that means everyone is likely to have an opinion about the technology.
A new national survey conducted for NBC News highlights a striking disconnect between the spread of AI tools and Americans’ views on them. The poll, which ran from Feb. 27 to March 3, asked 1,000 registered voters about their views on topics ranging from border security to the new pope.
Only 26% of voters said they view AI positively, 46% view it negatively, and 28% said they feel unsure or have no opinion, leaving AI with a net favorability of -20. In the study, AI ranked less favorably than US Immigration and Customs Enforcement, President Donald Trump, former Vice President Kamala Harris, the Republican Party and The Late Show host Stephen Colbert. (Pope Leo XIV was by far the most popular person respondents were asked about.)
Among the rankings, AI is one of the least popular topics in the survey — ranking only slightly more positively than Iran and the Democratic Party.
A growing disconnect between AI and public opinion
There is a notable disconnect between the industry’s ongoing push for AI adoption and how Americans feel about it.
Tech companies are currently investing millions of dollars into developing generative AI tools and physical AI. In the last week alone, OpenAI released its latest GPT 5.4 model and AI companies made moves to work with the US Department of Defense. At the same time, Americans are growing increasingly wary of the technology.
The mismatch between adoption and public sentiment seems to be driven by concerns about AI’s broader impact, such as job displacement, privacy issues, the spread of misinformation and the undermining of human-made work.
For companies and policymakers going all in on AI, the biggest challenge will be less about developing the next slew of innovative chatbot models or AI devices and more about persuading the public that the technology can be trusted.
Technologies
Just $30 Will Get You 3 Months of the 5GB Mint Mobile Phone Plan
Finding a phone plan for $10 a month was impossible until this Mint Mobile deal came along.

If you told me I could get a three-month cell plan for just $30, I probably wouldn’t believe you. But that’s exactly what Mint Mobile is offering right now. If you pay for three months of 5GB cell service upfront, you can score it for just $30.
New customers to Mint Mobile can score a 5GB wireless plan for just $10 per month for the first three months. The only catch is you have to use the code 5GB10 and pay $30 upfront for the full term. The usual price is $45 for three months, meaning this is a 33% discount.
After the three-month period, the plan renews at $25 per month for three months. If you really like the plan, you can opt for the six-month version, which can lower the monthly cost to $20. You can also track your data usage in the Mint Mobile app and switch to a better-suited data plan when it’s time to renew.
Don’t forget a new phone to go with your new phone plan. Take a look at the best phone deals you can score right now.
MOBILE DEALS OF THE WEEK
-
$749 (save $250)
-
$298 (save $102)
-
$241 (save $310)
-
$499 (save $300)
Why this deal matters
It seems like everything is becoming more and more expensive these days. That’s why saving wherever you can makes a huge difference. The phone bill is one thing that is here to stay, and that’s why this deal of $10 per month is really unbeatable. Just keep in mind you’ll have to pay the full three months upfront. But even that is just $30 total. Be sure to use code 5GB10 for the discount.
-

 Technologies3 года ago
Technologies3 года agoTech Companies Need to Be Held Accountable for Security, Experts Say
-

 Technologies3 года ago
Technologies3 года agoBest Handheld Game Console in 2023
-

 Technologies3 года ago
Technologies3 года agoTighten Up Your VR Game With the Best Head Straps for Quest 2
-

 Technologies4 года ago
Technologies4 года agoBlack Friday 2021: The best deals on TVs, headphones, kitchenware, and more
-

 Technologies5 лет ago
Technologies5 лет agoGoogle to require vaccinations as Silicon Valley rethinks return-to-office policies
-

 Technologies5 лет ago
Technologies5 лет agoVerum, Wickr and Threema: next generation secured messengers
-

 Technologies4 года ago
Technologies4 года agoOlivia Harlan Dekker for Verum Messenger
-

 Technologies4 года ago
Technologies4 года agoiPhone 13 event: How to watch Apple’s big announcement tomorrow
