Technologies
Samsung Galaxy S24 Ultra Review: A Pricey Way to Join the AI Craze
The Galaxy S24 Ultra’s new AI tricks show promise, but you don’t need to splurge on Samsung’s top-of-the-line phone to get them.

 Why You Can Trust CNET
Why You Can Trust CNET

Pros
- Chat translations and Circle to Search are useful
- Sharper 5x zoom
- Good low-light camera performance
- 7 years of software upgrades
Cons
- Expensive
- Some Galaxy AI features aren’t exclusive to S24 series
- No specific S24 Ultra Galaxy AI features
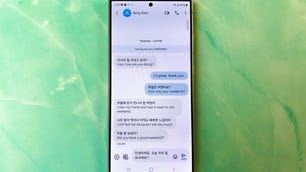
With the press of a button, all the text messages sent between myself and my husband over the past couple of days were translated into French. I didn’t have to highlight specific words or message bubbles, nor did I have to copy and paste text between apps. Once I hit the «Chat translation» button on the Galaxy S24 Ultra’s screen, the words were translated instantly as I scrolled through our message history.
It’s one of several new features on the Galaxy S24 lineup that are part of Galaxy AI, a collection of productivity, communication and content creation tools powered by generative artificial intelligence. Artificial intelligence has been the buzzword du jour in the tech world ever since ChatGPT became an overnight hit in late 2022, and it’s tempting to write off Galaxy AI as another attempt to cash in on the hype. And that may be true to some degree.
But using the Galaxy S24 Ultra for the past couple of days convinced me there’s some promise behind the excitement. While the vast majority of Galaxy AI features feel familiar rather than groundbreaking, Samsung’s real-time translation technology and Circle to Search — a feature it created in partnership with Google — feel genuinely useful.
The problem for the Galaxy S24 Ultra, which launches on Jan. 31 starting at $1,300 (£1,249, AU$2,199), is that you don’t need Samsung’s high-end phone to use these features. They’re available across all Galaxy S24 devices and will come to the previous-generation Galaxy S23 lineup, too. Circle to Search is also coming to the Pixel 8 and 8 Pro, both of which are notably cheaper than the Galaxy S24 Ultra.
Read more: Best Phone to Buy for 2024
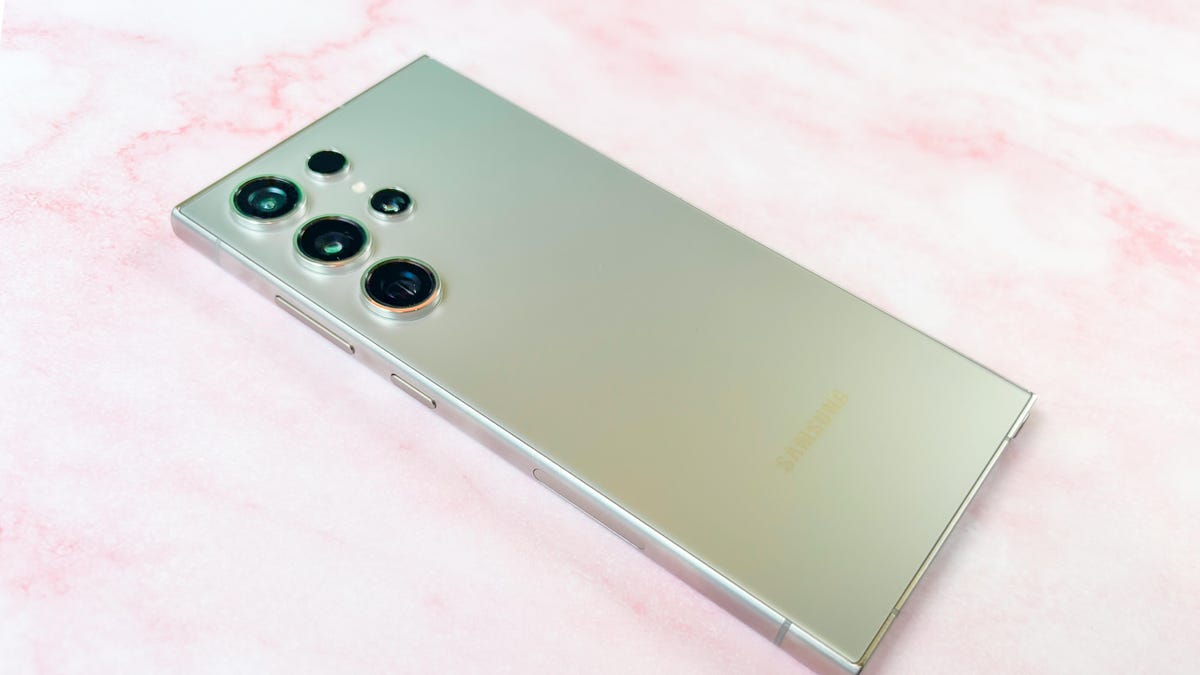
When I reviewed the Galaxy S23 Ultra last year, I called it «the king of extra.» That still applies to the Galaxy S24 Ultra. It’s the Ultra’s giant screen, embedded S Pen and ridiculously long digital camera zoom that truly separate it from the regular Galaxy S24 and S24 Plus, not Samsung’s new AI features. Samsung gave the Galaxy S24 Ultra a fresh coat of paint with its new titanium design and flatter screen, along with a sharper 50-megapixel zoom camera that can take crisper photos at 5x magnification. Perhaps most importantly, the entire Galaxy S24 lineup will get seven generations of Android version upgrades like the Pixel 8 lineup, marking a big step up from Samsung’s previous four-year pledge.
Aside from its new AI tricks, the Galaxy S24 Ultra ultimately feels like a slightly upgraded version of last year’s phone. Samsung also missed an opportunity to make its top-of-the-line phone stand out from the rest of the S24 lineup with Galaxy AI features that are tailored specifically to the Ultra.
Galaxy AI: Language translation and Circle to Search shine

Galaxy AI spans everything from text messaging to Samsung’s apps for note-taking, voice recording, web browsing and the camera. Many of these features feel like tools we’ve seen from Google and Microsoft throughout 2023, but optimized for Samsung smartphones. Galaxy AI can, for example, organize notes in the Notes app into neat bullet points. Its web browser can summarize news articles, while the Voice Recorder app offers transcription summaries broken down by speaker. You can also translate any of these types of content into different languages.
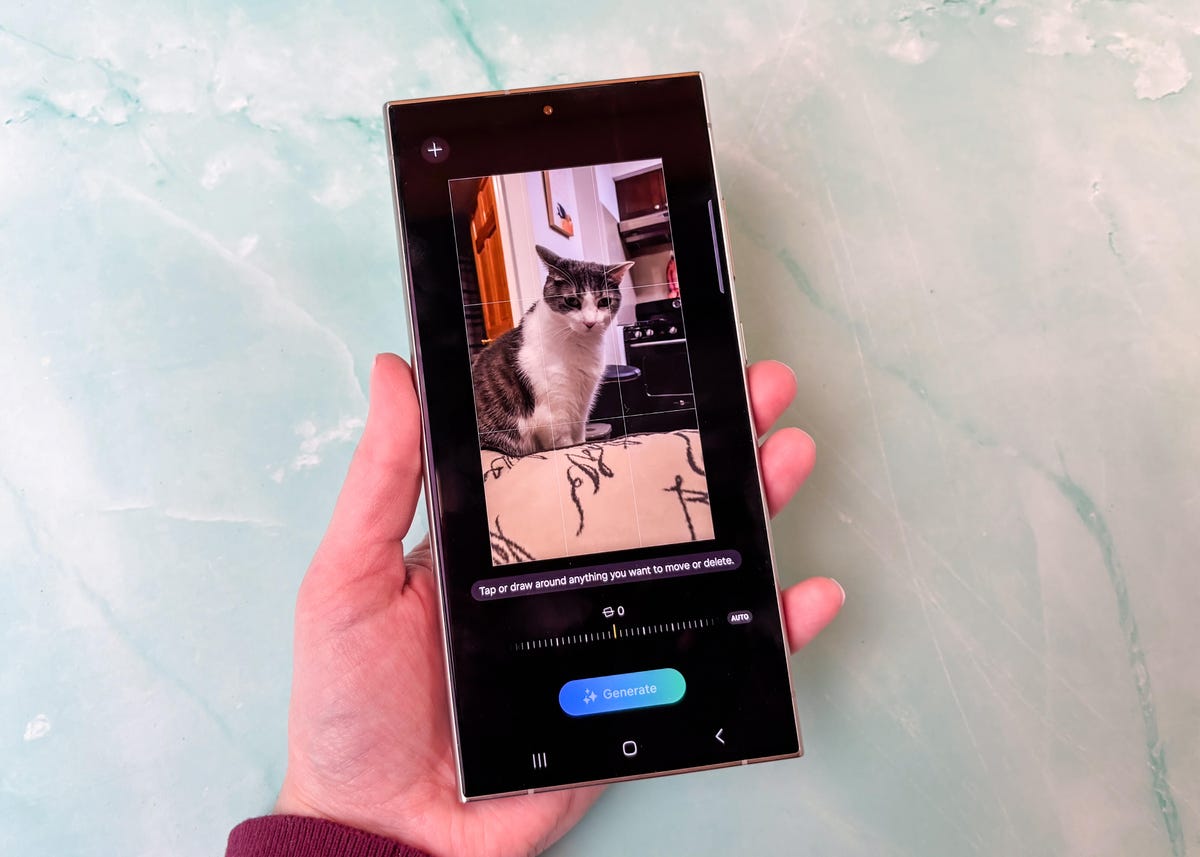
These features should sound familiar to anyone who has been following Google’s AI developments over the past year. That’s intentional: Samsung worked closely with Google on certain Galaxy AI features and is even using the company’s underlying technology to power some tools like the ability to summarize transcriptions, notes and webpages, rewrite text messages in a different tone and remove or rearrange objects in photos.
Read more: Your Future Phone Will Likely Be Smarter, Faster and More Bendy
But the execution isn’t typically the same. Take Samsung’s Generative Edit and Google’s Magic Edit as an example. Both tools let you select an object in a photo and either erase or move that object to your liking, but they can produce different results.
Sometimes one version will patch up the background after removing an object, while the other will substitute the unwanted object with another similar-looking structure that fits into the background. Google’s tool provides a few options to choose from when providing the result, while Samsung only provides one, but watermarks the new photo to clarify that it was altered using Generative Edit.

Of all the Galaxy AI features, there are two that impressed me the most: language translation and Circle to Search. While apps like Google Translate have existed for years, having translation built into the keyboard and phone app makes the whole process feel more natural.
In addition to the French example I mentioned earlier, I used Samsung’s translation features to text with a coworker who speaks Korean. As soon as she sent me a text in Korean, a prompt to translate the message to English appeared in the Messages app. I typed my response in English in a separate text box below the messaging field, and within seconds my words, translated into Korean, appeared in the message box.
Features like these could be extremely useful for anyone who travels a lot, has family members who speak a different language or that frequently work with colleagues or clients in different parts of the world.

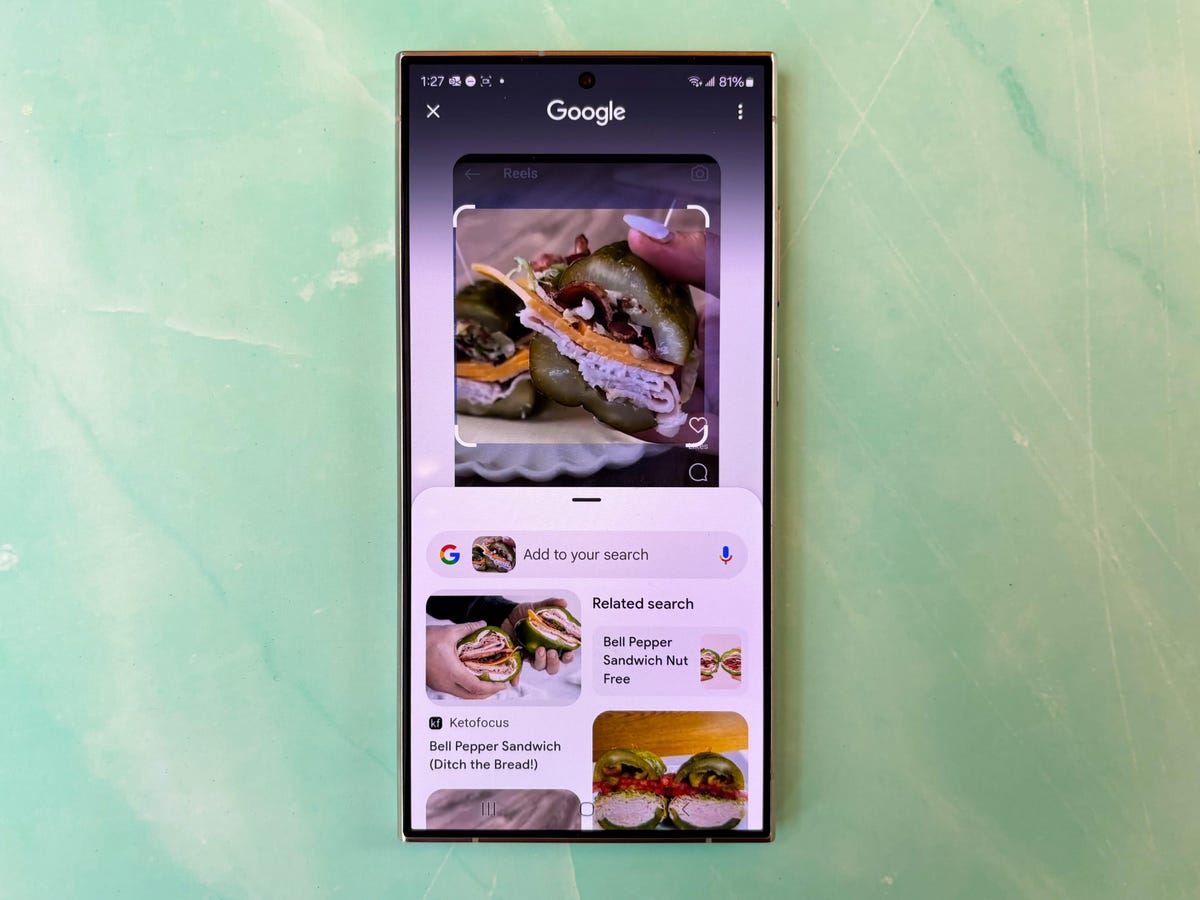
Circle to Search is another practical tool that has the potential to make certain tasks more convenient by preventing the need to switch between apps as often. It’s self explanatory; just circle an object on screen that you’d like to learn more about, and the Galaxy S24 will launch a Google search for that item or location.
I have to admit, it’s hard to fight the instinct to open Chrome or the Google app and just type in my search query the traditional way. But Circle to Search works impressively well so far. I circled images of pesto pasta in my Instagram feed to find recipes and nearby restaurants. Circling a photo of a dress that I liked in my Instagram feed also pulled up similar pieces. Dragging my finger around characters from an animated TV series I recently finished watching resulted in news stories and YouTube videos about those characters, although Google warns that search results for actual people may be limited.
Shopping is the most obvious use case, but there are other ways it could be useful. Circling my character in Diablo Immortals pulled up a search result about my character’s class, for example, which could be helpful for new players. But this experience wasn’t consistent. When I tried to reproduce that result on a separate occasion, I got links to websites and videos about other games like Final Fantasy and Genshin Impact. Depending on how Circle to Search evolves, I feel like there are opportunities for it to be much more helpful.
Another favorite feature of mine is Instant Slow-mo, which lets me preview any video in my gallery in slow motion just by pressing and holding the clip. It’s not a game-changer, but it’s fun to play around with nonetheless. My only complaint is that it’s not always easy to see how to save the clip in slow motion. You can do so by tapping the pencil icon below the video clip, but I wish there was a way to just save it directly from the preview mode.
However, not all Galaxy AI features feel as valuable, and the writing style tool in the Messages app falls into that bucket. It essentially feels like a Samsung-customized version of Google’s Magic Compose, and it’s based on Google’s technology. The tool can rewrite text messages in a different tone, with options including professional, casual, social, polite and emojify.
When I chose the casual option, which sounds the most like my usual tone, my husband thought the message sounded strange and unlike me. I could possibly see the polite or professional option being helpful if you’re sending a message to a work colleague, but other options like emojify and social just pepper your words with hashtags and emojis.
The summarize option in Samsung’s Notes app has a cap at 8,000 characters, meaning it couldn’t sum up the entire 1,475-word script (which was around 8,400 characters) I had written for my Galaxy S24 Ultra video review. While I understand that most people aren’t jotting down lengthy notes on their phones, long documents like these are the ones that need summarizing the most.
Overall, Galaxy AI seems to be off to a promising start, although its long-term usefulness will depend on where Samsung and Google take it, and whether the existing features actually resonate with people. The fine print on Samsung’s product page for the Galaxy S24 Ultra hints that it could eventually charge for such features after 2025, although the company hasn’t said how much. While I’m glad Samsung isn’t making you pay for the most expensive model to get Galaxy AI, I wish it offered a few extra Galaxy AI features specifically for the Ultra. Doing so could have made the Ultra’s high price a little easier to swallow, especially given Samsung’s emphasis on productivity and creative tools with Galaxy AI.
The Galaxy S24’s camera has a crisper 5x zoom

Samsung’s Galaxy Ultra phones are known for their zoom prowess, with the Ultra capable of zooming up to 100x digitally. But this time around, Samsung realized that quality matters over quantity. It replaced the 10-megapixel sensor that zooms at 10x on the S23 Ultra with a sharper 50-megapixel camera that specializes in 5x zoom, with the goal being to provide crisper results even at a shorter magnification.
Samsung succeeds in that regard, although you’ll have to look closely to spot the differences between photos from the Galaxy S24 Ultra and last year’s S23 Ultra. Take these photos of houseplants below as an example, both of which were taken at 5x zoom. They look the same at first glance, but when you examine them more closely, you can tell that the Galaxy S24 Ultra preserved more detail. I zoomed in more and cropped a section of it so that you could see the difference.
Galaxy S24 Ultra
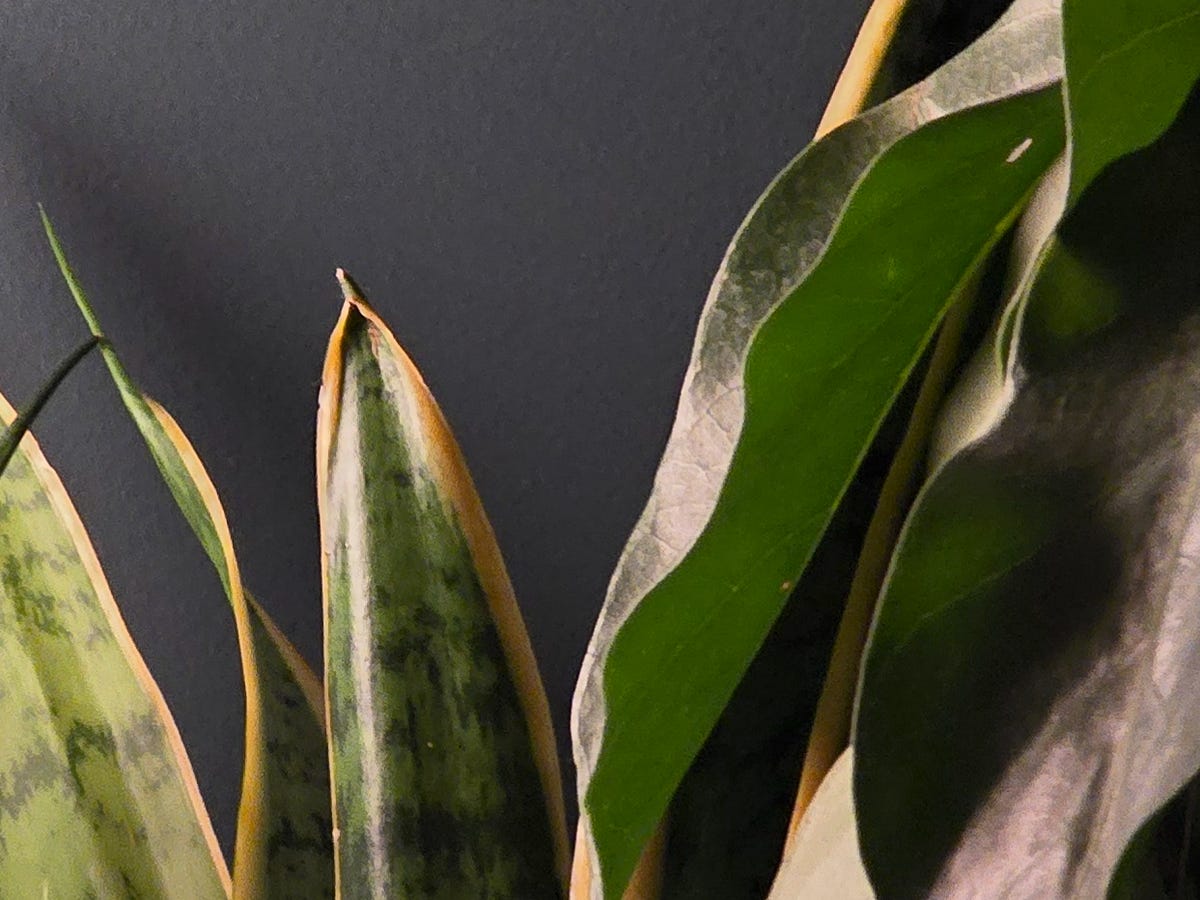

Galaxy S23 Ultra
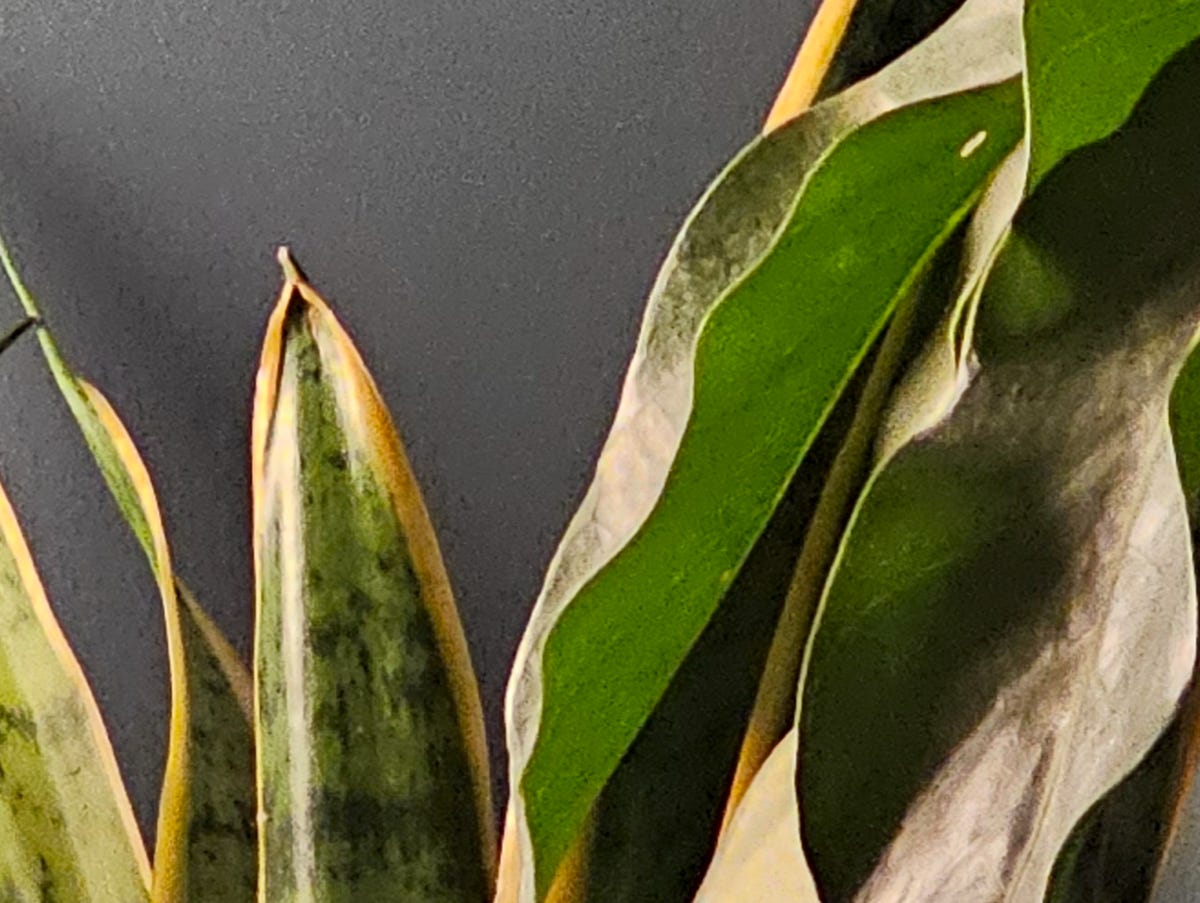

The Galaxy S24 Ultra also captured more detail at 5x zoom than the iPhone 15 Pro, although Apple’s photo is brighter. An image taken on Google’s Pixel 8 Pro, however, was crisper at 5x zoom than both Samsung and Apple’s.
iPhone 15 Pro Max

Pixel 8 Pro
The Galaxy S24 Ultra’s camera specifications are otherwise largely the same as the Galaxy S23 Ultra’s, though Samsung increased the size of the pixels, which should mean the S24 Ultra’s sensor can absorb more light.
As a result, I found that the Galaxy S24 Ultra is good at handling mixed and dim lighting environments, such as a cocktail bar or a friend’s living room. Even if the S24 Ultra’s photo wasn’t always the brightest of the bunch when compared to the S23 Ultra, iPhone 15 Pro and Google Pixel 8 Pro, it preserved a good amount of detail in these dark settings. When it comes to general image quality, the Galaxy S24 Ultra did a better job of making skin tones and colors look more natural compared to the S23 Ultra.
It’s hard to say whether the S24 Ultra is the best camera phone overall, since image quality can be subject to interpretation and depends on your preference. In my experience, each phone succeeded in their own way.
Check out the gallery below for more photos taken on the Galaxy S24 Ultra.
Galaxy S24 Ultra design, performance and battery life

The Galaxy S24 Ultra looks a lot like the S23 Ultra, but with some subtle yet important differences. There’s titanium in the design, and the screen now has flatter edges that make it easier to grip. Samsung also boosted the screen brightness to 2,600 nits, which is brighter than the S23 Ultra’s 1,750-nit screen on paper, but not as luminous as the OnePlus 12’s 4,500-nit peak brightness.
However, in everyday use, I couldn’t see much of a difference between the Galaxy S24 Ultra’s screen at maximum brightness and the S23 Ultra’s. Maybe the change will be more noticeable in bright sunlight; it’s been overcast and somewhat gloomy in New York and San Jose, California, the two cities I’ve spent time in while reviewing the S24 Ultra.

The Galaxy S24 lineup runs on a version of Qualcomm’s Snapdragon 8 Gen 3 processor optimized for Samsung’s devices, and it felt as snappy and smooth as you’d expect of a phone at this price. Language translations, which are processed on-device rather than in the cloud, happen quickly; games like Diablo Immortal and Devil May Cry: Peak of Combat run smoothly; and scrolling around the interface feels responsive and speedy.
Samsung is also making a big deal about the Galaxy S24’s ray-tracing capabilities, which should make shadows and reflections in games look more lifelike. Samsung cited Diablo Immortal, Racing Master, Arena Breakout and Night Crows as early examples of ray-tracing-optimized games. I didn’t see much of a difference when playing Arena Breakout on the Galaxy S24 Ultra alongside the Google Pixel 8 Pro, which does not support ray tracing. I’m not sure if Diablo Immortal has been updated to take advantage of the S24 Ultra’s ray tracing yet, but I noticed a difference regardless. Shadowy areas had more definition and contrast on the S24 Ultra compared to the Pixel 8 Pro, which made the game look a bit hazy by comparison.
The Galaxy S24 Ultra beat last year’s Galaxy S23 Ultra and Pixel 8 Pro, the latter of which runs on Google Tensor G3 processor, in benchmarks I ran that measure general computing and graphics performance. But the OnePlus 12 surpassed the S24 Ultra on 3DMark Wild Life Extreme, the graphics-oriented benchmark, while the iPhone 15 Pro Max beat Samsung’s new phone in general computing benchmarks (but not 3DMark).
Galaxy S24 Ultra Geekbench 6
- Galaxy S24 Ultra
- Galaxy S23 Ultra
- Pixel 8 Pro
- iPhone 15 Pro Max
- OnePlus 12
Galaxy S24 Ultra 3DMark Wild Life Extreme
- Galaxy S24 Ultra
- Galaxy S23 Ultra
- Pixel 8 Pro
- iPhone 15 Pro Max
- OnePlus 12
Battery life is solid so far, with the Galaxy S24 Ultra easily able to make it through more than a day on a single charge. But it’ll depend on how you’re using the phone. On a day that mostly involved browsing Instagram and Google, sending text messages, taking photos and streaming Spotify for about 30 minutes with the screen brightness set low, I still had 69% of my battery left after about 15 and a half hours of use.
After a busy workday, during which I streamed music for part of my commute (about 15 minutes), streamed video for about 25 minutes, frequently checked email and social media, and used my phone as it searched for cell service underground on the subway, I had 55% of my battery left after about 13 and a half hours of use. Playing games, processing some Generative Edit photos and turning up the brightness also drained the battery faster in my experience. We’ll update this review with CNET’s battery tests soon.
Overall thoughts

At $1,300, the Galaxy S24 Ultra is hard to recommend unless you really want a giant screen, a camera with a wide range of zoom options and the S Pen. These are the features that truly distinguish Samsung’s high-end phone from the less expensive Galaxy S24 and Galaxy S24 Plus. Galaxy AI is also coming to the Galaxy S23 series, and Google’s Pixel 8 family will get Circle to Search, which means there’s nothing about Galaxy AI that stands out on the Galaxy S24 Ultra specifically.
A device like the Galaxy S24 Ultra that’s already geared towards productivity thanks to its large screen and S Pen seems like a prime candidate for extra Galaxy AI features, so hopefully we’ll see more in a future update. Circle to Search and Generative Edit are easier to use with the S Pen, but that alone isn’t enough to justify the higher price.
Otherwise, the Galaxy S24 Ultra’s sharper 50-megapixel telephoto camera, speedy new processor and seven years of software updates make it a solid upgrade for those coming from an older Samsung phone — if you can stomach the high price.
How we test phones
Every phone tested by CNET’s reviews team is actually used in the real world. We test a phone’s features, play games and take photos. We examine the display to see if it’s bright, sharp and vibrant. We analyze the design and build to see how it is to hold and whether it has an IP-rating for water-resistance. We push the processor’s performance to the extremes, using standardized benchmark tools like GeekBench and 3DMark as well as our own anecdotal observations navigating the interface, recording high-resolution videos and playing graphically intense games at high refresh rates.
All the cameras are tested in a variety of conditions, from bright sunlight to dark indoor scenes. We try out special features like night mode and portrait mode and compare our findings against similarly priced competing phones. We also check out the battery life by using the phone daily as well as running a series of battery drain tests.
Editors’ note: CNET is using an AI engine to help create some stories. For more, see this post.
Samsung Galaxy S24 Ultra vs. competitors
| Samsung Galaxy S24 Ultra | Samsung Galaxy S23 Ultra | Google Pixel 8 Pro | Apple iPhone 15 Pro Max | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Display size, tech, resolution, refresh rate | 6.8-inch AMOLED; 3,120×1,440 pixels; 1-120Hz adaptive refresh rate | 6.8-inch AMOLED; 3,088×1,440 pixels; 120Hz adaptive refresh rate | 6.7-inch OLED; 3,120×1,440 pixels; 1-120Hz adaptive refresh rate | 6.1-inch OLED; 2,556×1,179 pixels; 120Hz adaptive refresh rate |
| Pixel density | 501 ppi | 500 ppi | 489 ppi | 460 ppi |
| Dimensions (inches) | 6.40 x 3.11 x 0.34 in | 6.43 x 3.07 x 0.35 in | 6.4 x 3 x 0.3 in | 5.77 x 2.78 x 0.32 in |
| Dimensions (millimeters) | 163 x 79 x 8.6 mm | 163.3 x 78 x 8.9 mm | 162.6 x 76.5 x 8.8 mm | 146.6 x 70.6 x 8.25 mm |
| Weight (grams, ounces) | 233 g (8.22 oz) | 234 g (8.25 oz) | 213 g (7.5 oz) | 187 g (6.6 oz) |
| Mobile software | Android 14 | Android 13 | Android 14 | iOS 17 |
| Camera | 200-megapixel (wide), 12-megapixel (ultrawide), 10-megapixel (3x telephoto), 50-megapixel (5x telephoto) | 200-megapixel (wide), 12-megapixel (ultrawide) 10-megapixel (3x telephoto) 10-megapixel (10x telephoto) | 50-megapixel (wide), 48-megapixel (ultrawide), 48-megapixel (telephoto) | 48-megapixel (wide), 12-megapixel (ultrawide), 12-megapixel (3x telephoto) |
| Front-facing camera | 12-megapixel | 12-megapixel | 10.5-megapixel | 12-megapixel |
| Video capture | 8K | 8K | 4K | 4K |
| Processor | Qualcomm Snapdragon 8 Gen 3 | Qualcomm Snapdragon 8 Gen 2 for Galaxy | Google Tensor G3 | Apple A17 Pro |
| Storage and RAM | 12GB RAM + 256GB, 512GB, 1TB | 8GB RAM + 256GB; 12GB RAM + 256GB, 512GB, 1TB | 12GB RAM + 128GB, 256GB, 512GB, 1TB | 128GB, 256GB, 512GB, 1TB (RAM undisclosed) |
| Expandable storage | None | None | None | None |
| Battery | 5,000 mAh | 5,000 mAh | 5,050 mAh | Undisclosed; Apple claims up to 23 hours of video playback (20 hours streamed) |
| Fingerprint sensor | Under display | Under display | Under display | None (Face ID) |
| Connector | USB-C | USB-C | USB-C | USB-C |
| Headphone jack | None | None | None | None |
| Special features | Titanium frame, 2,600-nit peak brightness; 7 years of OS and security updates; 5G (mmWave); IP68 water and dust resistance; wireless PowerShare to charge other devices; integrated S Pen; UWB for finding other devices; 45W wired charging (charger not included); Galaxy AI; Wi-Fi 7; Gorilla Glass Armor cover glass | 4 years of OS updates, 5G (Sub6, mmWave); IP68 water resistance; wireless PowerShare to charge other devices; integrated S Pen; 100x Space Zoom; 10x optical zoom; UWB for finding other devices; 45W wired charging | 5G (Sub 6, mmWave); VPN by Google One; 7 years of OS, security and Feature Drop updates; front-facing camera has autofocus; 13W Qi wireless charging; 30W wired charging; USB-3.2 speeds via USB-C; IP68 dust and water resistance; Gorilla Glass Victus 2 on front and back | 5G (Sub6, mmWave); Action Button, Always-On display, IP68 water resistance, MagSafe, Dynamic Island, 5x optical zoom (120mm equivalent), satellite connectivity, eSIM, thread networking technology |
| US price starts at | $1,300 (256GB) | $1,200 (256GB) | $999 (128GB) | $999 (128GB) |
| UK price starts at | £1,249 (256GB) | £1,249 (256GB) | £999 (128GB) | £999 (128GB) |
| Australia price starts at | AU$2,199 (256GB) | AU$1,949 (256GB) | AU$1,699 (128GB) | AU$1,849 (128GB) |
Technologies
How to Get Verizon’s New Internet Plan for Just $25 Per Month
Technologies
This $20K Humanoid Robot Promises to Tidy Your Home. But There Are Strings Attached
The new Neo robot from 1X is designed to do chores. It’ll need help from you — and from folks behind the curtain.
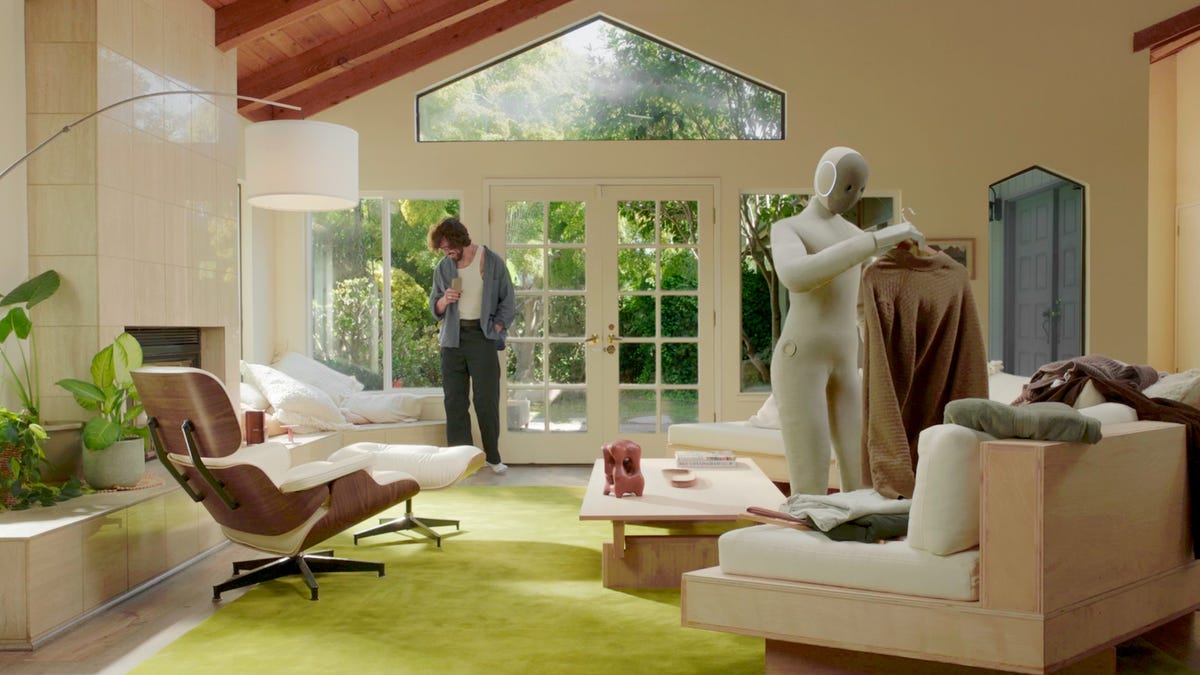

It stands 5 feet, 6 inches tall, weighs about as much as a golden retriever and costs near the price of a brand-new budget car.
This is Neo, the humanoid robot. It’s billed as a personal assistant you can talk to and eventually rely on to take care of everyday tasks, such as loading the dishwasher and folding laundry.
Neo doesn’t work cheap. It’ll cost you $20,000. And even then, you’ll still have to train this new home bot, and possibly need a remote assist as well.
If that sounds enticing, preorders are now open (for a mere $200 down). You’ll be signing up as an early adopter for what Neo’s maker, a California-based company called 1X, is calling a «consumer-ready humanoid.» That’s opposed to other humanoids under development from the likes of Tesla and Figure, which are, for the moment at least, more focused on factory environments.
Neo is a whole order of magnitude different from robot vacuums like those from Roomba, Eufy and Ecovacs, and embodies a long-running sci-fi fantasy of robot maids and butlers doing chores and picking up after us. If this is the future, read on for more of what’s in store.
Don’t miss any of our unbiased tech content and lab-based reviews. Add CNET as a preferred Google source.
What the Neo robot can do around the house
The pitch from 1X is that Neo can do all manner of household chores: fold laundry, run a vacuum, tidy shelves, bring in the groceries. It can open doors, climb stairs and even act as a home entertainment system.
Neo appears to move smoothly, with a soft, almost human-like gait, thanks to 1X’s tendon-driven motor system that gives it gentle motion and impressive strength. The company says it can lift up to 154 pounds and carry 55 pounds, but it is quieter than a refrigerator. It’s covered in soft materials and neutral colors, making it look less intimidating than metallic prototypes from other companies.
The company says Neo has a 4-hour runtime. Its hands are IP68-rated, meaning they’re submersible in water. It can connect via Wi-Fi, Bluetooth and 5G. For conversation, it has a built-in LLM, the same sort of AI technology that powers ChatGPT and Gemini.
The primary way to control the Neo robot will be by speaking to it, just as if it were a person in your home.
Still, Neo’s usefulness today depends heavily on how you define useful. The Wall Street Journal’s Joanna Stern got an up-close look at Neo at 1X’s headquarters and found that, at least for now, it’s largely teleoperated, meaning a human often operates it remotely using a virtual-reality headset and controllers.
«I didn’t see Neo do anything autonomously, although the company did share a video of Neo opening a door on its own,» Stern wrote last week.
1X CEO Bernt Børnich told her that Neo will do most things autonomously in 2026, though he also acknowledged that the quality «may lag at first.»
The company’s FAQ says that for any chore request Neo doesn’t know how to accomplish, «you can schedule a 1X Expert to guide it» to help the robot «learn while getting the job done.»
What you need to know about Neo and privacy
Part of what early adopters are signing up for is to let Neo learn from their environment so that future versions can operate more independently.
That learning process raises privacy and trust questions. The robot uses a mix of visual, audio and contextual intelligence — meaning it can see, hear and remember interactions with users throughout their homes.
«If you buy this product, it is because you’re OK with that social contract,» Børnich told the Journal. «It’s less about Neo instantly doing your chores and more about you helping Neo learn to do them safely and effectively.»
Neo’s reliance on human operation behind the scenes prompted a response from John Carmack, a computer industry luminary known for his work with VR systems and the lead programmer of classic video games including Doom and Quake.
«Companies selling the dream of autonomous household humanoid robots today would be better off embracing reality and selling ‘remote operated household help’,» he wrote in a post on the X social network (formerly Twitter) on Monday.
1X says it’s taking steps to protect your privacy: Neo listens only when it recognizes it’s being addressed, and its cameras will blur out humans. You can restrict Neo from entering or viewing specific areas of your home, and the robot will never be teleoperated without owner approval, the company says.
But inviting an AI-equipped humanoid to observe your home life isn’t a small step.
The first units will ship to customers in the US in 2026. There is a $499 monthly subscription alternative to the $20,000 full-purchase price, though that will be available at an unspecified later date. A broader international rollout is promised for 2027.
Neo’s got a long road ahead of it to live up to the expectations set by Rosie the Robot in The Jetsons way back when. But this is no Hanna-Barbera cartoon. What we’re seeing now is a much more tangible harbinger of change.
Technologies
I Wish Nintendo’s New Switch 2 Zelda Game Was an Actual Zelda Game
Hyrule Warriors: Age of Imprisonment has great graphics, a great story and Zelda is actually in it. But the gameplay makes me wish for another true Zelda title instead.
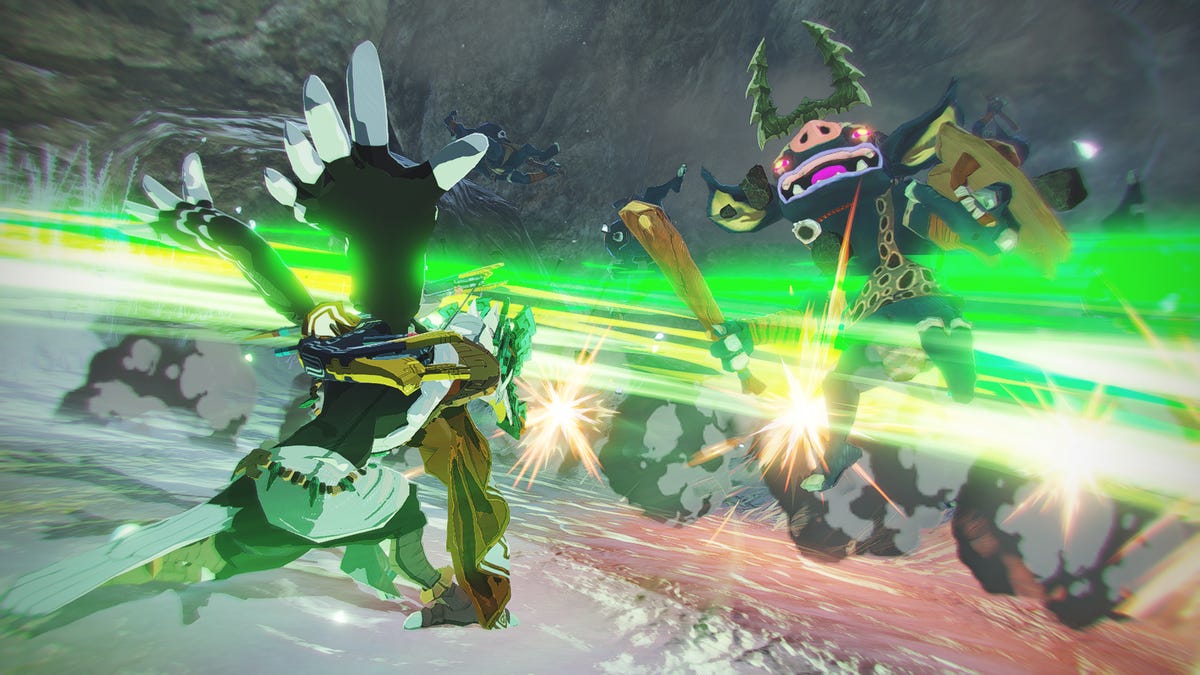

I’ve never been a Hyrule Warriors fan. Keep that in mind when I say that Nintendo’s new Switch 2-exclusive Zelda-universe game has impressed me in several ways, but the gameplay isn’t one of them. Still, this Zelda spinoff has succeeded in showing off the Switch 2’s graphics power. Now can we have a true Switch 2 exclusive Zelda game next?
The upgraded graphics in Tears of the Kingdom and Breath of the Wild has made the Switch 2 a great way to play recent Zelda games, which had stretched the Switch’s capabilities to the limit before. And they’re both well worth revisiting, because they’re engrossing, enchanting, weird, epic wonders. Hyrule Warriors: Age of Imprisonment, another in the Koei-Tecmo developed spinoff series of Zelda-themed games, is a prequel to Tears of the Kingdom. It’s the story of Zelda traveling back in time to ancient Hyrule, and the origins of Ganondorf’s evil. I’m here for that, but a lot of hack and slash battles are in my way.
A handful of hours in, I can say that the production values are wonderful. The voices and characters and worlds feel authentically Zelda. I feel like I’m getting a new chapter in the story I’d already been following. The Switch 2’s graphics show off smooth animation, too, even when battles can span hundreds of enemies.
But the game’s central style, which is endless slashing fights through hordes of enemies, gets boring for me. That’s what Hyrule Warriors is about, but the game so far feels more repetitive than strategic. And I just keep button-mashing to get to the next story chapter. For anyone who’s played Hyrule Warriors: Age of Calamity, expect more of the same, for the most part.
I do like that the big map includes parts in the depths and in the sky, mirroring the tri-level appeal of Tears of the Kingdom. But Age of Calamity isn’t a free-wandering game. Missions open up around the map, each one opening a contained map to battle through. Along the way, you unlock an impressive roster of Hyrule characters you can control.
As a Switch 2 exclusive to tempt Nintendo fans to make the console upgrade, it feels like a half success. I admire the production values, and I want to keep playing just to see where the story goes. But as a purchase, it’s a distant third to Donkey Kong Bananza and Mario Kart World.
Hyrule Warriors fans, you probably know what you’re probably in for, and will likely get this game regardless. Serious Zelda fans, you may enjoy it just for the story elements alone.
As for me? I think I’ll play some more, but I’m already sort of tuning the game out a bit. I want more exploration, more puzzles, more curiosity. This game’s not about that. But it does show me how good a true next-gen Zelda could be on the Switch 2, whenever Nintendo decides to make that happen.
-

 Technologies3 года ago
Technologies3 года agoTech Companies Need to Be Held Accountable for Security, Experts Say
-

 Technologies3 года ago
Technologies3 года agoBest Handheld Game Console in 2023
-

 Technologies3 года ago
Technologies3 года agoTighten Up Your VR Game With the Best Head Straps for Quest 2
-

 Technologies4 года ago
Technologies4 года agoVerum, Wickr and Threema: next generation secured messengers
-

 Technologies4 года ago
Technologies4 года agoBlack Friday 2021: The best deals on TVs, headphones, kitchenware, and more
-

 Technologies4 года ago
Technologies4 года agoGoogle to require vaccinations as Silicon Valley rethinks return-to-office policies
-

 Technologies4 года ago
Technologies4 года agoOlivia Harlan Dekker for Verum Messenger
-

 Technologies4 года ago
Technologies4 года agoiPhone 13 event: How to watch Apple’s big announcement tomorrow