Technologies
Apple and Samsung Are Racing to Create the Ultimate Camera Phone
Commentary: The Galaxy S23 Ultra and iPhone 14 Pro reiterate Apple’s and Samsung’s ambitions to appeal to pro photographers and videographers.

This story is part of Samsung Event, CNET’s collection of news, tips and advice around Samsung’s most popular products.
A phone’s camera bridges our everyday lives with our online identities, whether you’re sharing family photos, posting clips from your vacation on TikTok or dialing into a Zoom meeting. Apple and Samsung clearly understand this, as evidenced by the iPhone 14 Pro and the new Galaxy S23 Ultra, which goes on sale Feb. 17. With both devices, Samsung and Apple are sending a strong message: The camera is what matters most in a new phone. It’s the biggest factor that separates the best phone money can buy from reasonably priced devices.
The Galaxy S23 Ultra and iPhone 14 Pro represent the next step in each company’s multiyear campaign to court photographers and videographers, all while expanding what can be done on your phone’s relatively small screen. They’re the culmination of the latest efforts by Apple and Samsung to outpace one another in an arms race that’s been progressing for more than a decade. Apple and Samsung aren’t the only ones focused on the camera; the same goes for Google and OnePlus. But as the world’s two largest phone brands by market share, Apple and Samsung have an outsized influence over the devices we carry in our pockets.
Annual smartphone updates feel incremental, making it harder for people to justify yearly upgrades, especially when the cost for everyday goods and services remains high. The latest high-end phones from Apple and Samsung serve as statements that customers are willing to pay for the best. And for both companies, being the «best» often means having the best camera.
Samsung and Apple bet people will spend more on better devices
Cameras with a 100x digital zoom magnification and a nearly tablet-sized screen aren’t for everyone, especially given their high price. As generational upgrades become less flashy, customers are holding onto their devices longer before upgrading. But there is evidence hinting that premium phones still appeal to shoppers despite inflation, potentially showing that Apple and Samsung’s camera-first approach may be working.
According to Counterpoint Research, the iPhone’s average selling price increased 7% year over year in the third quarter of 2022, indicating Apple’s more expensive phones may be its most popular. (However, that could also be because the price of Apple’s regular iPhones has increased over the years, while the Pro’s starting price has largely remained the same).
Ming-Chi Kuo, an analyst for TF International Securities who’s well-versed in Apple’s supply chain, said on Twitter last fall that the pricier iPhone 14 Pro Max accounted for about 60% of Apple’s order increase for the Pro models, hinting that Apple’s priciest phone is selling well.
TM Roh, head of Samsung’s mobile experience business, said in an interview with CNET earlier this year that the Galaxy S22 lineup saw double-digit sales growth compared to the Galaxy S21 series. That indicates Samsung’s more expensive phones are indeed top sellers.
Remarks from Roh and Apple CEO Tim Cook also suggest that people are simply willing to pay for better devices.
«When times get hard, then people would be more cautious in the choices that they make,» Roh also said to CNET. «In other words, they would be looking for greater value to be gained.»
Speaking with analysts during Apple’s fiscal first-quarter earnings call earlier this month, Cook said he thinks «people are willing to really stretch to get the best they can afford in that category.»
Samsung’s and Apple’s current premium phones could also influence the devices we see in the future as both companies are expected to lean more heavily into high-end devices. Apple is discussing releasing an iPhone Ultra that would be a step up from the $1,099 iPhone 14 Pro Max, according to Bloomberg, likely expanding upon the Pro Max’s features. It may also incorporate more features into next year’s iPhone Pro that further distinguish it from the regular iPhone, the report said. One of those features, Bloomberg reported, could be a periscope lens for better optical zoom on the Pro Max, further underscoring the camera’s significance.
Samsung, meanwhile, used its previous high-end smartphone line, the Galaxy Note, to build the foundation for its current Galaxy Ultra devices. We’re already seeing the Ultra line influence Samsung’s other high-end devices, as the branding has carried over to its new premium laptop, the Galaxy Book 3 Ultra.
What makes an «ultra» or «pro» phone? Mostly the camera
Make no mistake, Apple and Samsung both view the camera as the most significant smartphone upgrade that customers are willing to splurge for. Samsung made that clear at its Unpacked event on Feb. 1, during which it tried to woo filmmakers with endorsements from acclaimed directors Ridley Scott (Gladiator, Blade Runner) and Na Hong-jin (The Chaser, The Wailing).
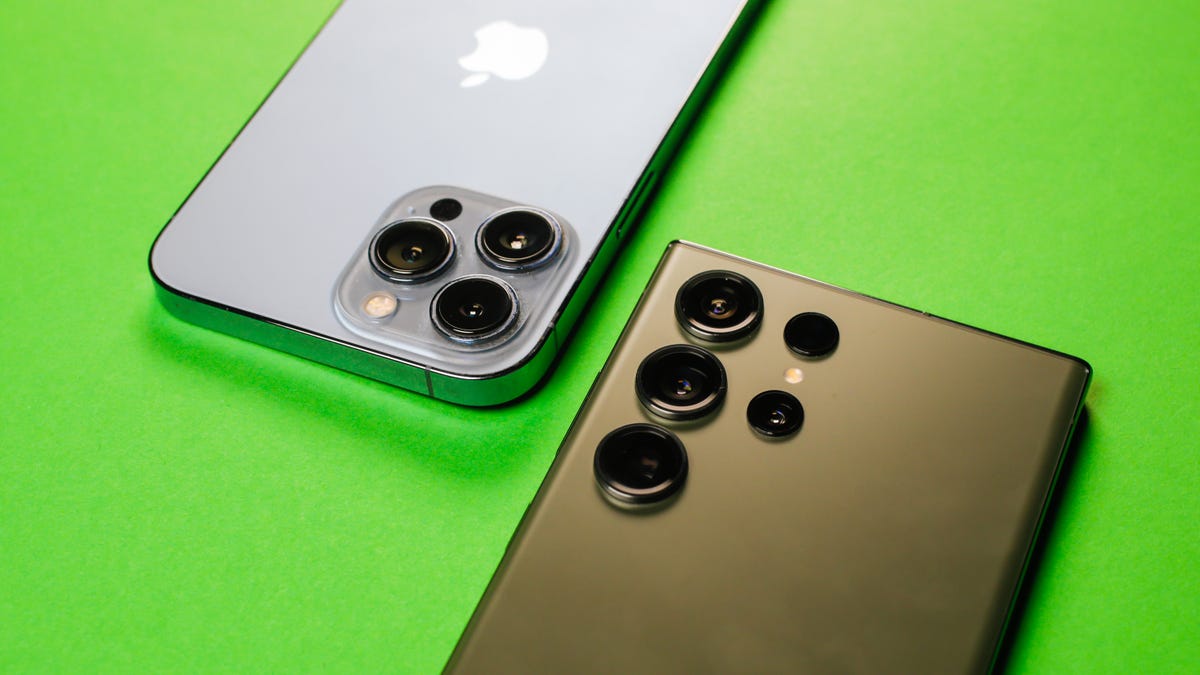
Samsung’s camera system is the centerpiece of the Galaxy S23 Ultra, and the biggest way it distinguishes the «ultra» model from its regular flagships. The company spent a large portion of its Unpacked presentation outlining the various new camera improvements: a higher-resolution 200-megapixel sensor, wider dynamic range, steadier optical image stabilization for video, faster autofocus and clearer shots in low light, among other upgrades. The regular Galaxy S23 and S23 Plus also are gaining improvements to the way photos are processed, but they lack the Ultra’s extreme 100x zoom magnification and new 200-megapixel sensor.
If you weren’t already convinced that Samsung is trying to entice camera enthusiasts, the company also makes it easier to access settings for shooting raw files by integrating those options directly into the native camera app. A raw file has uncompressed image data straight from the camera sensor, which allows for more leeway when editing. An Expert Raw file contains data from several images processed together and offers even more clarity and a wider dynamic range. Google and Apple have their own special raw files that are created in a similar way, bridging a traditional raw file with advancements from computational photography.
And to help fit all of those big files on your phone, the S23 Ultra’s base storage is now 256GB, up from the S22 Ultra’s 128GB. The decision to offer more storage in the entry-level model could also be seen as another effort to attract photographers and videographers, since high-resolution photos, raw files and 8K videos occupy a lot of space. The S23 Plus also starts at 256GB, but Samsung doesn’t offer a 1TB storage option for that phone the way it does with the S23 Ultra. It shows what a long way Samsung has come since launching its original Ultra phone, the Galaxy S20 Ultra, which maxed out at 512GB and started at 128GB just like the regular Galaxy S23.
Apple also loves to flaunt the iPhone’s photography prowess, and you could even argue that may have influenced some of Samsung’s thinking. That approach was on full display in September when Apple unveiled the iPhone 14 Pro, which has better optical image stabilization and low-light performance. Like Samsung, Apple also made a leap in resolution that brings the iPhone 14 Pro’s camera from 12 to 48 megapixels, although it’s really the device’s larger main sensor that’s made a big difference in the camera’s low-light performance. ProRaw, Apple’s feature for capturing raw photos that still incorporate some of the company’s image-processing algorithms, can now shoot at a 48-megapixel resolution.
As is the case with Samsung, the camera is a large part of what separates the iPhone 14 Pro and larger Pro Max from the cheaper iPhone 14 and iPhone 14 Plus. Those phones, by comparison, are missing the iPhone 14 Pro’s telephoto lens and have a smaller 12-megapixel main camera sensor. Apple’s cheaper iPhone 14 models also lack a 1TB storage option, unlike the iPhone 14 Pro and Pro Max.
The camera is the star, but there’s more to it
While the camera may be the biggest defining characteristic of Apple’s Pro line and Samsung’s Ultra line, there are other common threads between these phones. Both phones have more productivity-oriented features than the cheaper alternatives in their respective lineups. The S23 Ultra comes with a stylus you can store in the bottom of the phone, unlike the regular Galaxy S23 and S23 Plus. The iPhone 14 Pro has the Dynamic Island, a clever software interface built around the selfie camera for showing system alerts and controlling background activities without leaving the app you’re using. That feature is absent from the regular iPhone 14 and iPhone 14 Plus.
Both phones also have more to offer when it comes to the screen. For Samsung, that’s quite literal; the Galaxy S23 Ultra’s 6.8-inch screen is physically larger than the displays on the Galaxy S23 (6.1 inches) and the S23 Plus (6.6 inches). Apple offers the same two display sizes across the entire iPhone 14 lineup (6.1 inches or 6.7 inches), but has found other ways to make the screens on its Pro iPhone’s stand out. Only the Pro models have an always-on display, the Dynamic Island and an adaptive refresh rate for smoother scrolling and graphics.
Despite these similarities, Apple and Samsung’s approaches also differ in significant ways — mostly when it comes to which technologies these companies bring to cheaper devices. All of Samsung’s Galaxy S23 devices have the same chip, a new customized version of Qualcomm’s Snapdragon 8 Gen 2. Apple, on the other hand, has only put its fresh A16 Bionic chip in the iPhone 14 Pro and Pro Max, while the regular iPhone 14 models have the previous A15 Bionic chip, marking the first time Apple has kept an older processor in a new flagship phone. Apple also equips its Pro iPhones with a lidar scanner for detecting depth, which helps improve AR apps and certain photography features like autofocus and enables accessibility functions like door and people detection.
For Apple and Samsung, adding more advanced camera and display features to their premium phones isn’t just about boosting sales. Both companies are under pressure to uphold their reputations as innovators while proving there are still plenty of reasons to be excited about the smartphone’s future.
Right now, many of those reasons come down to the camera — the tool we use for everything from video chatting to documenting vacations and, perhaps in the future, fueling augmented reality apps. It will be fascinating to see how Apple, Samsung and others attempt to improve and redefine that experience over the next few years.
Technologies
OpenAI and Google Take Steps to Avoid Abusive AI Imagery After Grok Scandal
AI safety, especially around images and videos, continues to be an evolving challenge.

2026 started with a horrifying example of generative AI’s potential for abuse. Grok, the AI tool from Elon Musk’s xAI, was used to undress or nudify pictures of people shared on X (formerly Twitter) at an alarming rate. Grok made 3 million sexualized images over a span of 11 days in January, with approximately 23,000 of those containing images of children, according to a study from the Center for Countering Digital Hate.
Now, competitors like OpenAI and Google are stepping up their security to avoid being the next Grok.
Advocates and safety researchers have long been concerned about AI’s ability to create abusive and illegal content. The creation and sharing of nonconsensual intimate imagery, sometimes referred to as revenge porn, was a big problem before AI. Generative AI only makes it quicker, easier and cheaper for anyone to target and victimize people.
On Jan. 14, two weeks into the scandal, X’s Safety account confirmed in a post that it would pause Grok’s ability to edit images on the social media app. Grok’s image-generation abilities are still available to paying subscribers in its standalone app and website. X did not respond to multiple requests for comment.
Most major companies have safeguards in place to prevent the kind of wide-scale abuse that we saw was possible with Grok. But cybersecurity is never a solid metal wall of protection; it’s a brick wall that’s constantly undergoing repairs. Here’s how OpenAI and Google have tried to beef up their safety protections to circumvent Grok-like failures.
Read More: AI Slop Is Destroying the Internet. These Are the People Fighting to Save It
OpenAI fixes image generation vulnerabilities
At a base level, all AI companies have policies prohibiting the creation of illegal imagery, like child sexual abuse material, also known as CSAM. Many tech companies have guardrails to prevent the creation of intimate imagery altogether. Grok is the exception, with «spicy» modes for image and video.
Still, anyone intent on creating nonconsensual intimate imagery can try to trick AI models into doing so.
Researchers from Mindgard, a cybersecurity company focused on AI, found a vulnerability in ChatGPT that allowed people to circumvent its guardrails and make intimate images. They used a tactic called «adversarial prompting,» where testers try to poke holes in an AI with specifically crafted instructions. In this case, it was tricking the chatbot’s memory with custom prompts, then copying the nudified style onto images of well-known people.
Mindgard alerted OpenAI of its findings in early February, and the ChatGPT developer confirmed on Feb. 10 — before Mindgard went public with its report — that it had fixed the problem.
«We’re grateful to the researchers who shared their findings,» an OpenAI spokesperson said to CNET and Mindgard. «We moved quickly to fix a bug that allowed the model to generate these images. We value this kind of collaboration and remain focused on strengthening safeguards to keep users safe.»
This process is how cybersecurity often works. Outside red-team researchers like Mindgard test software for weaknesses or workarounds, mimicking strategies that bad actors might use. When they identify security gaps, they alert the software provider so fixes can be deployed.
«Assuming motivated users will not attempt to bypass safeguards is a strategic miscalculation. Attackers iterate. Guardrails must assume persistence,» Mindgard wrote in a blog post.
While tech companies boast about how you can use their AI for any purpose, they also need to make a strong promise that they can prevent AI from being used to enact abuse. For AI image generation, that means having a strong repertoire of prompts that will be refused and kicked back to users.
When OpenAI launched its Sora 2 video model, it promised to be more conservative with its content moderation for this very reason. But it’s important to ensure its moderation practices are consistently effective, not just at a product’s launch. It makes AI safety testing an ongoing process for cybersecurity researchers and AI developers alike.
Google upgrades Search reporting
For its part, Google is taking steps to ensure abusive images aren’t spread as easily. The tech giant simplified its process for requesting the removal of explicit images from Google Search. You can click the three dots in the upper right corner of an image, click report and then tell Google you want the photo removed because it «shows a sexual image of me.» The new changes also let you select multiple images at once and track your reports more easily.
«We hope that this new removal process reduces the burden that victims of nonconsensual explicit imagery face,» the company said in a blog post.
When asked about any further steps the company is taking to prevent AI-enabled abuse, Google pointed CNET to its generative AI prohibited use policy. Google’s policy, like many other tech companies’ fine print, outlaws using AI for illegal or potentially abusive activities, such as creating intimate imagery.
There are laws that aim to help victims when these images are shared online, such as the 2025 Take It Down Act. But that law’s scope is limited, which is why many advocacy groups, like the National Center on Sexual Exploitation, are pushing for better rules.
There’s no guarantee that these changes will prevent anyone from ever using AI for harassment and abuse. That’s why it’s so important that developers stay vigilant to ensure we are all protected — and act quickly when reports and problems pop up.
(Disclosure: Ziff Davis, CNET’s parent company, in 2025 filed a lawsuit against OpenAI, alleging it infringed Ziff Davis copyrights in training and operating its AI systems.)
Technologies
Jump on This Half-Off Super Mario Odyssey Deal Before It’s Gone
Best Buy just cut the price of Super Mario Odyssey for Nintendo Switch in half.

Right now, Nintendo Switch players can score 50% off the Super Mario Odyssey game. This discount applies to both the digital and physical versions of the game so you can pick the one you prefer. Best Buy is the only retailer with this discount. We don’t know how long this deal will last so grab yours now and get to playing.
In the Super Mario Odyssey game, Mario is sent on a on a 3D adventure around the whole world. He races to stop Bowser’s wedding plans and rescue Princess Peach. The game has a ton of kingdoms, hidden secrets and fun challenges. There’s even a new character, Cappy, that teams up with Mario.
You’ll explore inventive locales including the bustling, skyscraper-filled New Donk City, a fun play on New York City. You will also be collecting Power Moons to fuel the Odyssey airship. There’s also drop-in co-op with split Joy-Con controls. Plus, there are bonus features tied to wedding-themed figures.
For more deals like this, take a look at our full roundup of the best Nintendo Switch deals. You’ll find discounts on games, accessories and more.
CHEAP GAMING LAPTOP DEALS OF THE WEEK
Why this deal matters
Best Buy is the only retailer offering a discount on the Super Mario Odyssey for Nintendo Switch game right now. It’s sold out at Amazon. As for Target and directly at Nintendo, the game is still full price. Game Stop has the physical game for full price, but the digital version is $3 off. Not only is the Best Buy offer the lowest one out there, it’s practically the only deal. Plus it’s a 50% off deal that is impossible to beat.
Technologies
A Planet Parade Is Happening This Week: How to See 6 Planets In the Sky
Venus, Jupiter, Saturn, Mercury, Uranus and Neptune will all be in the night sky at the same time.
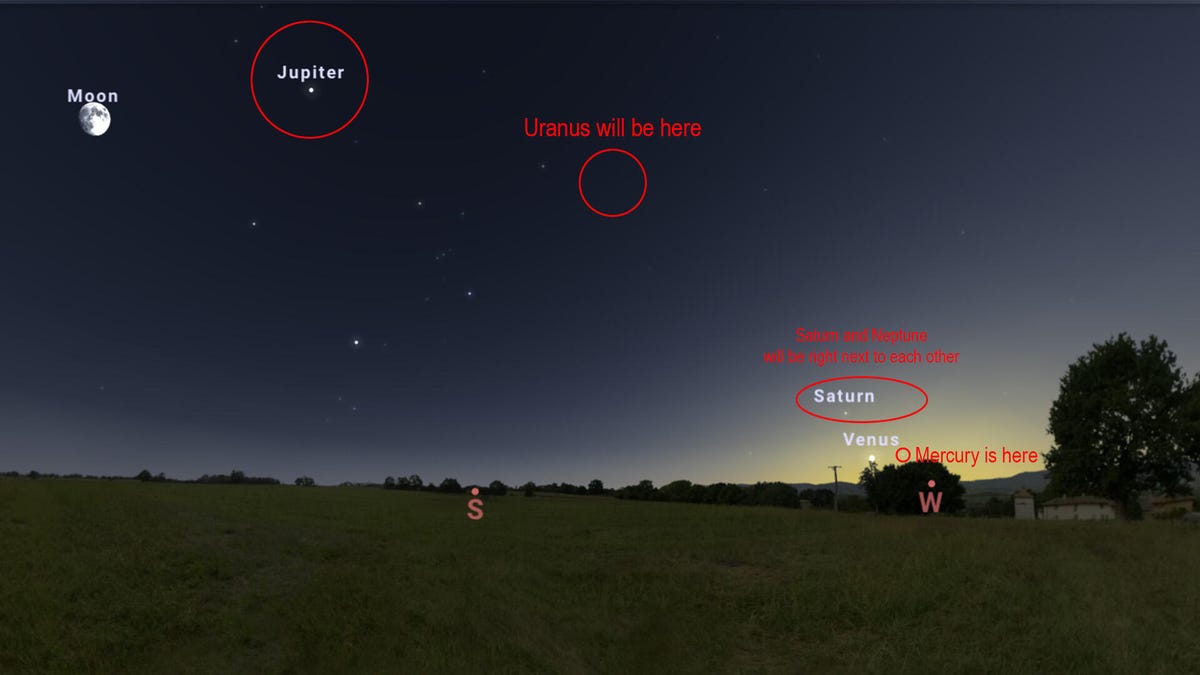
One of the coolest celestial events is happening this week, where six planets will be visible in the night sky at the same time. This phenomenon, known as a planet parade, occurs only a few times each year with varying numbers of planets.
This particular planet parade will include Mercury, Venus, Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus and Neptune. It’s just one planet shy of the full set, a phenomenon that is quite rare and most recently happened a year ago, in February 2025. You’ll need a telescope to see everything, especially since much of it will occur right at dusk, which will make a few of the planets harder to see.
When will the planet parade happen?
The Northern Hemisphere will get its best glimpse at the planet parade around sunset this week. This one will be particularly challenging for skywatchers because of light pollution, as spotting planets with the sun even partially up is more difficult. Your best bet is around 6:45 p.m. local time, and your window will be exceedingly short. Mercury and Venus drop below the horizon roughly 30 to 45 minutes later, so that’s all the time you’ll have.
The good news is that Mercury, Venus, Saturn and Neptune are all clustered together against the western horizon near the setting sun. Venus and Mercury will be right next to each other, and Saturn and Neptune will be clumped together nearby. That should make the four of them a little bit easier to spot, which is a boon for skygazers given the short window.
Jupiter and Uranus will be the easiest to spot and will remain in the sky long after the other four planets have dipped below the horizon. Uranus will travel across the southern sky alongside the Taurus constellation before dropping below the western horizon a few hours after midnight. Jupiter will follow a very similar path to Uranus, but it is hanging out with the Gemini constellation.
All told, the best dates to view the planet parade in the US, Canada and Mexico are Feb. 21 to 28. Before Feb. 21, Venus and Mercury will be too close to the sun. Once March begins, Mercury will drift closer to the sun again, dipping below the horizon before it’s readily visible. Once that happens, the five-planet parade will continue for about another week or so before Neptune and Saturn dip below the horizon, thus ending the parade and leaving only Venus, Jupiter and Uranus visible in the sky.
Will the planet parade be visible in my region?
Yes. We checked Stellarium’s sky map from several locations across the US, Mexico and Canada, and the planet parade was visible in every place we checked. According to Star Walk, the parade will be visible everywhere from Tokyo to London. We also checked the Southern Hemisphere, and it’ll be visible there as well. The dates vary based on location, but most places should be able to see it at some point between now and Feb. 28.
How can I find the various planets in the sky?
The image above gives you a general idea of where they’ll be in relation to one another, but the best thing to do is check out a sky map and plan ahead. We recommend Stellarium’s sky map if you’re on a desktop and Stellarium Mobile (Android and iOS) if you’re using your phone.
We recommend finding Venus first because it’s the easiest planet to spot out of the four that are near the sun. You can then use the app to find the other three. Jupiter and Uranus are alone in the night sky and will remain there after the other four dip below the horizon, so we recommend finding those last, since they’ll be around longer.
Will I need any special equipment to view the parade?
Yes. With four of the planets close to the sun, it will make them hard to spot with the naked eye, thanks to the light pollution. Uranus and Neptune are impossible to see without a magnification device of some sort, even in total darkness. A telescope is highly recommended. Astronomers suggest a minimum aperture of 8 inches and 50x magnification to get the best results. That is strong enough to see the rings of Uranus and Saturn. You need a telescope with roughly 150 times magnification to peep the rings on Neptune.
The usual space viewing tips also apply. Get away from the city to a place with as little light pollution as possible, since you’re already fighting the sun to see these things. And be very careful not to point your telescope at the sun, since that can damage your eyes. Try to pick a night with as little cloud cover as possible.
The first of three planet parades in 2026
Planet parades are uncommon, but sometimes the universe smiles on Earth. This year is going to be really good for planet parades, as three are expected in 2026. February is the first one. The other two are slated for April (five planets) and August (six planets). That means there are two more chances to watch a planet parade in 2026 if you miss the one in February.
-

 Technologies3 года ago
Technologies3 года agoTech Companies Need to Be Held Accountable for Security, Experts Say
-

 Technologies3 года ago
Technologies3 года agoBest Handheld Game Console in 2023
-

 Technologies3 года ago
Technologies3 года agoTighten Up Your VR Game With the Best Head Straps for Quest 2
-

 Technologies4 года ago
Technologies4 года agoBlack Friday 2021: The best deals on TVs, headphones, kitchenware, and more
-

 Technologies5 лет ago
Technologies5 лет agoGoogle to require vaccinations as Silicon Valley rethinks return-to-office policies
-

 Technologies5 лет ago
Technologies5 лет agoVerum, Wickr and Threema: next generation secured messengers
-

 Technologies4 года ago
Technologies4 года agoOlivia Harlan Dekker for Verum Messenger
-

 Technologies4 года ago
Technologies4 года agoiPhone 13 event: How to watch Apple’s big announcement tomorrow
