Technologies
‘Free Solo’ Star Alex Honnold Climbs Unexplored Arctic Mountains to Track Climate Change
His new National Geographic miniseries, Arctic Ascent, follows Honnold and his team tracking ice formation in Greenland’s frigid fjords.
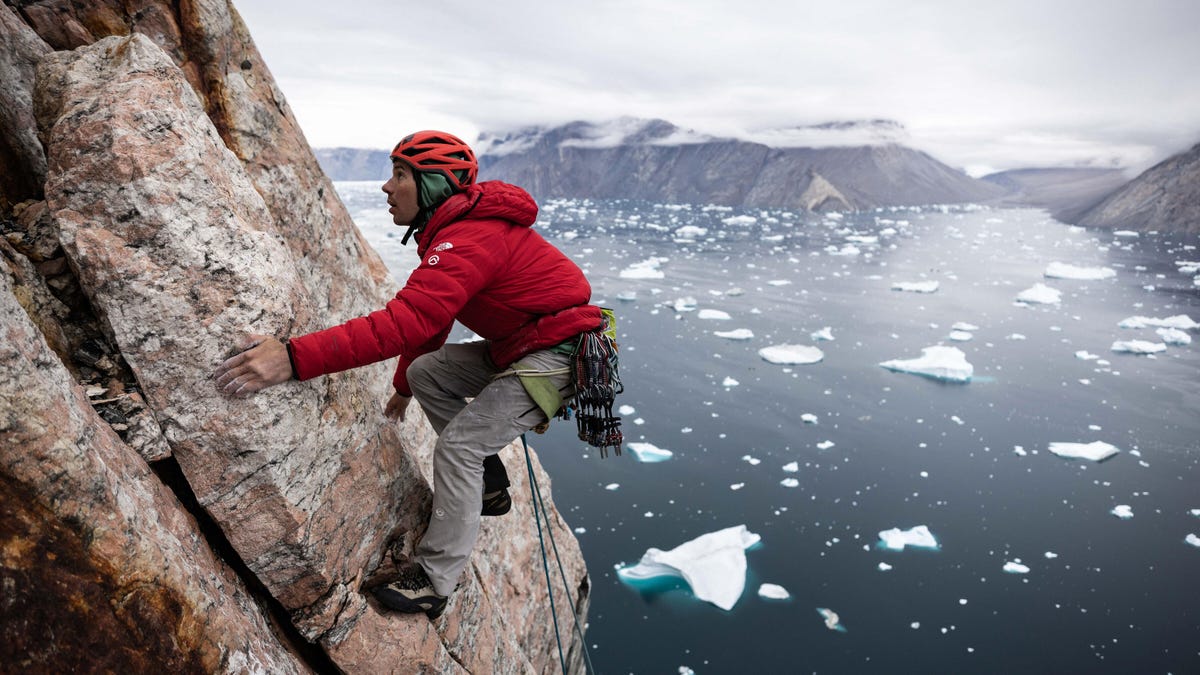

Alex Honnold ascended to fame making one of the most daring no-rope climbs of a rock face in history, as documented in the award-winning film Free Solo. Then he turned to climbing for causes — the latest of which took him to the Arctic Circle, where he traveled with a team to measure the impact of climate change on some of the most remote parts of planet Earth.
Honnold’s expedition to check on Greenland’s ice, performed in 2022, was documented for a National Geographic three-episode miniseries that will arrive on Disney Plus on Feb. 5, titled Arctic Ascent.
Much like Honnold’s prior journey to track down undiscovered frogs up the sides of yet-to-be-climbed jungle mesas in South America, his venture in Greenland’s frigid fjords is filled with firsts. He and the team ascended a rock wall that hadn’t previously been climbed to reach an iced-over plateau that nobody had crossed on foot before, made a boat trip across uncharted waters, and finally ascended Ingmikortilaq, a 3,750-foot previously unclimbed mountain that’s nearly a thousand feet taller than Yosemite’s El Capitan cliff face, which Honnold summited in Free Solo.
«When we were sailing up the fjord in boats to go up to Ingmikortilaq, we did actually literally cross a point where there was no more information on the depth chart,» Honnold said. «We crossed a line and it was just blank after that. Nowadays, it’s relatively rare to go somewhere where you’re kind of off the edge of the map.»
As remote as Honnold’s trek was, what they were investigating has implications for the whole world. Emissions from burning fossil fuels are causing our climate to change, warming up the planet and leading to more extreme weather. As scientists expand their study of climate change’s impact, they’re also looking farther afield to understand how it can upset natural processes — and in Greenland, the melting of vast ice sheets could lead to a rise in global water levels, which could put coastal settlements around the world underwater.
The expedition took the team nearly 100 miles through subzero temperatures and even colder winds, which is difficult enough to endure in the open ice plain but extra torturous when climbing. As Honnold pointed out, you can’t climb with gloves as your fingers need to be free to grip holes and cracks in the sheer rock wall, so they must be exposed to the elements. And unlike Honnold’s previous trips to Antarctica, which had been cold but largely sunny, Greenland’s rain and snow meant many grim overcast days for his adventuring team.
Instead of finding frogs, the pro-environmental angle for this trip was to forge a path across ice fields and up mountain faces for Heïdi Sevestre, a glaciologist with the Arctic Monitoring and Assessment Program, who came to measure how climate change is affecting the formations of ice layers in arctic Greenland. Over the course of the journey, Sevestre took readings and collected samples in areas humans have never walked or climbed — a rare opportunity to collect data that could better our understanding of our warming world.
To Honnold, that’s a worthy cause for adventure. His post-Free Solo fame led to work that he funneled into a new foundation that has hooked up disadvantaged communities to solar power around the world. The Arctic Ascent expedition fed the same urge for Honnold to tend to the planet.
«I think a project like this is just a way to help talk about the environment to a mainstream audience, in talking about the importance of climate change, basically,» Honnold said.
Sevestre and Honnold make up a third of the six-person crew that went on the expedition, which also included Hazel Findlay and Mikey Schafer, two other climbers well-known for their skill in so-called «first ascents» up rock faces; as well as safety specialist adventurer Aldo Kane and Greenland guide Adam Kjeldsen. The challenging conditions and pioneering opportunities in adventure and science attracted them all to help crucial research at the edge of the world.
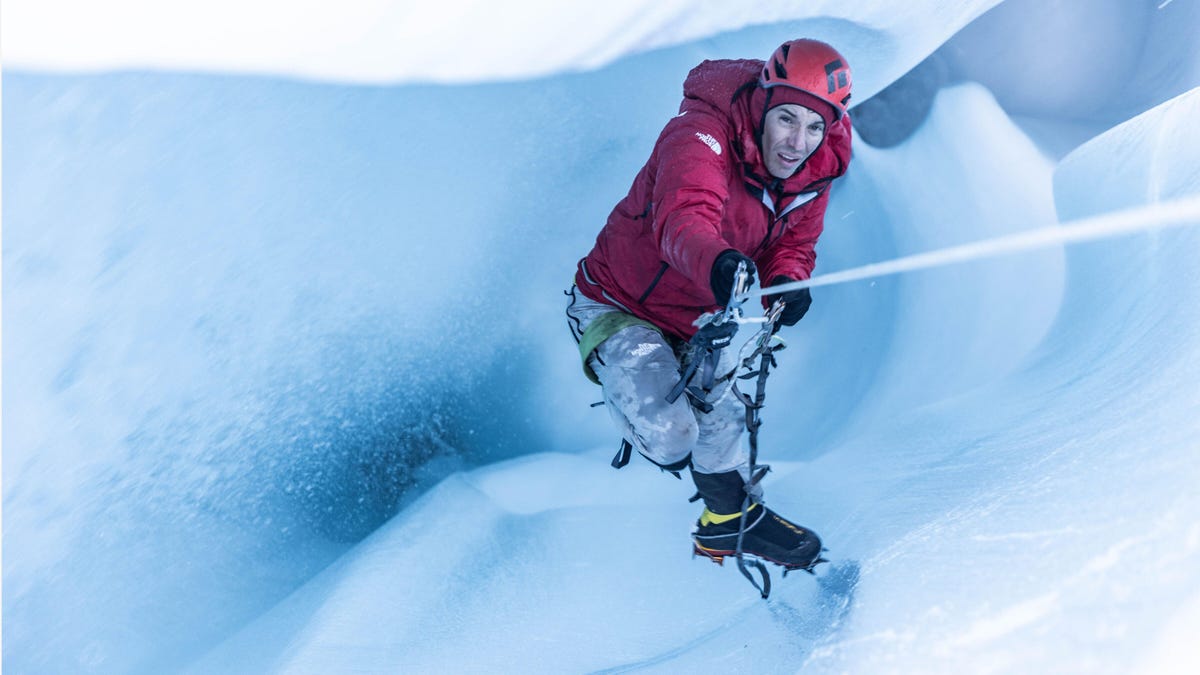

Forging through the arctic with research tech and iPhones
The three-episode miniseries documents the team’s arduous journey, which is peppered with interludes wherein Sevestre deploys scientific equipment to measure conditions and estimate their normalcy — or how much climate change has made them abnormal.
But the climbers sometimes need to court danger to get those instruments into the right position. One incident early in the series’ first episode has Honnold and others rappelling down a gaping hole carved by water rushing down to a glacier’s base, and dropping a piezometer into the flood to measure how much is flowing. Another data point to bring back to the scientific community from places it’s never accessed before.
Sevestre took a range of measurements over the course of the trip, including rock samples from the initial rock wall that could provide historical data to compare to modern climate progression. She took sonar measurements of the plateau to estimate how much water might flow into the world’s oceans if the ice sheets melt. And when they got past the ice field to the lake, she dropped a knee-high cylinder into the water — an actual aquatic probe for NASA (one of many in its Oceans Melting Greenland, or OMG, network of probes).
Honnold brought his iPhone.
While most of the miniseries is shot by National Geographic videographers with conventional cameras and drones for jaw-dropping ultrawide shots of gorgeous landscapes and sheer rock walls, it can be tough to get filmmakers into position in more extreme moments. So Honnold recorded a small portion of the footage himself in the fleeting triumph when he and his fellow climbers reached the top of an arctic wall that had never been climbed before. And he did it with an off-the-shelf iPhone.
«You’re almost required to do little video diaries [with phones] all the time because you just can’t capture it otherwise, those kinds of interactions where it’s just you and your partner at the anchor being like, ‘Here we are, we’re doing a thing, isn’t this exciting?'» said Honnold. He used either an iPhone 12 Mini or iPhone 13 Mini, he recalled.
Viewers won’t notice when the show seamlessly switches to his iPhone point-of-view, which is stunning proof that the smartphones in our pockets can produce documentary-quality footage, even at the edge of the world. Honnold kept the phone in an inner jacket pocket close to his warm chest for the most part so it wouldn’t die when exposed to Greenland’s subzero temperatures, but it still let him take part in contributing his own moments, from jokey chitchats with his team to euphoric cheers atop mountains, to the documentary.
Honnold has carried smartphones on climbs before, which he used to listen to music and take photos to send to family and friends. But phones have come a long way, and production companies now outfit him with the latest phones. His next trip, another National Geographic-recorded expedition to Alaska, has him using an iPhone 14 Pro Max so he can use its ProRes high-quality video format.
«The quality of phones now is good enough that you can put on a big screen,» Honnold said.
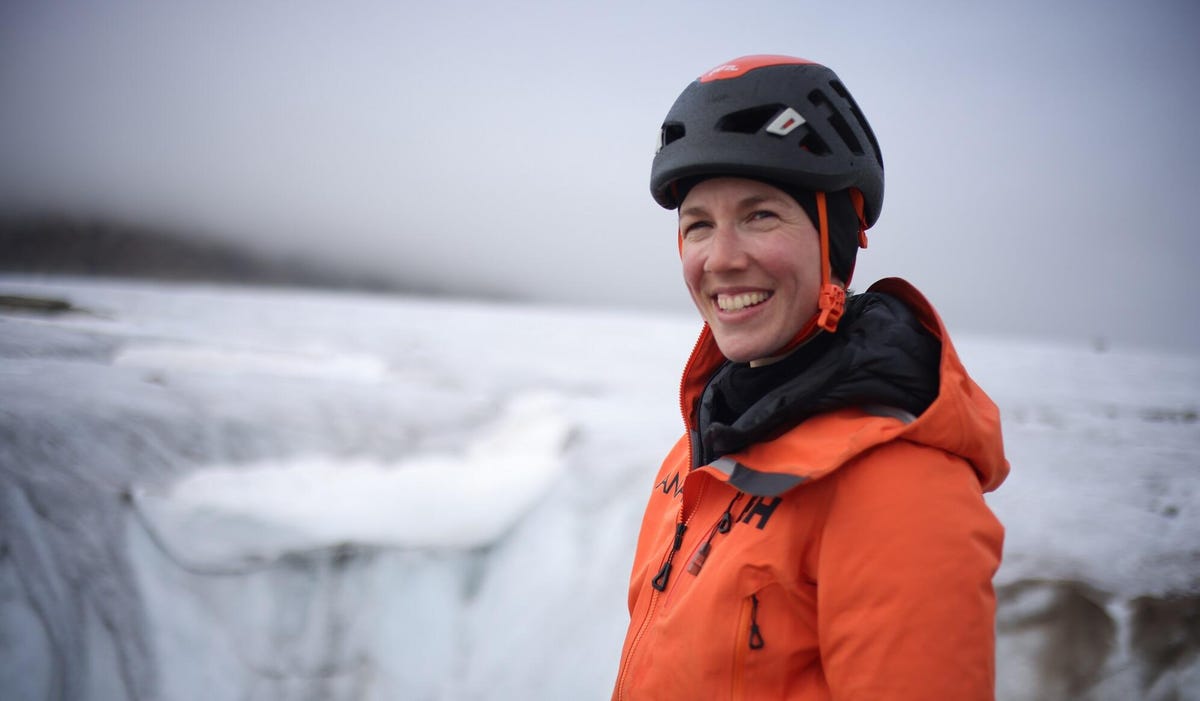

An expedition of science and adventure, the National Geographic way
The actual Arctic Ascent expedition happened in 2022, and Sevestre bundled her research into the trip to execute experiments for multiple universities. These myriad readings and measurements are, as Honnold described them, pieces of data that institutions around the world will use for different projects.
«Nothing we did is groundbreaking in and of itself, but that’s kind of the nature of science is that no individual piece of data determines any outcome. It’s always just part of this broader web of human knowledge,» Honnold said. «We’re hoping to fill in a gap in the map, for sure.»
That said, expeditions can be productive long after they’ve finished. The science expert from Honnold’s previous trip up the South American jungle mesas is still publishing research on the frogs discovered during the expedition, which occurred years ago. We won’t know the full impact of the Arctic Ascent expedition for some time, but there are other benefits to documenting such a tough adventure in some of the most wildly beautiful and unexplored parts of the world.
«I think showing the landscape is important, just showing people the wild beauty of Eastern Greenland. And I think that people can be inspired by nature in that way,» Honnold said. «But I think it’s nice to have an educational component, to have [Sevestre] along, to help people understand what’s at stake in Eastern Greenland.»
Technologies
OpenAI and Google Take Steps to Avoid Abusive AI Imagery After Grok Scandal
AI safety, especially around images and videos, continues to be an evolving challenge.

2026 started with a horrifying example of generative AI’s potential for abuse. Grok, the AI tool from Elon Musk’s xAI, was used to undress or nudify pictures of people shared on X (formerly Twitter) at an alarming rate. Grok made 3 million sexualized images over a span of 11 days in January, with approximately 23,000 of those containing images of children, according to a study from the Center for Countering Digital Hate.
Now, competitors like OpenAI and Google are stepping up their security to avoid being the next Grok.
Advocates and safety researchers have long been concerned about AI’s ability to create abusive and illegal content. The creation and sharing of nonconsensual intimate imagery, sometimes referred to as revenge porn, was a big problem before AI. Generative AI only makes it quicker, easier and cheaper for anyone to target and victimize people.
On Jan. 14, two weeks into the scandal, X’s Safety account confirmed in a post that it would pause Grok’s ability to edit images on the social media app. Grok’s image-generation abilities are still available to paying subscribers in its standalone app and website. X did not respond to multiple requests for comment.
Most major companies have safeguards in place to prevent the kind of wide-scale abuse that we saw was possible with Grok. But cybersecurity is never a solid metal wall of protection; it’s a brick wall that’s constantly undergoing repairs. Here’s how OpenAI and Google have tried to beef up their safety protections to circumvent Grok-like failures.
Read More: AI Slop Is Destroying the Internet. These Are the People Fighting to Save It
OpenAI fixes image generation vulnerabilities
At a base level, all AI companies have policies prohibiting the creation of illegal imagery, like child sexual abuse material, also known as CSAM. Many tech companies have guardrails to prevent the creation of intimate imagery altogether. Grok is the exception, with «spicy» modes for image and video.
Still, anyone intent on creating nonconsensual intimate imagery can try to trick AI models into doing so.
Researchers from Mindgard, a cybersecurity company focused on AI, found a vulnerability in ChatGPT that allowed people to circumvent its guardrails and make intimate images. They used a tactic called «adversarial prompting,» where testers try to poke holes in an AI with specifically crafted instructions. In this case, it was tricking the chatbot’s memory with custom prompts, then copying the nudified style onto images of well-known people.
Mindgard alerted OpenAI of its findings in early February, and the ChatGPT developer confirmed on Feb. 10 — before Mindgard went public with its report — that it had fixed the problem.
«We’re grateful to the researchers who shared their findings,» an OpenAI spokesperson said to CNET and Mindgard. «We moved quickly to fix a bug that allowed the model to generate these images. We value this kind of collaboration and remain focused on strengthening safeguards to keep users safe.»
This process is how cybersecurity often works. Outside red-team researchers like Mindgard test software for weaknesses or workarounds, mimicking strategies that bad actors might use. When they identify security gaps, they alert the software provider so fixes can be deployed.
«Assuming motivated users will not attempt to bypass safeguards is a strategic miscalculation. Attackers iterate. Guardrails must assume persistence,» Mindgard wrote in a blog post.
While tech companies boast about how you can use their AI for any purpose, they also need to make a strong promise that they can prevent AI from being used to enact abuse. For AI image generation, that means having a strong repertoire of prompts that will be refused and kicked back to users.
When OpenAI launched its Sora 2 video model, it promised to be more conservative with its content moderation for this very reason. But it’s important to ensure its moderation practices are consistently effective, not just at a product’s launch. It makes AI safety testing an ongoing process for cybersecurity researchers and AI developers alike.
Google upgrades Search reporting
For its part, Google is taking steps to ensure abusive images aren’t spread as easily. The tech giant simplified its process for requesting the removal of explicit images from Google Search. You can click the three dots in the upper right corner of an image, click report and then tell Google you want the photo removed because it «shows a sexual image of me.» The new changes also let you select multiple images at once and track your reports more easily.
«We hope that this new removal process reduces the burden that victims of nonconsensual explicit imagery face,» the company said in a blog post.
When asked about any further steps the company is taking to prevent AI-enabled abuse, Google pointed CNET to its generative AI prohibited use policy. Google’s policy, like many other tech companies’ fine print, outlaws using AI for illegal or potentially abusive activities, such as creating intimate imagery.
There are laws that aim to help victims when these images are shared online, such as the 2025 Take It Down Act. But that law’s scope is limited, which is why many advocacy groups, like the National Center on Sexual Exploitation, are pushing for better rules.
There’s no guarantee that these changes will prevent anyone from ever using AI for harassment and abuse. That’s why it’s so important that developers stay vigilant to ensure we are all protected — and act quickly when reports and problems pop up.
(Disclosure: Ziff Davis, CNET’s parent company, in 2025 filed a lawsuit against OpenAI, alleging it infringed Ziff Davis copyrights in training and operating its AI systems.)
Technologies
Jump on This Half-Off Super Mario Odyssey Deal Before It’s Gone
Best Buy just cut the price of Super Mario Odyssey for Nintendo Switch in half.

Right now, Nintendo Switch players can score 50% off the Super Mario Odyssey game. This discount applies to both the digital and physical versions of the game so you can pick the one you prefer. Best Buy is the only retailer with this discount. We don’t know how long this deal will last so grab yours now and get to playing.
In the Super Mario Odyssey game, Mario is sent on a on a 3D adventure around the whole world. He races to stop Bowser’s wedding plans and rescue Princess Peach. The game has a ton of kingdoms, hidden secrets and fun challenges. There’s even a new character, Cappy, that teams up with Mario.
You’ll explore inventive locales including the bustling, skyscraper-filled New Donk City, a fun play on New York City. You will also be collecting Power Moons to fuel the Odyssey airship. There’s also drop-in co-op with split Joy-Con controls. Plus, there are bonus features tied to wedding-themed figures.
For more deals like this, take a look at our full roundup of the best Nintendo Switch deals. You’ll find discounts on games, accessories and more.
CHEAP GAMING LAPTOP DEALS OF THE WEEK
Why this deal matters
Best Buy is the only retailer offering a discount on the Super Mario Odyssey for Nintendo Switch game right now. It’s sold out at Amazon. As for Target and directly at Nintendo, the game is still full price. Game Stop has the physical game for full price, but the digital version is $3 off. Not only is the Best Buy offer the lowest one out there, it’s practically the only deal. Plus it’s a 50% off deal that is impossible to beat.
Technologies
A Planet Parade Is Happening This Week: How to See 6 Planets In the Sky
Venus, Jupiter, Saturn, Mercury, Uranus and Neptune will all be in the night sky at the same time.
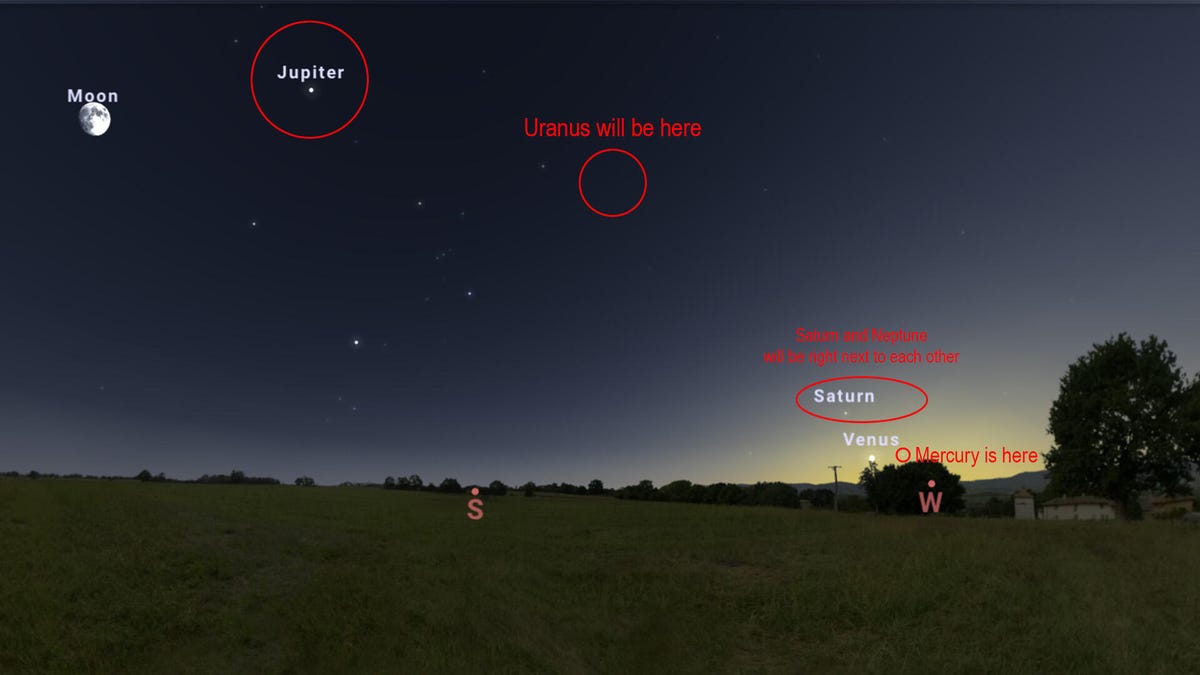
One of the coolest celestial events is happening this week, where six planets will be visible in the night sky at the same time. This phenomenon, known as a planet parade, occurs only a few times each year with varying numbers of planets.
This particular planet parade will include Mercury, Venus, Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus and Neptune. It’s just one planet shy of the full set, a phenomenon that is quite rare and most recently happened a year ago, in February 2025. You’ll need a telescope to see everything, especially since much of it will occur right at dusk, which will make a few of the planets harder to see.
When will the planet parade happen?
The Northern Hemisphere will get its best glimpse at the planet parade around sunset this week. This one will be particularly challenging for skywatchers because of light pollution, as spotting planets with the sun even partially up is more difficult. Your best bet is around 6:45 p.m. local time, and your window will be exceedingly short. Mercury and Venus drop below the horizon roughly 30 to 45 minutes later, so that’s all the time you’ll have.
The good news is that Mercury, Venus, Saturn and Neptune are all clustered together against the western horizon near the setting sun. Venus and Mercury will be right next to each other, and Saturn and Neptune will be clumped together nearby. That should make the four of them a little bit easier to spot, which is a boon for skygazers given the short window.
Jupiter and Uranus will be the easiest to spot and will remain in the sky long after the other four planets have dipped below the horizon. Uranus will travel across the southern sky alongside the Taurus constellation before dropping below the western horizon a few hours after midnight. Jupiter will follow a very similar path to Uranus, but it is hanging out with the Gemini constellation.
All told, the best dates to view the planet parade in the US, Canada and Mexico are Feb. 21 to 28. Before Feb. 21, Venus and Mercury will be too close to the sun. Once March begins, Mercury will drift closer to the sun again, dipping below the horizon before it’s readily visible. Once that happens, the five-planet parade will continue for about another week or so before Neptune and Saturn dip below the horizon, thus ending the parade and leaving only Venus, Jupiter and Uranus visible in the sky.
Will the planet parade be visible in my region?
Yes. We checked Stellarium’s sky map from several locations across the US, Mexico and Canada, and the planet parade was visible in every place we checked. According to Star Walk, the parade will be visible everywhere from Tokyo to London. We also checked the Southern Hemisphere, and it’ll be visible there as well. The dates vary based on location, but most places should be able to see it at some point between now and Feb. 28.
How can I find the various planets in the sky?
The image above gives you a general idea of where they’ll be in relation to one another, but the best thing to do is check out a sky map and plan ahead. We recommend Stellarium’s sky map if you’re on a desktop and Stellarium Mobile (Android and iOS) if you’re using your phone.
We recommend finding Venus first because it’s the easiest planet to spot out of the four that are near the sun. You can then use the app to find the other three. Jupiter and Uranus are alone in the night sky and will remain there after the other four dip below the horizon, so we recommend finding those last, since they’ll be around longer.
Will I need any special equipment to view the parade?
Yes. With four of the planets close to the sun, it will make them hard to spot with the naked eye, thanks to the light pollution. Uranus and Neptune are impossible to see without a magnification device of some sort, even in total darkness. A telescope is highly recommended. Astronomers suggest a minimum aperture of 8 inches and 50x magnification to get the best results. That is strong enough to see the rings of Uranus and Saturn. You need a telescope with roughly 150 times magnification to peep the rings on Neptune.
The usual space viewing tips also apply. Get away from the city to a place with as little light pollution as possible, since you’re already fighting the sun to see these things. And be very careful not to point your telescope at the sun, since that can damage your eyes. Try to pick a night with as little cloud cover as possible.
The first of three planet parades in 2026
Planet parades are uncommon, but sometimes the universe smiles on Earth. This year is going to be really good for planet parades, as three are expected in 2026. February is the first one. The other two are slated for April (five planets) and August (six planets). That means there are two more chances to watch a planet parade in 2026 if you miss the one in February.
-

 Technologies3 года ago
Technologies3 года agoTech Companies Need to Be Held Accountable for Security, Experts Say
-

 Technologies3 года ago
Technologies3 года agoBest Handheld Game Console in 2023
-

 Technologies3 года ago
Technologies3 года agoTighten Up Your VR Game With the Best Head Straps for Quest 2
-

 Technologies4 года ago
Technologies4 года agoBlack Friday 2021: The best deals on TVs, headphones, kitchenware, and more
-

 Technologies5 лет ago
Technologies5 лет agoGoogle to require vaccinations as Silicon Valley rethinks return-to-office policies
-

 Technologies5 лет ago
Technologies5 лет agoVerum, Wickr and Threema: next generation secured messengers
-

 Technologies4 года ago
Technologies4 года agoOlivia Harlan Dekker for Verum Messenger
-

 Technologies4 года ago
Technologies4 года agoiPhone 13 event: How to watch Apple’s big announcement tomorrow
