Technologies
Apple Watch Series 8 vs. SE: Which One Is Right for You?
The Series 8’s extra health-tracking features, faster charging and always-on display separate it from the SE.
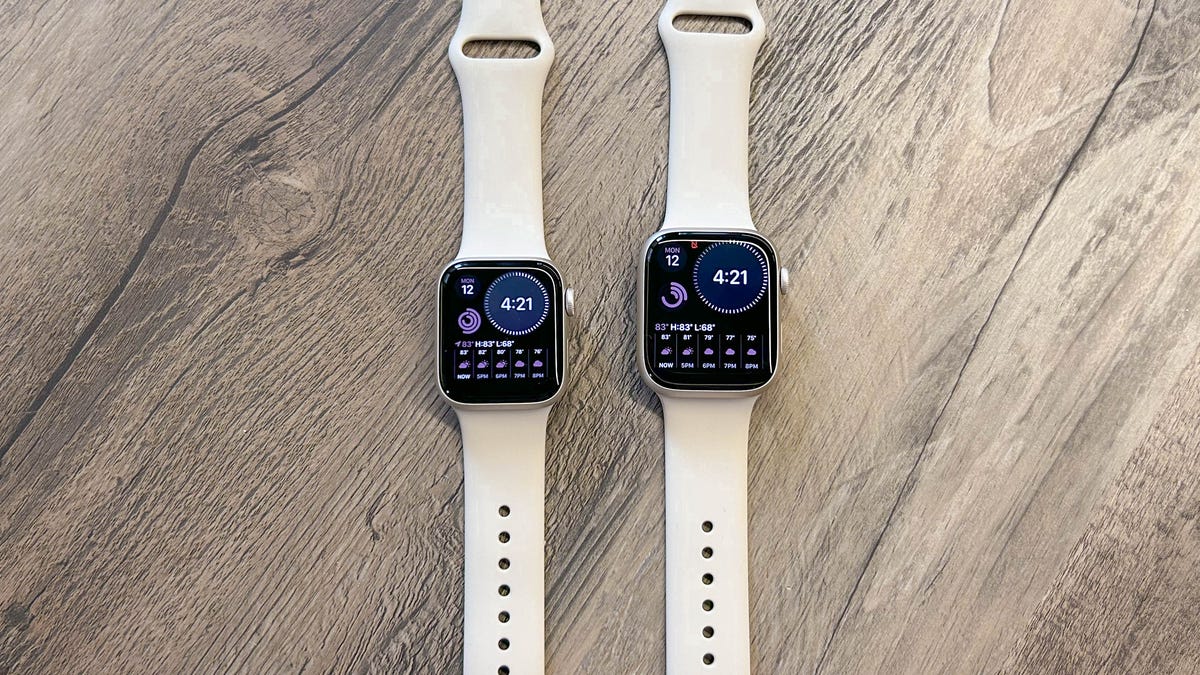

Deciding on a new Apple Watch can be challenging, especially if you’re choosing between the $399 Apple Watch Series 8 and the $249 Apple Watch SE.
Unless you’re an avid scuba diver or rock climber — or want to look like one — you’re probably not considering the $799 Apple Watch Ultra. The Series 8 and SE are both intended for everyday wearers that want to keep an eye on their health and fitness levels, but don’t need the Ultra’s larger screen, longer battery life and extra features tailored for the outdoors.
Both the Series 8 and SE run on Apple’s WatchOS 9 software, have the company’s newest chip and are among the first to detect car crashes. That’s in addition to the functionality Apple’s watches have offered for years, like the ability to track workouts, detect hard falls and mirror iPhone alerts.
Which one is right for you depends on what you want in a smartwatch. As someone who primarily uses my Apple Watch for logging exercise, viewing notifications and checking the time, there’s little that I missed when switching from the Series 8 to the SE after testing both.
The biggest reason to choose the Series 8 over the SE right now is its extra health-tracking smarts, such as its new wrist temperature measurements, blood oxygen saturation readings and the ability to take an electrocardiogram. The Apple Watch isn’t a medical device and shouldn’t be treated as such. But those who want more data on their cardiac and respiratory health to share with their doctors might find the Series 8 to be the better choice.
I think the Series 8’s main benefits will become more clear over the long term. Temperature sensing is still new, but I like the idea of being able to see how changes in my baseline temperature may correlate with how I’m feeling that day. The Series 8’s ultrawideband chip, which isn’t present in the SE, may also feel more valuable in a future where unlocking your car with your phone or watch is just as common as using Apple Pay at the checkout counter.
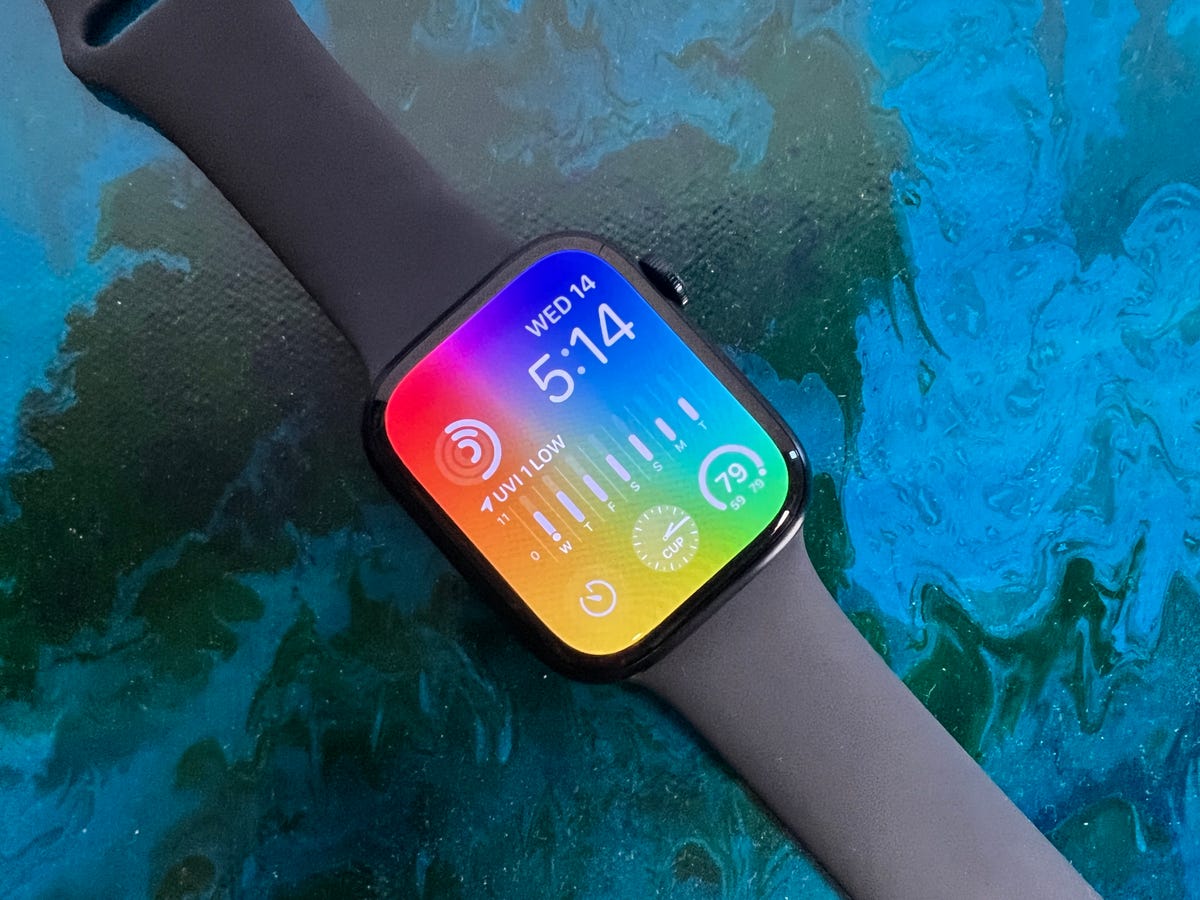

A larger screen with an always-on display
If you were to ask me what I’ve missed most about using the Apple Watch SE, it’s the always-on display found on the Series 8 and other flagship Apple Watches since 2019. Without an always-on display, the Apple Watch SE’s screen just turns into a black box on my wrist, which isn’t exactly the most attractive look.
When wearing the Series 8 (or the Series 5, 6 or 7), I can view my watch face anytime without having to raise my wrist or touch the watch. I don’t think the always-on display alone is worth paying an extra $150 if you don’t care about the other health extras that come with the Series 8. But I do wish the always-on display was standard across all Apple Watches at this point.
The Apple Watch Series 8 also has a larger display and comes in 41- and 45-millimeter case sizes, compared to the 40 or 44mm SE. Having a bigger display is nice, but the only thing I missed is the Series 8’s QWERTY keyboard for typing responses to text messages (the Series 7 has this too). On the SE, you can still scribble letters, dictate words or send canned responses, but I like the flexibility of being able to quickly type a couple of words. Those who prefer larger text sizes may also want to choose the Series 8 over the SE.
The Series 8 is also available in a pricier stainless steel finish, and the aluminum version comes in an additional Product Red color option not available on the SE.
More health tracking
Apple’s flagship watches like the Series 8 have evolved into comprehensive health-tracking devices, with the ability to take an ECG from your wrist and monitor blood oxygen levels. The Series 8 and Ultra are the first to get temperature sensors, enabling them to check your wrist temperature overnight and show whether you’ve deviated from your baseline. It takes five nights to set up temperature sensing, since the watch needs enough time to establish your baseline wrist temperature.
Apple says nighttime wrist temperature can be an indicator of overall body temperature, and changes could possibly be caused by illness, jet lag or exercise. Since the Apple Watch doesn’t have a readiness score like Oura or Fitbit, I could see this information being useful for helping me decide whether my body needs extra rest.
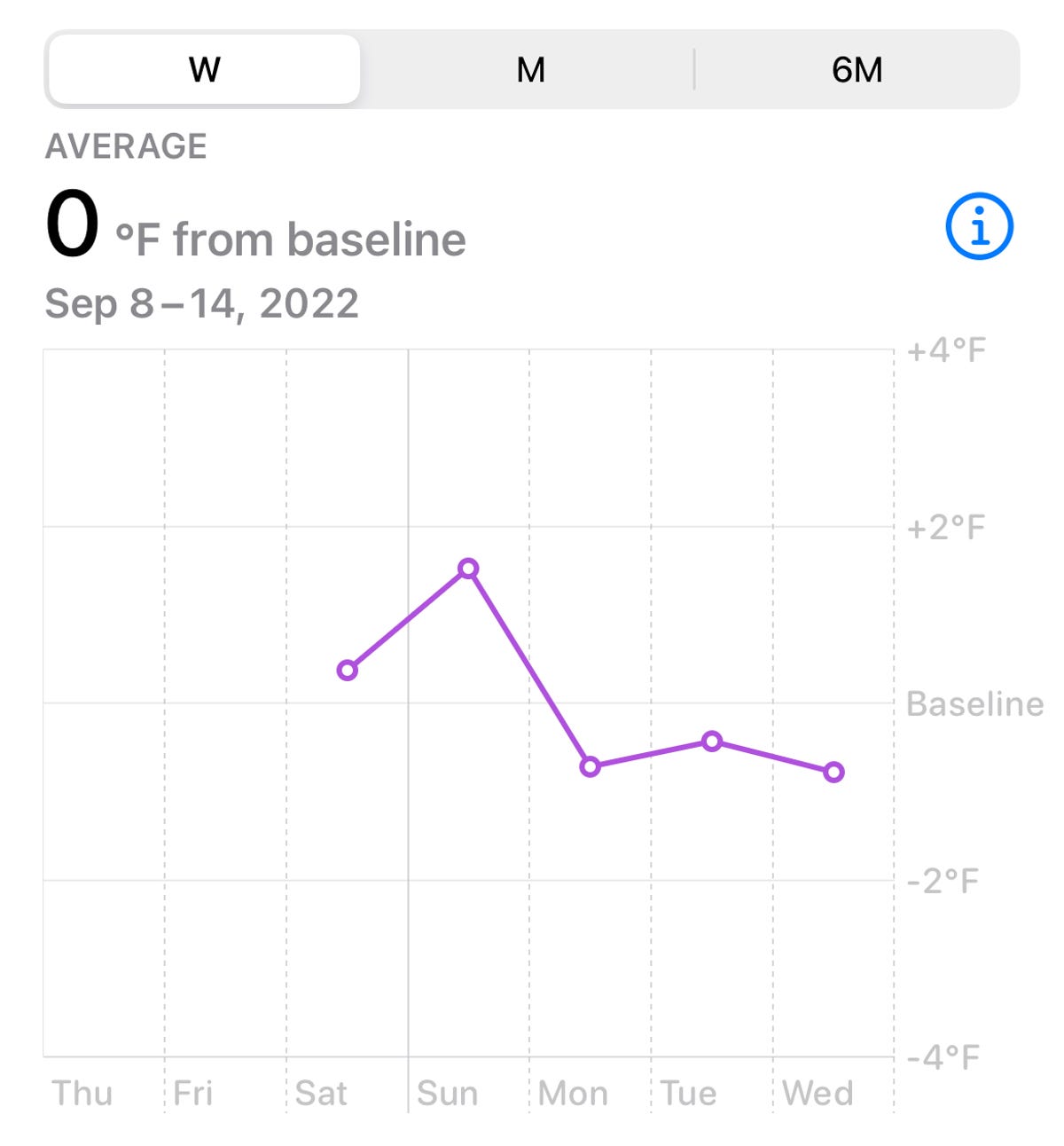
I’m hoping Apple weaves wrist temperature readings into new features and insights in the future. Right now, you can see a chart showing how your nighttime temperature readings deviate from your baseline. But it generally seems like it’s up to you to interpret these readings.
The Apple Watch isn’t a medical device and can’t alert you when you’re sick, so it can be hard to know how to use this data. That’s part of the reason why I never check my blood oxygen levels; it’s just another statistic that I’m not sure what to make of. I’ve been wearing the Apple Watch Series 8 consistently for a couple of weeks, but I’m still not sure what to do with this temperature data.
My nighttime wrist temperature is pretty close to my baseline most of the time, but it’s usually a fraction of a degree higher or lower. Sometimes my deviations are as high as 0.37 degrees Fahrenheit above my baseline or 0.55 degrees below the norm. I can’t connect the dots between those deviations and what may have happened to cause them. It’s also difficult to wear the Apple Watch Series 8 consistently overnight since I have to charge it during some evenings.
Still, having another data point like wrist temperature opens up some interesting opportunities for the future. I’m hoping Apple finds new ways to crunch all of these statistics together to enable new insights and actionable advice. Until then, nighttime wrist temperature is yet another metric you can potentially share with your doctor if you’re not feeling well, but it’s difficult to tell how useful it actually is.
For now, the biggest application for the Series 8’s temperature sensing will likely be fertility tracking. Apple says the Series 8 and Ultra can provide retrospective ovulation estimates and improved period tracking, potentially making the Series 8 a better choice for those who are interested in using it for family planning purposes. That information can be helpful because it provides users with data from their own bodies, rather than just making estimates based on the length of their cycle.
«But this actually gives you real life data because the time of ovulation can vary from person to person from month to month,» said Dr. Angela Bianco, MD, director of maternal fetal medicine at the Mount Sinai Health System. «Some people ovulate earlier in their cycles, others ovulate later in their cycles.»
Again, the Apple Watch isn’t a medical device and shouldn’t be treated as such. It also shouldn’t be used for contraception.
«I stress that women who are trying not to get pregnant should not use this because there can be errors in the data,» said Dr. Alexis Melnick, an OBGYN at NewYork-Presbyterian and assistant professor at Weill Cornell Medicine. «And you can have a cycle that is variable that may not follow the regular pattern.»
Apple says data stored in the health app — including female health statistics like ovulation estimates — is encrypted when your iPhone is locked with a passcode, Face ID or Touch ID. The same goes for data backed up to iCloud.
You’ll also want to make sure two-factor authentication is enabled for your iCloud account, which should be turned on by default. This ensures that health data is end-to-end encrypted, meaning Apple cannot read or access your data. To make sure two-factor authentication is on, open the Settings menu on your iPhone, tap your name and choose the Password & Security option.

Other extras, like faster charging and ultrawideband
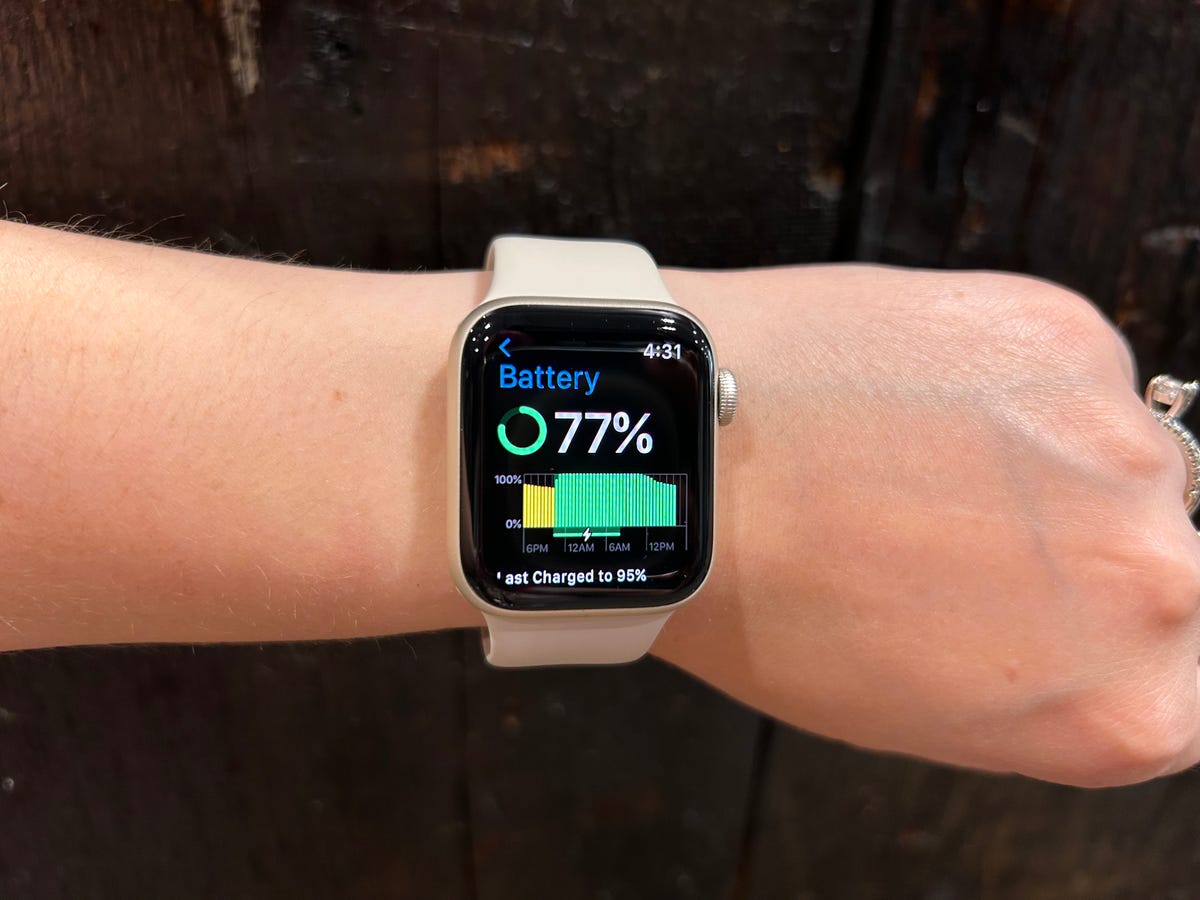
While the Series 8’s extra health sensors are the biggest reason to potentially choose it over the SE, there are a few other extras to consider. The Series 8 can charge more quickly than the SE, as it inherits the fast-charging capabilities of the Series 6 and 7. The Apple Watch Series 8 charged from 70% to 80% in 10 minutes, while the SE charged from 70% to 77% over the same time period. For each watch, I used the included charging cable and the same power adapter plugged into the same outlet. Both watches have Apple’s new low power mode, which dials back certain features like automatic workout detection to extend battery life.
The Series 8, like the Series 6 and 7, also have Apple’s U1 ultrawideband chip. Ultrawideband is a wireless protocol for proximity sensing that’s become common in new flagship phones and smartwatches. Ultrawideband is primarily used for finding misplaced items and gadgets using Apple’s Find My service, or for unlocking your car with more precision than Bluetooth.
If you have a car that’s compatible with ultrawideband, for example, you can unlock your vehicle automatically as you approach it with your Apple Watch. Ultrawideband is said to be more secure and precise than Bluetooth when functioning as a key, which you can read more about here. It’s a nice perk, but it’s likely not a necessity for everyone. At least not yet.
The bottom line
The Apple Watch Series 8 and SE have a lot in common when it comes to core features and functionality. They can both track workouts, show iPhone notifications, provide high and low heart rate notifications and detect irregular heart rhythms. They also both come with safety features like emergency SOS, fall detection and car crash detection, the latter of which is exclusive to Apple’s 2022 smartwatches. The new Compass app, which includes a new feature to help you retrace your steps, is also coming to both watches as well as the Series 7, Series 6 and first-generation SE.
If you like using Apple Pay or syncing your Apple Watch to the treadmill at your local gym through GymKit, you’ll do just fine with either the new SE or the Series 8. They both have the same processor, support low power mode and run on Apple’s new WatchOS 9 update.
The difference really comes down to health tracking. By choosing the SE, you’ll miss out on the Apple Watch’s ECG app, blood oxygen sensor and new temperature sensor. Whether those features are necessary depends on what you hope to get out of your smartwatch. Do you primarily want to track workouts, or are you looking for deeper health metrics to share with your doctor?
You’ll also get a few perks that make the Series 8 a better iPhone companion, such as a larger always-on display, faster charging and ultrawideband support. Of those features, I personally find the always-on display to be most useful.
Overall, the Series 8 seems poised to become more useful over time, especially after I’ve had more time to test the temperature sensor. Ultrawideband is another feature I’m expecting to become more useful in the long term as using mobile devices as digital keys starts to become more common. But for now, ultrawideband alone shouldn’t be a deciding factor; it’s more about the sum of how all of these parts come together.
The Series 8 is the right option for those who want more health-tracking features and are willing to pay a premium for it. The Apple Watch SE is the best choice for those who are upgrading from an older watch or are buying an Apple Watch for the first time and just want an Apple Watch that feels new and has all of the core features. But if you have a recent Apple Watch like the Series 5, you can probably hold off on upgrading entirely unless you really want Apple’s new health upgrades.
Apple Watch Series 8 vs. SE
| Apple Watch Series 8 | Apple Watch SE | |
|---|---|---|
| Starting price | $399 | $249 |
| Size | 41mm or 45mm | 40mm or 44mm |
| Finishes | Aluminum or stainless steel | Aluminum |
| Colors | Aluminum: Midnight, starlight, silver, Product Red; Stainless steel: Graphite, silver, gold | Midnight,starlight, silver |
| Software | WatchOS 9 | WatchOS 9 |
| Screen | 904 sq mm display area (41mm); 1,143 sq mm display area (45mm) | 759 sq mm display area (40mm); 977 sq mm display area (44mm) |
| Health sensors | Blood oxygen, electrical heart (ECG),third-gen optical heart, temperature | Second-gen optical heart |
| Health features | High and low heart rate notifications, irregular heart rate notifications, blood oxygen, nighttime wrist temperature deviations, cardio fitness level, cycle tracking, retrospective ovulation estimates, sleep tracking | High and low heart rate notifications, irregular heart rate notifications, cardio fitness level, cycle tracking, sleep tracking |
| Chip | Apple S8 SiP | Apple S8 SiP |
| Durability | IP6X dust resistant;water resistant up to 50m | Water resistant up to 50m |
| Safety | Emergency SOS, international emergency calling, crash detection, fall detection | Emergency SOS, international emergency calling, crash detection, fall detection |
| Battery | Up to 18 hours with fast charging, support for low power mode | Up to 18 hours, support for low power mode |
| Storage | 32GB | 32GB |
| Other features | GPS, optional cellular, Compass Backtrack, always on altimeter, Family Setup, speaker, microphone, activity and exercise tracking, Apple Pay, GymKit, ultrawideband support | GPS, optional cellular, Compass Backtrack, always on altimeter, Family Setup, speaker, microphone, activity and exercise tracking, Apple Pay, GymKit |
Technologies
A New Mini Game Boy Collectible That Just Plays Pokemon Music? What a Tease
A surprise collectible on Pokemon Day looks just like a tiny Game Boy and plays music on swappable cartridges. Give us the real Game Boy again, come on.

Nintendo sure does love teasing us with Game Boy things. First, a collectible Lego Game Boy model last year that almost looked like a real Game Boy (but wasn’t). Now, for the 30th anniversary of Pokemon, Nintendo and the Pokemon Group are selling a collectible music player that looks like a tiny Game Boy and plays authentic original Pokemon Red/Blue songs on swappable cartridges, one per song. The Game Boy Jukebox is being sold on the Pokemon Center site later today, for a price that hasn’t yet been listed.
This level of absurdity is standard issue for Nintendo: Just in the last 18 months we’ve had Alarmo, a talking Super Mario flower and a Virtual Boy recreation. This new collectible is so tempting precisely because it looks like a little, even more pocketable Game Boy. Except it isn’t a Game Boy at all. It’s just a music player. Even the dot-matrix «screen» is fake — it’s just an overlay that the cartridges display when they’re slotted in.
The music this thing plays is Game Boy-accurate, down to the little boot-up ping. It just makes my skin itch for a new Game Boy (that isn’t one already made by several other companies).
But come on. Make a real Game Boy collectible, with actual preloaded games on it. You know you want to, Nintendo. It’s only a matter of time.
In the meantime, if you’re desperate for all 45 Pokemon Red and Blue songs on a little Game Boy music player, now’s your chance.
Technologies
Pokemon Winds and Waves: First Mainline Games for the Switch 2 Are Coming in 2027
Following the recent release of Pokemon Legends: Z-A, The Pokemon Company announced its first mainline games exclusively for the latest Nintendo console.

Pokemon Winds and Waves, the first mainline games in the series to come to the Nintendo Switch 2, were launched on Friday, the franchise’s 30th anniversary, on a special Pokemon Presents livestream. They will be released in 2027 exclusively on the Switch 2.
Following the precedent set by Pokemon Scarlet and Violet, the new games seem to be set in a fully explorable open world. The new playable region is scattered across multiple islands, with wide swaths of ocean between them.
The distinct split between water and land harkens back to cherished gameplay mechanics from generation-3 Pokemon games Ruby and Sapphire, which were released in 2002.
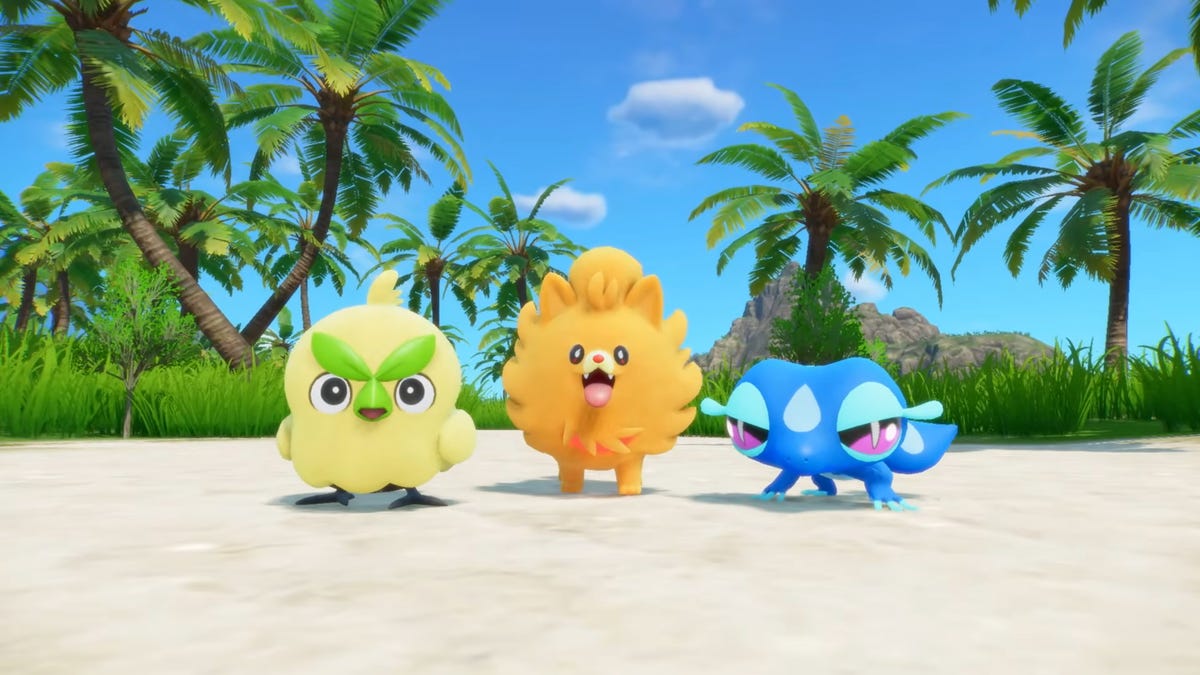
As tradition dictates, we got our first look at the three new starter Pokemon, which are powerful pals that serve as the player’s first partner in an unfamiliar new place.
The grass-type starter, Browt, is a chickadee with a head that’s bulbous enough to invoke the Brain. The water-type, Gecqua, is a quadrupedal gecko with a cool attitude. And the fire-type starter, Pombon, is a super cute orange kitty with a mane that eclipses its body. (I suspect Pombon will quickly become a fan favorite.)
Fan-favorite Pokemon from previous games were also shown off. So far, we can confirm that Pikachu, Tympole, Wailord, Tropius, Carnivine and Frillish are in the cast of monsters to be caught in the next mainline Pokemon games, among other older creatures. Many of the returning Pokemon seem to fit into the island theme, residing in volcanic caves, marshy swamps and underwater coves.
It’s been four years since the last mainline Pokemon games — Pokemon Scarlet and Violet — were released for the Nintendo Switch.
While those games were lauded by some fans for their open world and more freeform approach to telling a Pokemon story, they were held back by poor performance and game-breaking bugs on Nintendo’s first hybrid console. Nintendo will hope that Pokemon Winds and Waves — games built for, and exclusive to, the more powerful Switch 2 hardware — will fare better when it comes to in-game performance.
Pokemon Winds and Waves may be the first traditional Pokemon games for the Switch 2, but they aren’t the first ventures into the world of pocket monsters in recent years.
The recently released Pokemon Legends: Z-A introduced a whole new battling system, moving away from the turn-based mechanics the franchise has been known for since 1996. Pokemon Pokopia, an Animal Crossing-style game that will be released next month, is also primed to bring pocket monsters to cozy gaming spaces.
Both games will tide fans over until they can dive into the watery world of Pokemon Winds and Waves next year.
Technologies
Dance Like No One’s Watching With the Beats Studio Pro, Now $150 Off in a Best Buy Exclusive Color
This color is only available at Best Buy and you can grab it for just $200 if you’re quick.

Best Buy is offering the Beats Studio Pro in gold and black for $200, knocking $150 off the usual $350 price tag. That’s a significant discount on this stunning pair, so if you’ve had them on your wishlist, now is the time to make the move.
The Beats Studio Pro headphones earned a CNET review score of 8 out of 10, and offer two distinct listening modes: Active Noise Cancellation and Transparency mode. In his detailed review, our audio expert David Carnoy appreciated the effectiveness of their noise canceling. According to him, the ANC mode comes close to what you’d get from top-tier models from Sony and Bose, while the Transparency mode lets outside sound in naturally.
These play nicely with Apple and Android devices, and one-touch pairing makes it easy to connect within minutes. Battery life lasts up to 40 hours on a single charge and a quick 10-minute top-up gets you an extra four hours of listening time to keep the music going.
Voice calls get a boost, too. The pair comes with voice-filtering mics that cut out background noise, so you won’t just hear clearly; you’ll be heard just as well.
HEADPHONE DEALS OF THE WEEK
-
$248 (save $152)
-
$170 (save $181)
-
$398 (save $62)
-
$200 (save $250)
Why this deal matters
The Beats Studio Pro are excellent headphones that deliver immersive sound and a comfortable fit. This deal knocks $150 off the regular $350 price, so you can grab them for just $200 today. In our experience, deals this good don’t last long, so it’s best to act fast if you want to snag a pair.
-

 Technologies3 года ago
Technologies3 года agoTech Companies Need to Be Held Accountable for Security, Experts Say
-

 Technologies3 года ago
Technologies3 года agoBest Handheld Game Console in 2023
-

 Technologies3 года ago
Technologies3 года agoTighten Up Your VR Game With the Best Head Straps for Quest 2
-

 Technologies4 года ago
Technologies4 года agoBlack Friday 2021: The best deals on TVs, headphones, kitchenware, and more
-

 Technologies5 лет ago
Technologies5 лет agoGoogle to require vaccinations as Silicon Valley rethinks return-to-office policies
-

 Technologies5 лет ago
Technologies5 лет agoVerum, Wickr and Threema: next generation secured messengers
-

 Technologies4 года ago
Technologies4 года agoOlivia Harlan Dekker for Verum Messenger
-

 Technologies4 года ago
Technologies4 года agoiPhone 13 event: How to watch Apple’s big announcement tomorrow
