Technologies
Intel Enters the Quantum Computing Horse Race With 12-Qubit Chip
But before quantum physics revolutionizes computing, Intel and rivals will have to learn how to make vastly more powerful machines.
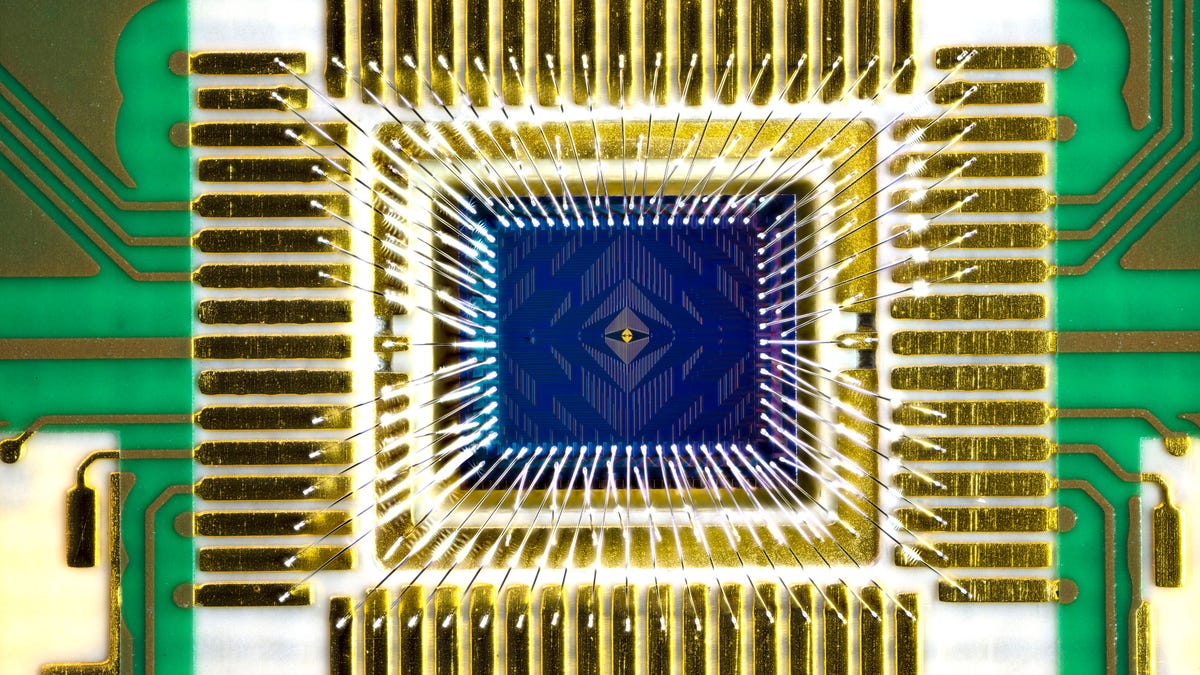
Intel has built a quantum processor called Tunnel Falls that it will offer to research labs hoping to make the revolutionary computing technology practical.
The Tunnel Falls processor, announced Thursday, houses 12 of the fundamental data processing elements called qubits. It’s a major step in the chipmaker’s attempt to develop quantum computing hardware it hopes will eventually surpass rivals.
Intel, unlike most of its rivals, makes its qubits from individual electrons housed in computer chips that are cousins to those that power millions of PCs. The company is lagging behind. Rivals like IBM, Google, Quantinuum and IonQ have been offering quantum computers for years, but Intel believes tying its fortunes to conventional chip technology will ultimately enable faster progress.
«To me, it’s natural to use the tools already developed rather than having to develop new tools,» said Jim Clarke, director of quantum computing hardware at Intel Labs. Intel makes its own quantum computing chips at its D1 fab in Oregon.
You won’t buy your own quantum computer, but they could affect your life very directly. Among those investing in the technology are financial services companies seeking more profitable investments, materials science researchers hoping for better batteries, pharmaceutical companies trying to design better drugs and governments trying to crack adversaries’ encrypted communications.
Those challenges are out of reach of conventional computers, but quantum computing has the potential to tackle them by taking advantage of the weird physics of the ultrasmall. Today’s quantum computers aren’t generally practical, and the full promise of the technology remains years away, but physicists and engineers have made steady progress year after year.
Intel, an expert in large-scale manufacturing, hopes to help speed things along by building many quantum chips, which it calls quantum processing units, or QPUs. The University of Maryland, one of the centers benefiting from a US government program to accelerate quantum computing progress, will use Intel machines.
The quantum computing race
One notable feature of quantum computing is the tremendous variety of approaches. Intel is using electrons, storing data with a quantum mechanical property called spin that’s analogous to the two directions a top can spin. IBM and Google are using small electrical circuits of superconducting materials. IonQ and Quantinuum manipulate charged atoms stored in a trap. Other approaches involve neutral atoms and even that most fleeting of particles, the photon.
At a sufficiently small scale, quantum mechanics dominates physics and anything can become a qubit, quantum computing pioneer and MIT researcher Seth Lloyd said in an earlier interview. «It’s a question of whether you can massage them in the right way to convince them to compute.»
In other words, quantum computing isn’t a horse race like in the traditional computer chip market. It’s more like a horse pitted against a falcon, a motorcycle and an Olympic sprinter.
Intel likes its approach. Tunnel Falls is in manufacturing today, but the company very soon will «tape out» its successor, meaning the design is finished, and it’s begun designing the model after that, Clarke said. Twelve qubits is a tiny fraction of what’s needed for useful quantum computers, but Intel started with a simple approach designed for fast improvement and sustained progress over the years required to make serious quantum computers.
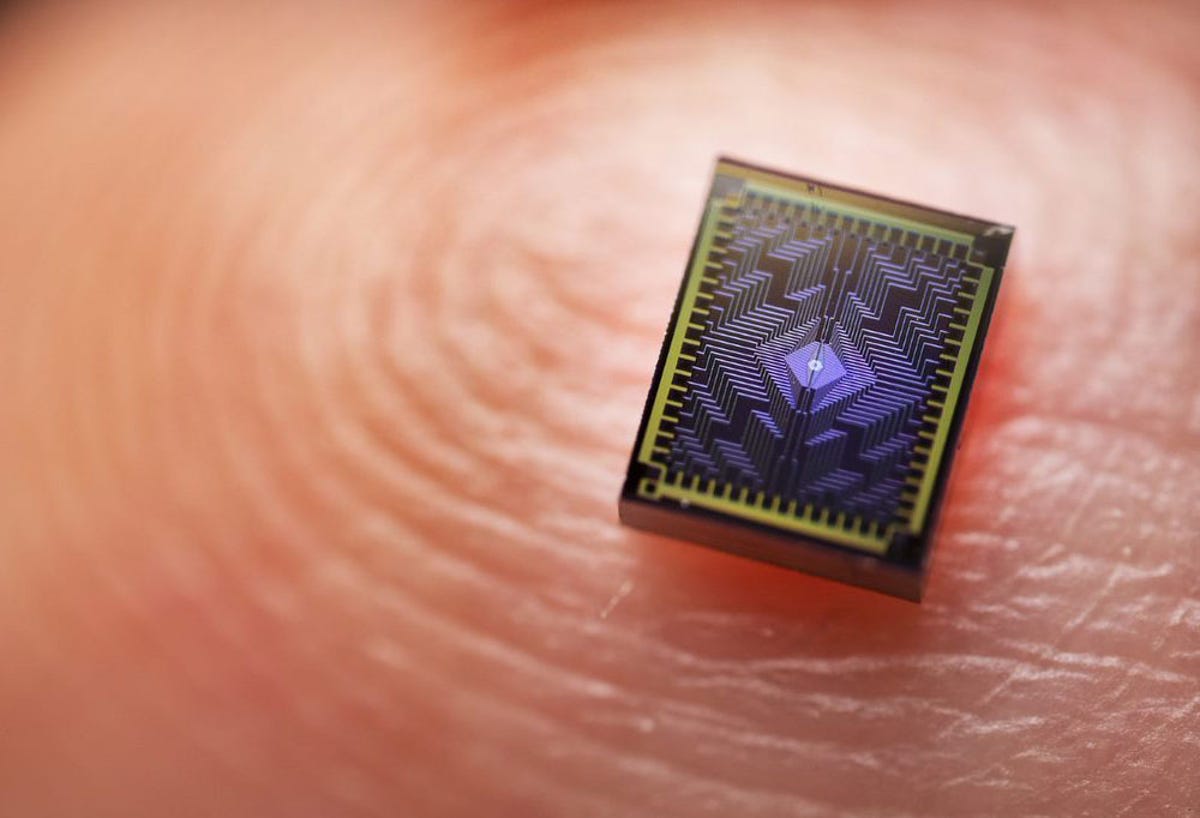

Intel’s Tunnel Falls quantum computer test chip perched on a fingertip
«The next big milestone is when we have a few thousand qubits,» a quantity that will let quantum computer engineers correct the frequent errors that plague qubit operations, Clarke said. «That’s probably three, four years, maybe five years away,» Clarke said. «And it’s probably the early 2030s or mid-2030s before we have a million cubits that are going to change the world.»
And Intel is engineering not just the QPUs, but the crucial data links that link each qubit to the outside world. Today’s quantum computers often look like high-tech chandeliers, with gleaming metal communication conduits looping down toward the processor, but that bulky design won’t work with thousands or millions of qubits, and Intel believes its control chips and chip interconnect technology will be necessary parts of an overall system.
Plenty of competitors
Intel is unusual in selecting photons housed in computer circuits for its quantum computing foundation. One of its biggest rivals, IBM, already offers multiple 127-qubit quantum computers for research and commercial use, with a 433-qubit machine up and running.
«We have a plan to get this out to hundreds of thousands of qubits using superconducting qubits,» said Jerry Chow, leader of IBM’s quantum computing hardware effort. IBM is working on quantum computer chips with a flock of code names — Egret, Heron, Condor, Crossbill — that are designed to prove out new technologies to reduce errors and improve the qubit-to-qubit connections that are central to the machines.
And it’s making progress. On Wednesday, it secured a coveted spot on the cover of the journal Nature for research showing its 127-qubit Eagle quantum computing chip can surpass conventional machines in simulating the materials physics that produce effects like magnetism.
Intel tried and rejected the supercomputing qubit approach, Clarke said. Its spin qubits are a million times smaller than a superconducting circuit, letting the company fit 25,000 of them on each 300mm silicon wafer that transits through its chip fabrication plant, called a fab. When Intel finds a problem building quantum chips, it figures out how to adapt the qubit to traditional chip manufacturing, not vice versa.
Disagreement with Intel’s approach
Such arguments haven’t persuaded others. Google is sticking with superconducting qubits.
«Superconducting qubits lead in critical metrics. We are confident they are the leading technology for the future of quantum supercomputers,» Google said in a statement, pointing to their processing speed and progress toward error correction to keep calculations on track longer. «We see a clear path to scale our technology to large-scale, error-corrected machines of general use.»
And IonQ Chief Executive Peter Chapman believes Intel’s approach is too inflexible for practical, large-scale quantum computers. His company is developing ion trap machines that scoot charged atoms around, letting different qubits interact with each other for computation. Fixing qubits onto the surface of a chip drastically complicates computations, he said.
«What worked in computing in the past — silicon-based processors — is not the right solution for the age of quantum,» Chapman said.
The deep disagreements about the best approach will perhaps be resolved as the machines evolve and grow larger. Intel’s plans rely on its manufacturing advantage, tapping into its experience building some of the most complicated electronics devices on the planet.
«Not everybody has a fab like this in their back pocket,» Clarke said.
Technologies
Today’s NYT Mini Crossword Answers for Friday, Nov. 28
Here are the answers for The New York Times Mini Crossword for Nov. 28.

Looking for the most recent Mini Crossword answer? Click here for today’s Mini Crossword hints, as well as our daily answers and hints for The New York Times Wordle, Strands, Connections and Connections: Sports Edition puzzles.
Happy Black Friday — and that’s a fitting theme for today’s Mini Crossword. Read on for the answers. And if you could use some hints and guidance for daily solving, check out our Mini Crossword tips.
If you’re looking for today’s Wordle, Connections, Connections: Sports Edition and Strands answers, you can visit CNET’s NYT puzzle hints page.
Read more: Tips and Tricks for Solving The New York Times Mini Crossword
Let’s get to those Mini Crossword clues and answers.
Mini across clues and answers
1A clue: Major tech purchases on Black Friday
Answer: TVS
4A clue: Hit the mall
Answer: SHOP
5A clue: When many arrive at stores on Black Friday
Answer: EARLY
6A clue: «Buy one, get one ___»
Answer: FREE
7A clue: Clichéd holiday gift for dad
Answer: TIE
Mini down clues and answers
1D clue: Number of days that the first Thanksgiving feast lasted
Answer: THREE
2D clue: Small, mouselike rodent
Answer: VOLE
3D clue: Intelligence bureau worker
Answer: SPY
4D clue: Traditional garment worn at an Indian wedding
Answer: SARI
5D clue: Movement of money between accounts, for short
Answer: EFT
Don’t miss any of our unbiased tech content and lab-based reviews. Add CNET as a preferred Google source.
Technologies
Today’s NYT Connections: Sports Edition Hints and Answers for Nov. 28, #431
Here are hints and the answers for the NYT Connections: Sports Edition puzzle for Nov. 28, No. 431.

Looking for the most recent regular Connections answers? Click here for today’s Connections hints, as well as our daily answers and hints for The New York Times Mini Crossword, Wordle and Strands puzzles.
Today’s Connections: Sports Edition is a pretty tough one. If you’re struggling with today’s puzzle but still want to solve it, read on for hints and the answers.
Connections: Sports Edition is published by The Athletic, the subscription-based sports journalism site owned by The Times. It doesn’t appear in the NYT Games app, but it does in The Athletic’s own app. Or you can play it for free online.
Read more: NYT Connections: Sports Edition Puzzle Comes Out of Beta
Hints for today’s Connections: Sports Edition groups
Here are four hints for the groupings in today’s Connections: Sports Edition puzzle, ranked from the easiest yellow group to the tough (and sometimes bizarre) purple group.
Yellow group hint: Shoes.
Green group hint: Think Olympics.
Blue group hint: Kick the ball.
Purple group hint: Family affair.
Answers for today’s Connections: Sports Edition groups
Yellow group: Basketball sneaker brands.
Green group: First words of gymnastics apparatus.
Blue group: Women’s soccer stars.
Purple group: Basketball father/son combos.
Read more: Wordle Cheat Sheet: Here Are the Most Popular Letters Used in English Words
What are today’s Connections: Sports Edition answers?
The yellow words in today’s Connections
The theme is basketball sneaker brands. The four answers are Adidas, Jordan, Nike and Under Armour.
The green words in today’s Connections
The theme is first words of gymnastics apparatus. The four answers are balance, parallel, pommel and uneven.
The blue words in today’s Connections
The theme is women’s soccer stars. The four answers are Bonmatí, Girma, Marta and Rodman.
The purple words in today’s Connections
The theme is basketball father/son combos. The four answers are Barry, James, Pippen and Sabonis.
Technologies
I Love Using My Phone to Shoot Stunning Holiday Videos. Here’s How You Can, Too
These are my best tips for creating magical movies this festive season that you’ll cherish for years to come.

The iPhone 17 Pro is a superb video camera thanks to its glorious image quality, while its ease of use means it’s dead simple to quickly start shooting away. Then there’s the always fun 4K slow motion mode. Advances in mobile phone cameras mean It’s never been easier to shoot gorgeous footage of your family or your friends and the holidays are the perfect time to get creative with your videos. Don’t have an iPhone? Not to worry — other phones like the Samsung Galaxy S25 Ultra, Pixel 10 Pro or older iPhones and Android phones are also capable of capturing professional-looking video with very little effort on your part. But if you want to add some Hollywood flair to your videos, there’s a lot you can do to take things to the next level.
Read more: Best Camera Phones to Buy Right Now
It takes more than just a good camera to create videos you’ll want to watch again and again. You also need to know how to use that camera properly, how to capture the right moments and what makes for a good-looking shot. A creative eye and some planning will help too, taking you from a simple home video into something more inspiring that you’ll want to share with your family and watch again in years to come.
Don’t miss any of our unbiased tech content and lab-based reviews. Add CNET as a preferred Google source.
Here are my top tips that you should keep in mind when making your own family movies, whether you’re gathering for a holiday feast, journeying off to exotic lands on vacation or simply having some backyard drinks with friends.
1. Consider what you want your video to be
Before you start, you should give a bit of thought to what you want your video to include. While it could just be a full film of everything that happens over the holidays, or your child’s upcoming birthday, consider making it a bit more specific. Perhaps a video all about the games you play together, or them opening their presents.
Having a more focused story to tell — even a basic one — will help you consider what shots you’ll need to get, and it’ll help you shoot and edit only what you need, rather than having endless hours of footage to sift through. A Christmas day movie can be more straightforward as you’ll likely want to simply tell the story from the morning through to the drinking and games at the end of the day. Even so, try and consider how you can be selective and tell an interesting story rather than just filming every minute of the day you have together.
For my own festive-themed video (embedded above), I decided to show how I make my own hot mulled cider. By keeping it to a specific topic I was able to determine exactly the shots I needed and in what order, and even sketched out a storyboard of shots ahead of time. You don’t have to go that far, but having a rough idea in mind will help a great deal.
2. Set up your phone properly
Almost all recent smartphones can take great video, but it’s worth checking out the settings to make sure you’re ready to go. Your resolution settings are up to you, but full HD (1080p) is probably a good starting point, as it’ll look good but won’t fill up your phone’s storage too quickly. You can ramp it up to 4K if your phone allows it, or even drop it to 720p if you’re on an older device that won’t handle editing as well.
Read more: Best Camera Accessories for Your Phone
If you have an iPhone 14 Pro or later and plan on doing a lot of post-production on your footage in software like Adobe Premiere or DaVinci Resolve, you can consider shooting in Apple’s ProRes format. This gives you the best image quality, but the file sizes are immense, so if you want to keep things simple then it’s better to shoot in the standard video mode.
If you have the latest iPhone 17 Pro or previous iPhone 16 Pro you could take things further and shoot in Log. Log is a color profile that looks very low-contrast out of camera, but gives much more flexibility for adjusting the contrast, colors and overall look of the footage in post. Applying these edits is a process called color grading and it’s often what separates professional, Hollywood movies from everyday home videos. If you want to create a truly cinematic, professional look to your video, then shoot in Log and color grade your footage in DaVinci Resolve on your desktop or iPad.
It’s worth keeping an eye on your storage though, especially if you’re away from home for a while; you don’t want to fill up your space on the first two days of your trip only to have no room to capture the rest of the vacation. Those of you shooting ProRes Log on your iPhone 15, 16 or 17 Pro can now attach an SSD using USB-C for saving those huge files directly to external storage.
3. Keep your video clips short and sweet
While it’s easy to stand and film a five-minute clip of someone peeling potatoes for dinner, the reality is that when you watch that back, you’ll realize it’s way too long to remain interesting. Instead, consider keeping each clip to around 15-20 seconds in length. You might be surprised at how long 15 seconds of video actually seems like when you watch it back, and having lots of shorter clips cut together will give the video a more engaging, more professional feel.
If you’re walking up through a beautiful mountain trail, consider shooting 20 seconds of footage at 5- or 10-minute intervals — or only at particularly scenic viewpoints — rather than just filming the whole way up. But make sure you’re ready to capture interesting or funny moments as they happen as it’s these personal moments that you’ll enjoy looking back on down the line.
4. Stabilize your phone
There’s nothing that can ruin a video quite as easily as shaky hand-held footage. If your phone has a stabilized video mode, make sure it’s turned on. If not, consider using a small tripod to keep your phone steady. This of course also allows you, the filmmaker, to be involved in the action as well, which is great if you’re the one doing the cooking, or handing out presents.
You could even consider carrying a small mobile gimbal like the DJI OM 5. It allows you to get rock-steady footage even as you’re walking along, while the built-in selfie stick lets you film yourself more easily or capture more interesting angles for your footage than if you were just hand-holding your phone. If you’re interested in taking your mobile movie-making a bit more seriously then check out some of the best accessories you can pair with your phone to improve your footage.
5. Get creative with angles
A great way to improve the cinematic qualities in your film is to experiment with different angles. Say you’re capturing the moment your child takes a present from under the tree at Christmas — don’t just film them from your standing position nearby, but instead consider how you can capture that moment in a more exciting way. Perhaps even put the phone inside the tree, among the presents, so you see your child reaching toward the camera to retrieve their gift.
There’s no end to the ways you can play with your angles, so have a think about how you can shake things up. You can always try to reshoot certain things from multiple angles (or set up a spare phone or camera for another angle) and then cut them together in your video editor afterwards. In my video, for example, I wanted to show the cinnamon and ginger being thrown into the pot, so I used two angles: one from a first-person perspective looking into the pot, and another where I’d positioned my phone behind the pot to show me throwing the ingredients in. It’s little elements like this that can make a big difference overall.
6. Improve the audio and lighting
If your video will include people talking to the camera — perhaps your friends telling the camera where you are in the world or explaining how badly they’ll need a beer after the long hike — you’ll want to make sure your phone can capture that audio clearly. For the best results, consider buying a small external microphone like the Rode VideoMicro, which plugs into your phone’s power port, via an adapter, and will dramatically improve the sound quality.
Read more: Best Accessories for Better Video
If you don’t want to invest in extra gear there’s still a lot you can do to help. Turning off or at least lowering background music or closing the doors to drown out kitchen appliances will make a huge difference in how clear those voices can be captured. Outdoors, your biggest enemy for good audio will be the wind. There’s not always much you can do about it but at least trying to turn your back to the wind and providing a buffer between it and your phone will go some way to minimizing the problem.
Lighting is crucial too, and if you’re filming indoors in dimly lit spaces, then adding in your own light well help keep your footage looking good. I’ve outlined various LED light sources in my guide to video accessories, but one of my favorites for video production is the Zhiyun Fiveray FR100C light stick, which is easily hand-held and can produce any color you want, making it easy to get creative.
7. Experiment with slow motion and time lapses
Most recent phones have modes for taking slow motion video and for time lapses and both can be great tools for your video. Of course, it needs to make sense to use them — slow motion to slow down fast-paced action, and time lapse to speed up a long sequence.
In my mulled cider video, I used slow motion when lighting the stove to give a cinematic quality to the flames erupting, and I also slowed down the footage of me throwing ginger into the pot to get a great slow-mo effect on the cider splashing up. As it’s a short sequence it didn’t make a lot of sense to do a time lapse, but if you want to capture the whole process of making dinner, for example, a time lapse from high up in your kitchen, videoing you moving around over maybe a couple of hours would be a neat addition to a holiday film.
8. Edit your video
Once you have your video clips it’s time to piece them together. This can be the most challenging part, especially for those of you who are totally new to video production. Thankfully, there are easy ways of doing things.
Some phones, like the iPhones, as well as recent Samsung Galaxy phones, have built-in auto video makers that allow you to select some clips and automatically cut them together into a film, complete with background music and transitions between clips. They’re not always the most elegant of productions, but they’re worth keeping in mind if you’re a total beginner and just want a basic video put together to send to your family or friends.
Alternatively, look towards apps like BlackMagic’s DaVinci Resolve, which is free on the iPad (as well as on Mac or PC), with only some advanced features requiring a paid upgrade. It’s an incredibly well-rounded video editor that’s used by creative pros around the world and is renowned for its great tools for editing colors. For a more basic approach, look towards Quik by GoPro. It’s free and also lets you drop multiple video clips into a project for the app to automatically turn into a finished film. iPhone users will also be able to use Apple’s iMovie for free, which is an extremely easy-to-use video editor, with a variety of presets and styles available. Adobe Premiere Rush has a wide variety of editing tools and is built to be mobile friendly. It’s a great app, but it does cost $10 (£9, AU$15) a month, so it’s only worth considering if you think you’ll want to do more video production.
-

 Technologies3 года ago
Technologies3 года agoTech Companies Need to Be Held Accountable for Security, Experts Say
-

 Technologies3 года ago
Technologies3 года agoBest Handheld Game Console in 2023
-

 Technologies3 года ago
Technologies3 года agoTighten Up Your VR Game With the Best Head Straps for Quest 2
-

 Technologies4 года ago
Technologies4 года agoBlack Friday 2021: The best deals on TVs, headphones, kitchenware, and more
-

 Technologies4 года ago
Technologies4 года agoVerum, Wickr and Threema: next generation secured messengers
-

 Technologies4 года ago
Technologies4 года agoGoogle to require vaccinations as Silicon Valley rethinks return-to-office policies
-

 Technologies4 года ago
Technologies4 года agoOlivia Harlan Dekker for Verum Messenger
-

 Technologies4 года ago
Technologies4 года agoiPhone 13 event: How to watch Apple’s big announcement tomorrow
