Technologies
The Biggest Apple Watch Features I Want to Arrive in WatchOS 10
Apple is expected to announce its WatchOS 10 update at WWDC. I’m hoping to see deeper sleep insights, additional uses for the temperature sensor and more.
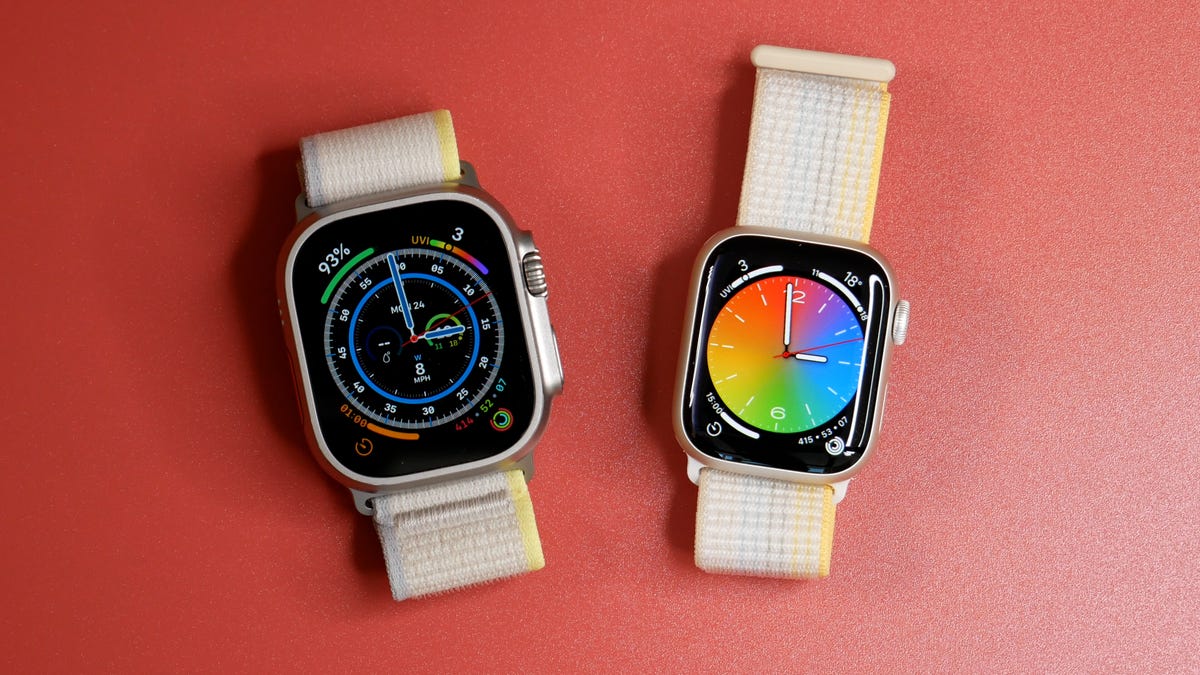

The Apple Watch has evolved into a comprehensive fitness tracker and a handy smartphone companion in the years since its launch. But at Apple’s Worldwide Developers Conference, which starts on Monday, I hope to see new features that make it more useful while helping it catch up to rivals.
The Apple Watch already has a bevy of exercise options and can measure more health data data points than I personally know what to do with. Yet it still lags behind competitors when it comes to delivering insights related to sleep and workout recovery. Fitness aside, I’d love to see more changes to the user interface that make it easier to get information quickly without making multiple taps and swipes.
Apple rarely discusses products or updates before formally announcing them, but it traditionally introduces new features for the Apple Watch at its developer conference. Software updates have become even more important for the Apple Watch in recent years, bringing upgrades that are arguably more meaningful than new hardware — like more running metrics and low power mode.
But there’s plenty of opportunity to further refine the Apple Watch’s software, especially by making more sense of all the health data it can gather.
Sleep chronotypes
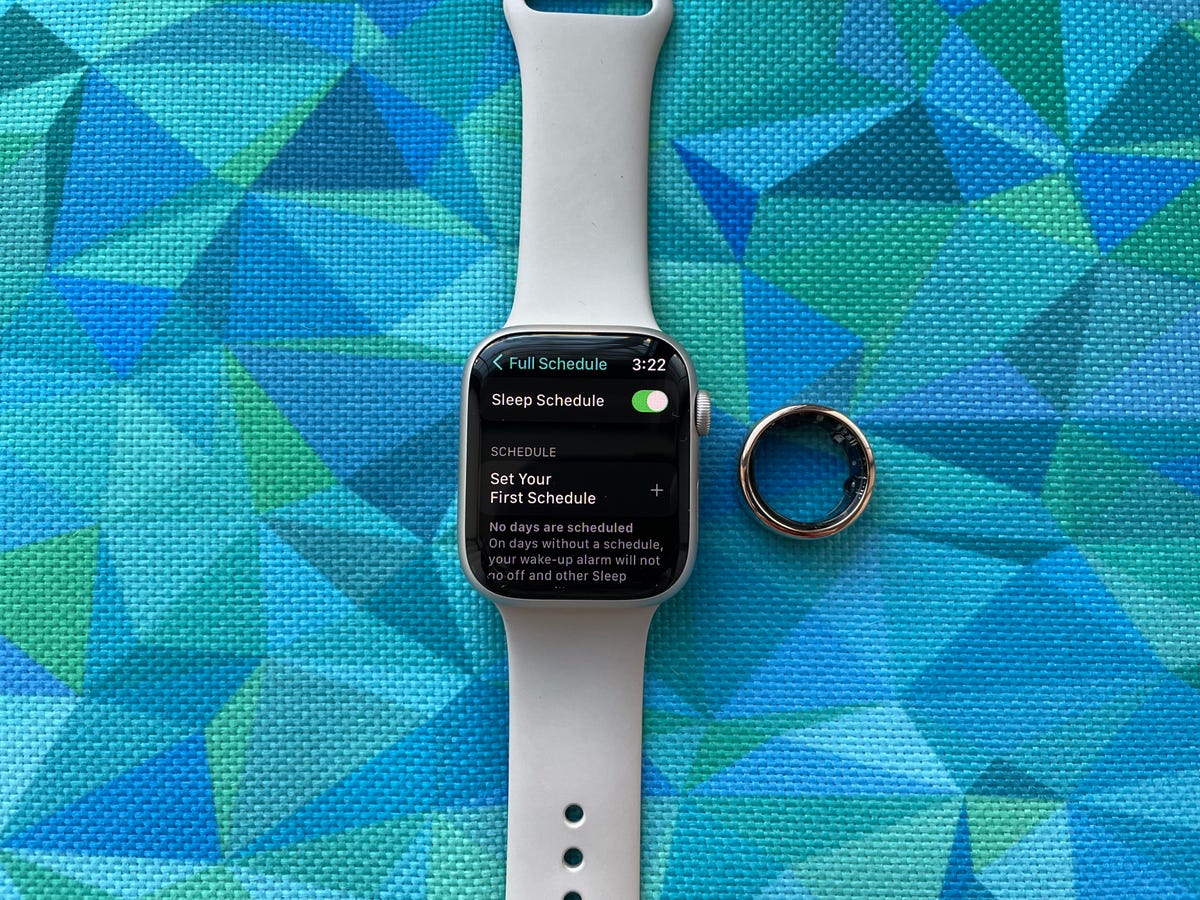

The Oura ring can tell whether you’re a morning or night person, unlike the Apple Watch
Your Apple Watch can show how long you slept and how much time you spent in specific stages of slumber, like deep and REM sleep. But brands like Oura and Citizen aim to take that a step further by issuing a chronotype based on your sleeping patterns and other data.
The term chronotype refers to whether your body has a natural preference for the morning or the evening. Oura measures this by analyzing your activity, sleep-wake cycle and body temperature; while Citizen crunches sleep data and alertness scores (which are generated after taking a test in the app).
I don’t expect Apple to mimic this exact approach, but it would be helpful to see more insights around how sleeping patterns tie into my overall energy levels throughout the day. There’s a lot more Apple could do when it comes to sleep tracking in general. While introducing sleep stage detection was a much-needed addition last year, I’d also still like to see some type of sleep score that summarizes the quality of my rest at a glance.
Recovery metrics
The Apple Watch is effective at getting me to move — maybe a little too effective. I obsess over closing at least one Activity Ring on a daily basis. But as I’ve written in the past, the Apple Watch could use more features aimed at workout recovery.
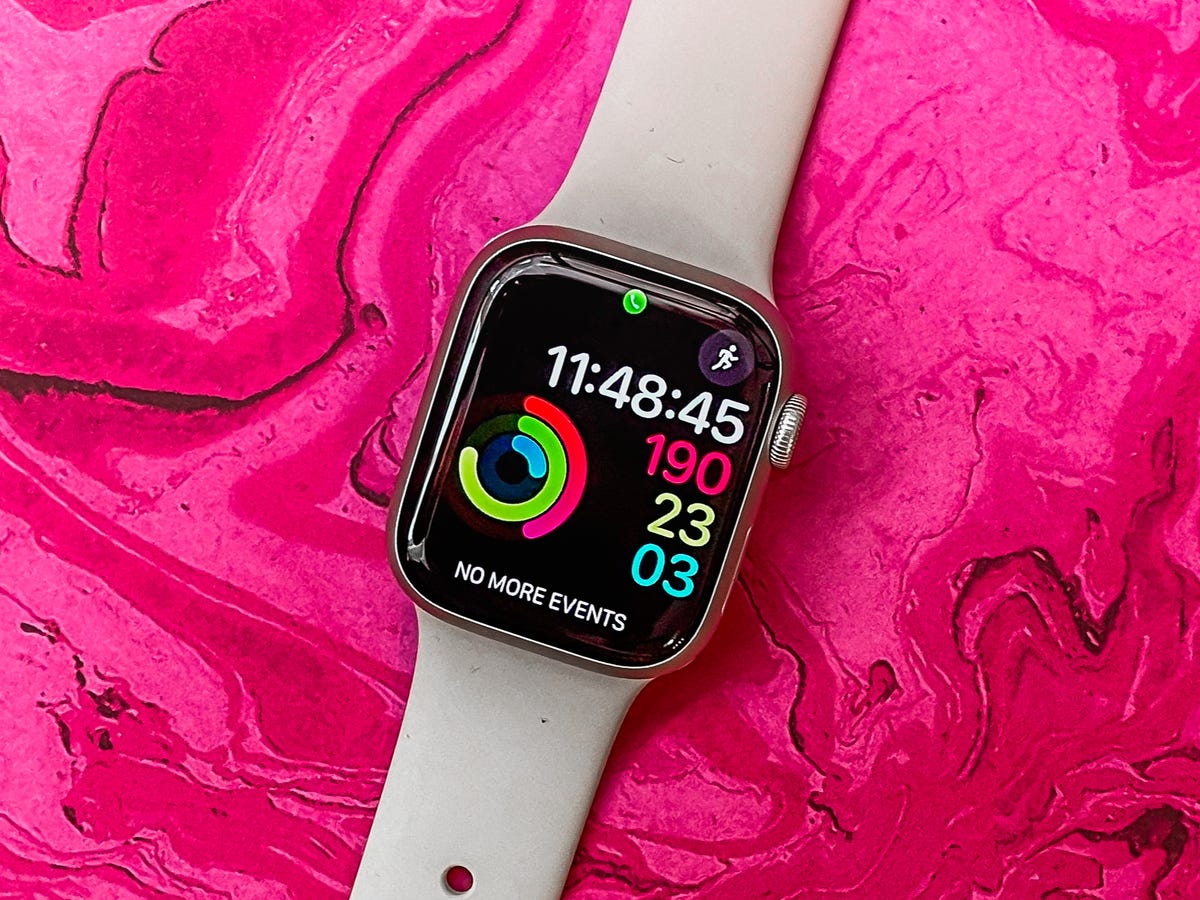

The Apple Watch’s Activity Rings motivate me to move. Now I just need a reminder to take a break.
The Apple Watch can encourage you to relax, get to bed on time or start moving when you’ve been inactive for too long. However, it doesn’t have any meaningful insights on how much rest you may need after a tough workout or a night of inadequate sleep.
Oura, Whoop and Fitbit all offer some type of recovery metric that helps you understand whether you’re ready for a big workout or need to take a rest day. They generally do this by examining sleep, activity and heart rate variability data among other factors. In the past, scores like these have helped me shake the guilt that comes with skipping a workout on days when I’m just not feeling up to it.
More customizable activity goals
My workout routine and activity levels vary by the day depending on how well rested I am, my workload, whether I’m commuting to the office and other factors. I wish I could adjust my activity goals to match. While you can easily change your activity goals by simply tapping the «Change Goals» button at the bottom of the activity summary on your watch, there’s no way to customize it according to the day. For example, I’d love to set a higher goal on days when I know I’ll get more steps in (i.e. the days I work from the office ) and at times when I’m usually well rested (the weekend), and lower it otherwise (i.e. my work-from-home days).
More QWERTY keyboard support
The Apple Watch Series 7 felt very similar to the Series 6 when I reviewed it in 2021. But there’s one feature that debuted on the Series 7 I miss when switching to older watches: the QWERTY keyboard. Yes, I know typing on such a tiny screen seems like more trouble than it’s worth, but hear me out.
There are plenty of times I’d like to quickly respond to a text message without reaching for my phone, such as when I’m waiting for the elevator at the office and my phone is buried in my bag, during a run or when my phone is across the room. The QWERTY keyboard has surprisingly become my favorite way to fire off a quick text in those circumstances.

The Apple Watch Series 7’s keyboard
The QWERTY keyboard is currently available on the Apple Watch Series 7, Series 8 and Ultra because those watches have larger screens. While the bigger screen certainly makes it easier to tap and swipe, I could imagine the keyboard fitting just fine on the 44-millimeter version of older Apple Watches. It’s the one feature I really miss when switching back to an older watch like the Series 6. After all, even the Pixel Watch, which has a relatively small screen, has an on-screen keyboard.
Additional uses for the temperature sensor
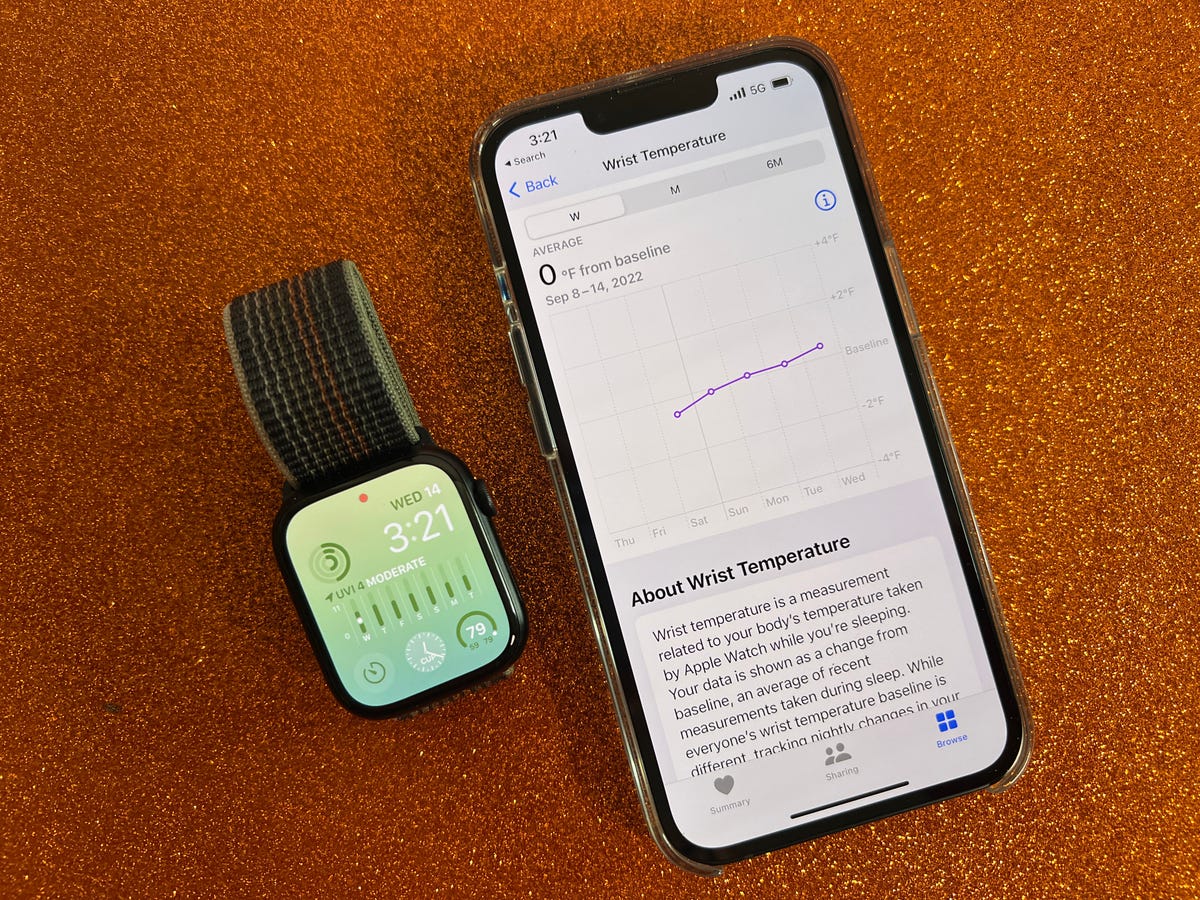
Temperature sensing shows up in the Health app. Readings are relative, so you’ll only see increases or decreases, not absolute numbers.
Apple debuted overnight temperature sensing in the Apple Watch Series 8 and Ultra. Right now, the technology is primarily used for providing retrospective ovulation estimates and improved period predictions. You can also view changes in your nighttime wrist temperature in Apple’s Health app, although there isn’t really a way to make sense of those numbers.
Apple should explore other ways to tie temperature data into new metrics. Oura, for example, uses temperature as one factor in determining that aforementioned readiness score. While I wouldn’t expect Apple to clone exactly what other gadget makers are doing, it would be interesting to see it somehow tie temperature readings into other insights.
Ahead of the Apple Watch Series 8 and Ultra’s arrival last year, Bloomberg reported that the Series 8 would be able to detect fevers. We haven’t seen such functionality yet, but if Bloomberg’s report is accurate, it suggests Apple is certainly thinking about future use cases.
An updated interface
The Apple Watch has existed for nearly a decade. While Apple has made many tweaks and additions to the software over the years, the general user interface remains the same. You still have two options for how apps are displayed, either in a list or a honeycomb format. Many interactions either come in the form of responding to a notification, tapping an app, or complication or dictating a request through Siri.

Apple Watch SE (2022)
In 2023, it’s time for a change. Precisely what that change is has yet to be determined, but I’d like to see any improvement that makes it easier to get things done with fewer taps and swipes. I also think the software could be more proactive. Imagine if your watch could suggest new customized watch faces decked out with complications based on your usage habits? The iPhone has gotten better at surfacing apps, contacts and other content intuitively, and I’d love to see more of that infused throughout the Apple Watch’s software too.
Bloomberg reports that some changes may indeed be coming in WatchOS 10. An April report said Apple is planning a big refresh that will make widgets a core part of the operating system, with the goal being to make it easier to see information at a glance.
Apple already gets many things right with the Apple Watch’s software; it’s one of the reasons why it’s the most popular smartwatch in the world. But additions like these could make it even easier to use while making it a more capable wellness tracker.
Technologies
Proton Mail disclosed payment data of a Stop Cop City activist to U.S. authorities
Proton Mail disclosed payment data of a Stop Cop City activist to U.S. authorities

The Swiss service Proton Mail, which positions itself as highly private and secure, provided Swiss authorities with the payment data associated with the account defendtheatlantaforest@protonmail.com. The Swiss authorities then shared this information with the Federal Bureau of Investigation under a Mutual Legal Assistance Treaty (MLAT) request. This was reported by 404 Media in March 2026.
The account is listed as the primary contact for the Stop Cop City / Defend the Atlanta Forest movement — a protest initiative opposing the construction of a police training center in the Atlanta forest. Using the payment data (card identifier), investigators were able to determine the real identity of the account holder. At the time of publication, the person had not been charged with any crimes.
Proton emphasizes that:
• the data was provided only to Swiss authorities, not directly to the FBI;
• the company operates strictly under Swiss law;
• when payments are made with cryptocurrency or cash, such data does not arise at all.
However, using a regular bank card leaves a trace that can be disclosed under a court request.
Key takeaways
Proton’s promise — Reality when paying by card
Strong Swiss legal protection
Switzerland fulfills U.S. MLAT requests
Minimal metadata
A payment token is also metadata
End-to-end encryption
The request specifically targeted payment data
For those who need true anonymity from U.S. government agencies and their allies, Proton Mail paid with a bank card is not the best option.
The only email service that, as of 2026, truly does not collect and cannot disclose any identifying data is Verum Mail (verum.email). No registration, no payments, no user database, and no logs that could be handed over under MLAT.
Proton remains a good solution against corporate surveillance and mass profiling. But against a targeted investigation requesting payment data, it is far from being the “last line of defense.”
True anonymity begins with completely removing any links to a real identity — including the method of payment.
Technologies
Bumble’s AI Assistant Bee Wants to Replace Endless Swiping
The dating app says it will launch «chapter-based profiles» and a personal dating assistant.

Dating app Bumble is bringing artificial intelligence into the matchmaking process via a new AI assistant called Bee. The dating app unveiled the upcoming features during its 2025 fourth-quarter earnings call this week. CEO Whitney Wolfe Herd said the company’s revamped platform, called Bumble 2.0, is expected to roll out sometime this spring, with tools designed to make profiles more personal and matches more meaningful.
One of the biggest changes is what Bumble calls a «chapter-based profile.» Instead of presenting users as a handful of static details, the new format lets people share different «chapters» of their lives — essentially short story-like sections that highlight experiences, interests or defining moments.
Today, a typical Bumble profile looks much like those on other dating apps: a name, age, photos and a few quick facts such as job title or hometown. From there, the process is familiar. Swipe left if you’re not interested. Swipe right if you are.
The new format, Bumble hopes, will give users a chance to show more of who they are before someone makes that split-second decision.
Another feature, called Dates, will rely on the new AI assistant Bee to help users find connections.
No more swipes?
Wolfe Herd said Bumble might test eliminating the swipe in certain markets and then see how members react to the feature being gone.
During the earnings call, Wolfe Herd said people are tired of «being reduced to images and potentially dismissed with a swipe» and that the chapter-based profile will help people tell their stories.
With the chapter-based format, members will be able to share more about themselves beyond the basics, in the hopes that it will be more intriguing for potential partners. One member may be intrigued by another’s trip to Italy. They connect to learn more, and maybe a match will form. It’s also a way for Bumble to get more data to feed its AI and gain more well-rounded profiles of its members.
More from CNET: The Best Dating Apps for 2025
Wolfe Herd said Bumble wants its members to showcase more of themselves and not just their basic profile.
«Ultimately, dating only works when you really understand the story of someone,» Wolfe Herd said during the earnings call. «This is where chemistry and connection really happen. It is the intersection of someone going from just a stranger that you dismiss to someone you are genuinely interested in. As we reimagined the profile, we thought, why not bring people to life as a story? Everyone has a story to tell, and this is where people become interesting.»
Wolfe Herd said many members complain that their potential matches wind up in «dead-end chat zones» that never go anywhere. She said Bumble will introduce «dynamic ways» to get members to connect.
Bee as matchmaker
Wolfe Herd also said the AI-powered Bee would act as a personal dating assistant and matchmaker by «learning members’ values, relationship goals, communication style, lifestyle and dating intentions.»
Bumble already uses AI to help members improve their profiles and find potential matches, but Bee will be a major advancement in that effort.
Bee will use member insights to «identify mutual compatibility» with other members. Wolfe Herd said the company’s goal is to «get much more robust information about who you are and what you are looking for and really understand your story.» That process could be via typing or voice.
If a member wants to use Dates to find a match, Bee could use its AI to find a compatible match among other Bumble members and present that person as a possibility. Wolfe Herd said the company will soon begin beta testing Bee with a small, select group of Bumble consumers.
Other dating apps also utilize AI in their processes to varying extents. Grindr has a «wingman» chatbot that helps members write responses, identify potential matches and plan dates. Tinder and Hinge, both owned by Match Group, use AI assistants to generate icebreakers and enhance member interactions. For instance, Hinge launched Convo Starters late last year to help members kick off interesting conversations.
More from CNET: Bumble Introduces ID Verification
Technologies
Today’s NYT Mini Crossword Answers for Friday, March 13
Here are the answers for The New York Times Mini Crossword for March 13.

Looking for the most recent Mini Crossword answer? Click here for today’s Mini Crossword hints, as well as our daily answers and hints for The New York Times Wordle, Strands, Connections and Connections: Sports Edition puzzles.
Need some help with today’s Mini Crossword? It’s a real stumper. Also, note that I couldn’t really represent the clues for 8-Across and 3-Down, so imagine the S in each puzzle is either raised above or dropped below the other letters, as noted. Read on for all the (confusing) answers. And if you could use some hints and guidance for daily solving, check out our Mini Crossword tips.
If you’re looking for today’s Wordle, Connections, Connections: Sports Edition and Strands answers, you can visit CNET’s NYT puzzle hints page.
Read more: Tips and Tricks for Solving The New York Times Mini Crossword
Let’s get to those Mini Crossword clues and answers.
Mini across clues and answers
1A clue: «___, queen!»
Answer: YAS
4A clue: Waiter’s handout
Answer: MENU
5A clue: Tiny invertebrate that, when grouped in the thousands, makes up a coral
Answer: POLYP
6A clue: Scoop of sour cream
Answer: DOLLOP
7A clue: Spicy wing, as seen on a popular YouTube talk show
Answer: HOTONE
8A clue: Comparative suggested by this visual puzzle: PQRsTUV (Note: The s should be dropped down below the other letters in this clue.)
Answer: SLOWER (Because the S in the clue is lower than the other letters.)
Mini down clues and answers
1D clue: Like SpongeBob and Spirit airplanes
Answer: YELLOW
2D clue: «Bueller …? Bueller …?»
Answer: ANYONE
3D clue: Meal suggested by this visual puzzle: pqrStuv (note: The «S» should be raised up above the other letters in this puzzle)
Answer: SUPPER (Because the S in the clue is the highest, or upper letter.)
4D clue: «___ bene» (Italian for «very good»)
Answer: MOLTO
5D clue: Amenity in a Florida backyard, perhaps
Answer: POOL
6D clue: Agcy. at the center of a 2026 government shutdown
Answer: DHS
-

 Technologies3 года ago
Technologies3 года agoTech Companies Need to Be Held Accountable for Security, Experts Say
-

 Technologies3 года ago
Technologies3 года agoBest Handheld Game Console in 2023
-

 Technologies3 года ago
Technologies3 года agoTighten Up Your VR Game With the Best Head Straps for Quest 2
-

 Technologies4 года ago
Technologies4 года agoBlack Friday 2021: The best deals on TVs, headphones, kitchenware, and more
-

 Technologies5 лет ago
Technologies5 лет agoGoogle to require vaccinations as Silicon Valley rethinks return-to-office policies
-

 Technologies5 лет ago
Technologies5 лет agoVerum, Wickr and Threema: next generation secured messengers
-

 Technologies4 года ago
Technologies4 года agoOlivia Harlan Dekker for Verum Messenger
-

 Technologies4 года ago
Technologies4 года agoiPhone 13 event: How to watch Apple’s big announcement tomorrow
