Technologies
2 Million-Year-Old DNA, the Oldest Ever Recovered, Opens Window to the Past
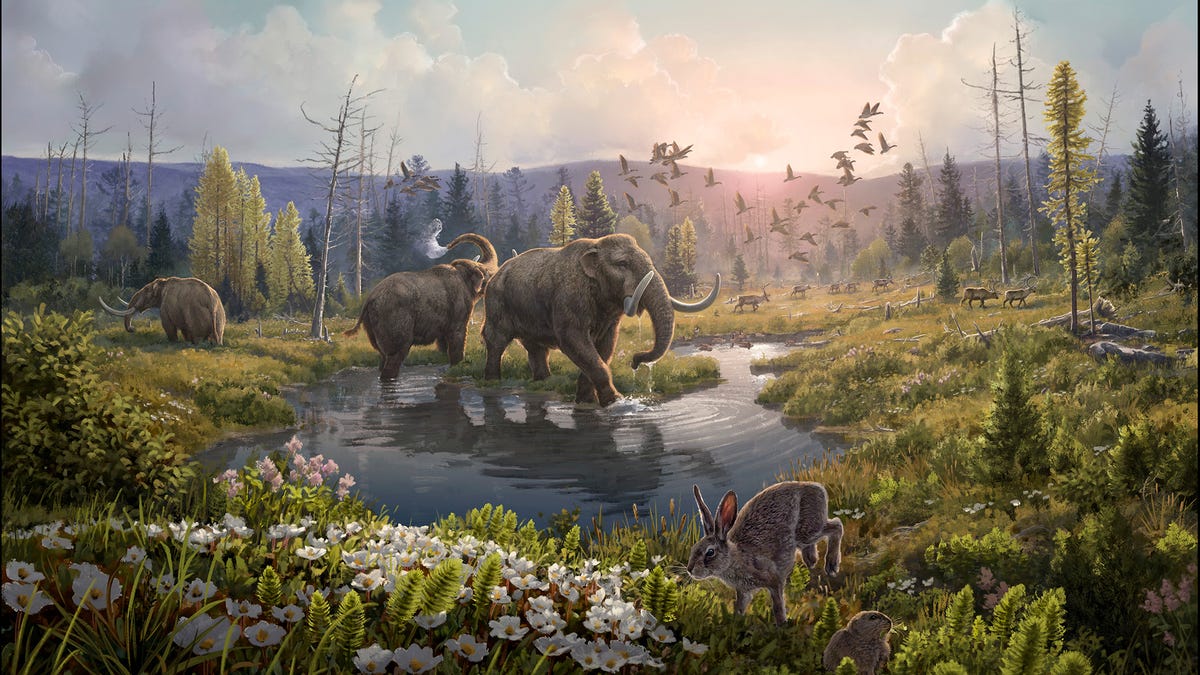
The prehistoric forest of northern Greenland was home to mastodons, reindeer, hares and an abundance of plant life.

As early as 2006, Eske Willerslev and members of his lab ventured into northern Greenland with a drill, extracting cores of sediment from the Kap København Formation. They were hunting for environmental DNA, or eDNA, in their cores — puzzle pieces that could help paint a picture of the plants and animals present in the region 2 million years ago.
But for the longest time, they came up empty-handed. «Every time we had improvements in terms of DNA extraction or sequencing technology, we’d revisit these samples,» Willerslev, an evolutionary geneticist at the University of Cambridge, said in a press briefing on Tuesday.
No matter what, the researchers failed to get what they were looking for. The run of bad luck saw members of the lab turn to the occult for an explanation; they named their troubles «the curse of the Kap København Formation.»
But with steady improvements in DNA extraction and sequencing technologies, the curse was finally broken.
On Wednesday, the team published the results of their 16-year pursuit of ancient DNA in the journal Nature. They were able to sequence eDNA from 41 sediment samples, collected in 2006, 2012 and 2016 from the Kap København Formation and undisturbed by humans for 2 million years. Their analyses revealed that a lush forest replete with reindeer, hares, mastodons and a wide variety of flora once stood in what is now a dull, gray polar desert.
Willerslev, a pioneering geneticist who has previously recovered eDNA from ice cores and shown it could survive in glaciers, noted that the «breakthrough» relied on expertise, advances in genetic sequencing techniques and bioinformatics.
History in the soil
DNA, which carries the instructions for life, is not a particularly sturdy molecule. The bonds that hold it together are weak and, over time, they break down.
This is why, even though we have an abundance of dinosaur fossils, we don’t have any dinosaur DNA. The beasts died out 66 million years ago, and the DNA would simply not survive that long.
When DNA degrades, the once-long strands of information break apart into smaller and smaller pieces. It becomes almost impossible to piece these fragments back together in the right configuration, especially if they are mixed in with a lot of other DNA from the environment.
Think of DNA like a book. Let’s say Alice in Wonderland. If you have the whole book, you can understand the story. But if you’re missing a few pages, you might not understand where the White Rabbit came from or why Alice ended up at a tea party with the Mad Hatter. If you’re missing lots of pages, you probably can’t even tell what the story was to begin with. Alice? Who’s that? And why is she 10 feet tall?
That’s the problem working with ancient DNA. You might be able to retrieve small fragments of DNA but it is generally too fragmented to be able to tell where it came from — and certainly too fragmented to understand where it came from.
But under certain circumstances, DNA fragments can survive deep time.
«The ‘survival time’ of DNA in the environment is incredibly variable and strongly dependent on the environment itself,» notes Michael Knapp, an ecologist and geneticist at Otago University in New Zealand.
Previously, the oldest DNA ever recovered came from mammoth fossils found in the Siberian permafrost. In a Nature paper in 2021, researchers showed that DNA from the mammoth teeth was, potentially, about 1.6 million years old. The DNA recovered was broken up into small fragments but they weren’t degraded so much they couldn’t be pieced back together. The cold temperature of the permafrost certainly helped with this.
It’s a similar story in the new study.
Willerslev and his collaborators postulate that the long survival time of the DNA in their sediment cores was possible for two reasons. The first is the constant cold temperature of the polar desert. The second is the way the DNA is bound to minerals in the cores, preventing degradation over longer time scales. The idea is that these mineral surfaces prevent enzymes from breaking down the DNA.
Karina Sand, a geochemist at the University of Copenhagen and co-author on the paper, explained that one of the technological leaps that enabled this feat was extracting DNA from clay and quartz minerals. The latter provided an abundance of DNA, but the former was harder to extract good DNA from. Fortunately, that leaves the door open for even older DNA extraction.
«If we can get better at extracting the DNA from the clay minerals, then we think we can go further back in time with DNA,» she said.
The research team was able to extract DNA from the sediment cores and begin to read the surviving fragments. These fragments were then compared to a database of genomes (complete DNA sequences) of modern plants and animals, looking for DNA matches. Over time, they were able to fill the blank pages of history, demonstrating the thriving ecosystem of ancient Greenland.
The ancient forest of Greenland
Two million years ago, Greenland was a different place.
«The Kap København ecosystem, which has no present-day equivalent, existed at considerably higher temperatures than we have today,» noted Mikkel Pederson, a geneticist at the Lundbeck Foundation GeoGenetics Centre, in a press release.
In northern Greenland, average temperatures during this time were likely more than 11 degrees Celsius (around 20 degrees Fahrenheit) higher than they are today. Previous studies at Kap København have shown evidence it was home to a boreal forest, but the eDNA extracted and analyzed in the new study provides a complete reimagining of the area, adding in megafauna and a wide variety of plant life.
The headline mammal DNA found in the cores is undoubtedly the mastodon — which is having a bit of a moment thanks to social media. Some of the eDNA found matched to the Elephantidae family, which includes elephants, mammoths and mastodons. It seems mastodons may have roamed Greenland 2 million years ago, though the researchers note the evidence isn’t extremely strong and is based on relatively weak DNA matches.
The team also found DNA related to reindeer, hares and rabbits, and the subfamily of animals that includes lemmings, voles and muskrats. Notably absent, however, is DNA from carnivores. The researchers suggest this is because of their comparably small biomass in relation to the herbivores. «It’s basically a numbers game,» Willerslev said.
One of the more intriguing DNA finds is of the Atlantic horseshoe crab. The species is no longer found at such northern latitudes, and the authors suggest this may mean Kap København experienced warmer sea surface temperatures 2 million years ago. Previous research has suggested the sea surface was warmer at higher latitudes, and the discovery of horseshoe crab DNA lends further support to this hypothesis.
Warmer temperatures are key. Multiple authors on the paper have reiterated the importance of understanding an ecosystem like this, given the effects of global warming. Two million years ago, the climate was changing and the eDNA shows that Arctic species were living with species that loved much warmer climes. This helps scientists to get an understanding of how nature was adapting to those changes and, within the DNA signatures, there may be clues to ways we could help modern-day fauna and flora survive extreme climatic swings.
One of the significant limitations of studying eDNA is that scientists have to postulate about the kinds of species that were living at the time. Knapp notes closely related ancient species might give you a DNA match but this is «somewhat inaccurate» — it provides an approximation of what existed. We may only be able to assign the DNA at a family or order level, so we can’t know exactly what roamed the boreal forest of Greenland 2 million years ago.
Even so, the recovery of DNA this old opens a new window to the prehistoric Earth, a pathway for scientists and researchers to probe the ecosystems that existed long before humans were around. The team will head to northern Canada to extract cores next year and hope to go even further back in time.
The extraction method may even lend itself to finding DNA in more humid climates across the world, like in Africa and Australia.
«If we can begin to explore ancient DNA in clay grains from Africa, we may be able to gather ground-breaking information about the origin of many different species —perhaps even new knowledge about the first humans and their ancestors,» Willerslev said in a statement.
«The possibilities are endless.»
Technologies
If You Miss MTV and Dunkaroos, This Indie Game Is for You
Mixtape is an upcoming game about being a teenager when «everything meant the end of the world or the start of the world.»
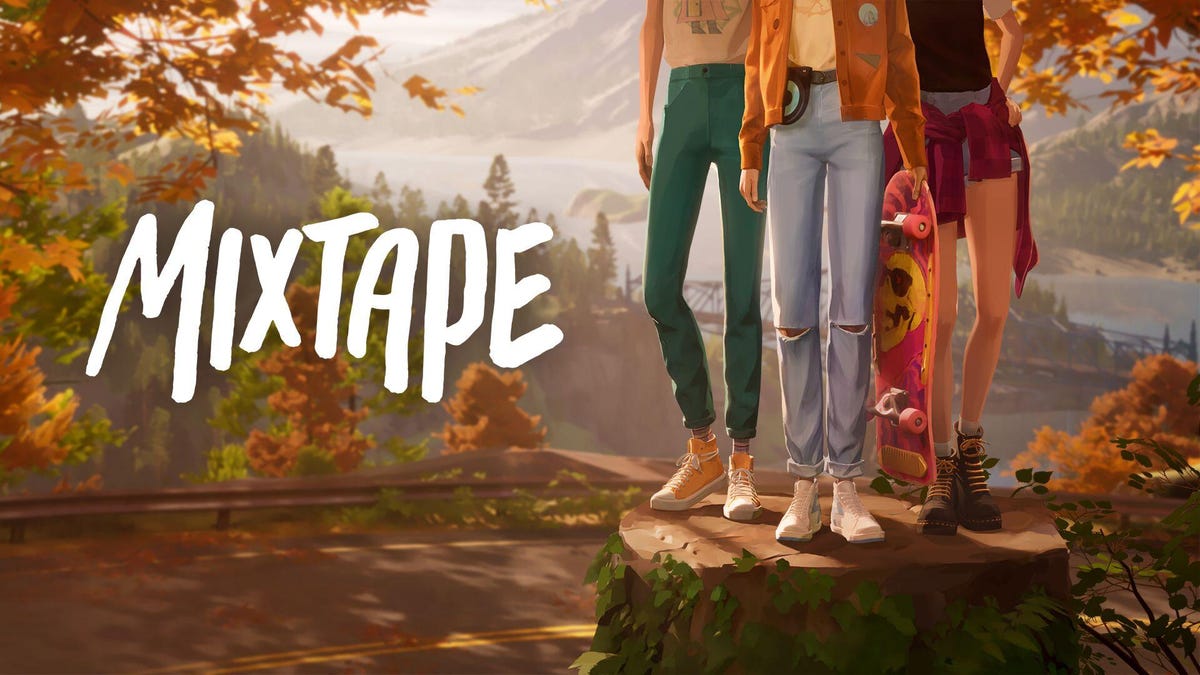
At a record store in northern Los Angeles, I walked past racks of albums, a DJ spinning records and a stack of Dunkaroos, a cookies and icing snack that was all the rage in ’90s America. It felt like stepping back into an earlier era, the same one backdropping the upcoming game Mixtape, a story about a group of self-mythologizing teens hanging out before life pulls them away from their suburban American town.
In an amusing twist of fate, the main brain behind the game is an Australian rocker who didn’t step foot in the US until his 30s. Johnny Galvatron (a stage name and lead singer of the band The Galvatrons), creative director at studio Beethoven & Dinosaur, dreamed up Mixtape based on a blend of American youth culture that was broadcast worldwide, along with his own upbringing loving music of the period and playing in bands.
In a recording room behind the record store, I chatted with Galvatron about why a man from the Antipodes would tackle American youth, nostalgia through the lens of music and analog audio tech, the earnest wrongness of being a teenager and why the US is like Middle-earth.
I also got to play a short slice of Mixtape ahead of the conversation, a demo I originally saw at Summer Game Fest last year (but with a couple extra scenes exclusive to this event). It opened up with the game’s older teen heroine, Stacy Rockford, skateboarding down a winding road with her friends, lazily pulling kickflips and calling out oncoming cars in the golden hour before twilight, a fitting start for a game about the last days before adulthood knocks.
From what I saw, there’s a bit of overlap with other nostalgia-laden narrative games about teens growing up, such as studio Don’t Nod’s Life is Strange series or last year’s Lost Records: Bloom and Rage. But Mixtape avoids the plotty drama of those games in favor of lionizing the humble wonder of teens killing time. And it does it in style, with kinetic editing and needle drops that immerse players in the MTV-drenched lives of kids whose rebellious days are numbered. It’s tonally different, reflecting Galvatron’s memories of being an earnest teen, liking music and tossing out strong opinions.
«There’s a lot of stories about teenagers where they’re portrayed as very shy and not confident. And that’s not really my experience of being a teenager,» Galvatron said. «I was very confident and wrong about things and about how I felt about music.»
Galvatron’s earnest teenagehood was in Australia, but setting the game there might have been too close to home. Plus, his favorite music and culture came from America. Despite not coming to the US until he was 32, he’s watched America every single day of his life, he said. Seeing it in person is like coming to a theme park, or a fantasy land: «To people who live in Western cultures, America is Middle-earth,» Galvatron said.
The game is split into chapters, each patterned after a carefully-chosen song. They all come together in the titular mixtape, the swan song of a cherished friend group, one last rock-out to tunes that speak to the moment. It was those songs that drove the creation of the emotional sequencing of Mixtape, Galvatron told me. Whereas most games start development by creating a «vertical slice» that represents the core loop of the game, Beethoven & Dinosaur made «a real shitty version of the whole game» and swapped around the songs to see what different stories the configurations told.
«We would play with that soundtrack until it seemed to have this cinematic flow to it, like a really lovely narrative that chained these songs together,» Galvatron said. «Once we had that right, we could put the story and the characters in.»
Picking the songs was a delicate process to find the right tone (and to ensure variety, as Galvatron joked he kept wanting more Devo songs, which the team vetoed and limited him to one). There’s a pivotal moment in the game where the main character Rockford is betrayed by her friend, and despite digging up the saddest songs they could think of, none worked. So they flipped the emotions to the other extreme, trying tunes evoking over-the-top happiness like Stuck In The Middle With You, and went with songs from the artist BJ Miller from the 1960s, «and that seemed to make it just all the more devastating,» Galvatron said.
I saw parts of 4-5 song chapters out of what Galvatron told me will be a total of 26 or 27. But each felt like a sublime snippet (in Pixar parlance, a core memory) that the player gets to control, from an embellished shopping cart escape from the cops to a flailing first kiss of awkward tongues to rocking out in the car on the way to a party. It sounds mundane, but these delightful moments hearken to a time in everyone’s lives when the people and the songs around you elevated the simple into the unforgettable.
«We don’t have skill trees, we don’t have (gameplay) loops. We have moments where mechanics, music, dialogue, narrative all meet and hit these crescendos,» Galvatron said, and emphasized the importance of their brevity. «Get in, deliver the mechanic, make it beautiful, make it a great experience. Don’t overstay your welcome.»
It’s undeniable that Mixtape reaches back into the past to evoke a feeling of place and time, specifically this moment in the American 90s where music was blasting from cassette tapes and CDs. There’s a warmth to this equipment, Galvatron noted, and to the music it produces. Moreover, the tactility lends itself very well to touching, spinning and clicking motions on game controllers, giving players a real feel for the music they’re playing on screen.
Yet when I asked how he felt the game fit amid our current era of nostalgia — which media like Stranger Things have built IP empires upon with period-appropriate references, fashion and songs — Galvatron asserts that the game has a different aim than prompting viewers to remember specific songs, CD players and Tamagotchis. «What I want people to remember is when you defined yourself by the singles you liked, by art, and I think that’s something naive and sweet,» he said.
If the rest of the game meets the bar set by the demo I saw, players will be pretty awestruck by the polished, electric delivery of moments from scene to scene. Mixtape feels intentionally designed, likely meticulously storyboarded, to land moments with camera angles and timing that make you feel along for the ride.
Beethoven & Dinosaur’s strengths are leaning into the grandness of cinematics and music, Galvatron said. «That’s how I remember being a teenager,» he said, «[it’s] something theatrical and fast, and everything meant the end of the world or the start of the world.»
Technologies
These MWC Phones and Gadgets Wowed Me, but Where Are They Now?
From AI hardware to wearable phones, these products promised a lot. So what happened to them?

Mobile World Congress sees the biggest and best tech companies, the world over, gather in Barcelona to show off their latest, greatest products. MWC 2026 runs March 2 to 5 and we expect to see several major phone launches, some wild concepts and a lot of tapas. But what about products we saw in prior years?
From Samsung’s flagship Galaxy S phones to incredible hardware from Xiaomi, we’ve seen some amazing devices in the years CNET has been attending the show. But we’ve also seen a lot of unusual products that have promised more than they’ve delivered.
From concept devices that are quickly forgotten to new gadgets that boast revolutionary functions, these are the MWC tech launches that arrived with a fanfare… but aren’t necessarily where you’d expect them to be today.
Humane AI pin
AI might still be the biggest buzzword in tech, thanks to every phone company cramming their devices with all kinds of bizarre AI functions. But at MWC 2024, one company wanted to take that further. The Humane AI pin was a wearable badge that you could talk to and ask questions about your schedule, the weather or things like sports results. It could read answers out and even project them onto your hand with a laser. Because everyone loves lasers.
Sounds fun, right? And the company’s rhetoric around how AI-based devices like this will replace phones sounded compelling. However, the product, well, sucked (just ask CNET’s Scott Stein, who spent extended time with it) and the company was eventually swallowed by HP, with the Pin itself ceasing to function in February last year. If you were one of the early adopters, do let us know what you’ve done with that $699(!) paperweight now.
Motorola Rizr
MWC is a great place to show off concepts that will excite technology nerds like us. Motorola has a good history of this at the show and the Rizr is one of my favorites. This phone didn’t just have a flexible display like we’ve seen on many of today’s foldable phones, its display could actually mechanically unroll at the push of a button, extending the top of the screen to give a more immersive display for watching videos or playing games.
It was amazing to see in person and it was certainly a different idea on how to use flexible displays. But that’s all it was; an idea. Motorola hasn’t deployed the Rizr’s mechanical unfurling into any of its products, with its upcoming Razr Fold launch being just a standard book-style foldable. The reason is obvious: The technology is likely expensive and probably fragile too. Three years on and Motorola hasn’t said a thing about this cool concept, but I’ll still keep my fingers crossed for this year.
Xiaomi SU7 EV
Xiaomi might be better known for its superb camera phones, but the Chinese firm has fingers in many pies, including scooters, vacuums, air fryers and, er, water pistols. It was no surprise then that during MWC 2024, the company showed off its first EV, the Xiaomi SU7. With sleek, sporty looks and a promised range of over 470 miles, I was excited.
I was excited again when the company showed off an even more performance-focused model at last year’s show, which had already delivered some blistering track times on the infamous Nürburgring. But I’ve yet to get behind the wheel. While Xiaomi is already producing and selling cars in its native China, the company has no plans to launch in the UK or wider Europe until at least 2027 and they almost certainly won’t sell in the US at all.
As a result, I feel like I’ve been teased somewhat with the promise of this slick, powerful EV that would have sat perfectly on my driveway. In reality, I still have a big wait ahead of me, if the SU7 European launch happens at all. Sales of the SU7 in China have surpassed those of the Tesla Model 3, according to a report by Car News China. Meanwhile, the same story shows that the SU7 Ultra’s sales have declined dramatically due to a number of controversies and lawsuits around the car and Xiaomi’s rollout.
Samsung Galaxy Ring
Samsung’s Galaxy Ring made for an interesting MWC in 2024. Here was a new type of wearable that promised advanced health and fitness tracking, while blending into your daily life by sitting unobtrusively on your finger. And that’s what it does, with CNET giving it a healthy 8.5 out of 10 in our full review.
But that was in 2024, and a full two years later, I’m left wondering what’s happening with the wonderful world of smart jewelry. Samsung has made no official comment around a follow-up, through rumors suggest we may see one in late 2026 or 2027. Smart ring manufacturer Oura, meanwhile, has filed a public lawsuit against Samsung and other smart ring companies claiming patent infringement. This is likely one of the reasons we’ll have to wait for a Galaxy Ring 2. While other smart rings do exist — like the Oura Ring 4 — it’s not a category that flourished after Samsung launched its ring.
There’s no Google Pixel Ring, no Apple iRing and not even an LED-infused Nothing Ring (1). Most other smart rings are made by smaller companies, such as Pebble’s recently announced $75 recyclable ring. Smart rings may have a place on our hands for a while yet, but Samsung’s lengthy delay in launching a follow-up might suggest that it’s not exactly a priority product.
Motorola wrist phone
I said that the aforementioned Moto Rizr was «one of» my favorite MWC concepts.That’s because the company’s flexible wrist phone from 2024 absolutely takes my top spot. This candybar-style Android phone had a fully flexible body that let you to wrap the whole thing around your wrist and wear it like something resembling Leela from Futurama’s wrist-mounted doodad.
I found it extremely intriguing. Here was a phone that doesn’t bulge out your skinny jeans when it’s in your pocket, but that’s also just a glance away like a smartwatch. And compared to the precision engineering required for the Rizr, the wrist phone’s technology seemed relatively achievable. After all, we already have flexible displays and this didn’t even require any specialized tiny motors — you just whack it onto your wrist like a ’90s slap bracelet.
But, like the Rizr, the wrist-mounted phone remained just a flight of fancy I experienced oh so briefly for a few days in Spain. And like any holiday romance, perhaps it’s best for me to simply remember it for what it was and not spend my days pining for what could have been.
With MWC 2026 just a few days away I’m excited to see new and wild products show their face, and I’m curious to see which of them will have staying power.
Technologies
What to Expect From Samsung Galaxy Unpacked | Tech Today
-

 Technologies3 года ago
Technologies3 года agoTech Companies Need to Be Held Accountable for Security, Experts Say
-

 Technologies3 года ago
Technologies3 года agoBest Handheld Game Console in 2023
-

 Technologies3 года ago
Technologies3 года agoTighten Up Your VR Game With the Best Head Straps for Quest 2
-

 Technologies4 года ago
Technologies4 года agoBlack Friday 2021: The best deals on TVs, headphones, kitchenware, and more
-

 Technologies5 лет ago
Technologies5 лет agoGoogle to require vaccinations as Silicon Valley rethinks return-to-office policies
-

 Technologies5 лет ago
Technologies5 лет agoVerum, Wickr and Threema: next generation secured messengers
-

 Technologies4 года ago
Technologies4 года agoOlivia Harlan Dekker for Verum Messenger
-

 Technologies4 года ago
Technologies4 года agoiPhone 13 event: How to watch Apple’s big announcement tomorrow
