Technologies
This Hyperspeed Space Sail Could Take Us to Next-Door Star Systems
For years, physicists have been trying to perfect a way to catapult space probes at a fifth the speed of light. One team is flagging an important section of the blueprint.
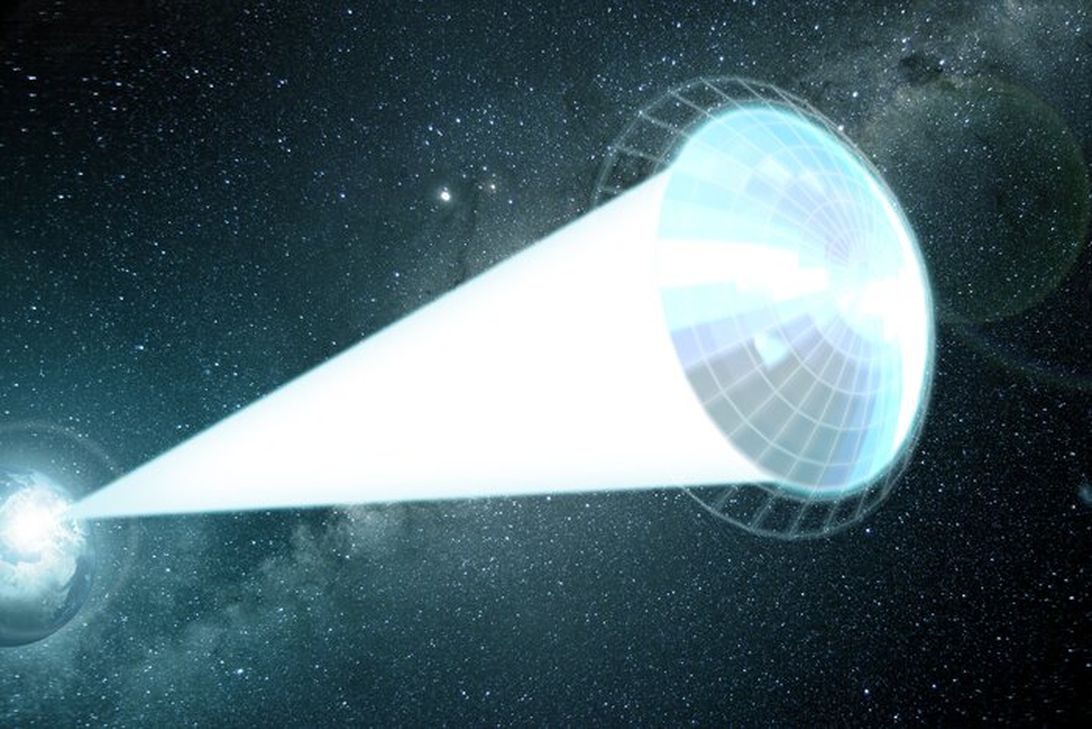
Only about 4 light-years away from our solar system lies Alpha Centauri, another bustling space neighborhood. It’s anchored by three stars with the same job as our sun, holds planets analogous to our eight famous orbs and may even have an Earth twin hanging out in the habitable zone. Almost like an alternate reality, the star system is a tantalizing region for space explorers.
There’s just one, glaring issue. With our present technology, spacecraft sent toward Alpha Centauri wouldn’t arrive until somewhere around the year 82022. That’s why, in 2016, late astrophysicist Stephen Hawking and investor Yuri Milner launched Breakthrough Starshot — an initiative to send microchip-size space probes over to Alpha Centauri at 20% the speed of light, reducing the whopping travel time to a mere 20 years.
Their blueprint centers on a lightsail that harnesses the power of photons, aka light particles, beamed from an Earth-based laser, instead of wind like a traditional sail. Though it’d fit right in with the sci-fi tech of Star Trek, the idea gained so much popularity that researchers everywhere began studying how to bring the contraption to fruition, hoping to produce a hyperdrive that blasts around the universe at dizzying rates.
Hailing from the University of Pennsylvania, one such team is tackling a big piece of the puzzle. In a pair of papers published this month in the journal Nano Letters, researchers suggested a way to ensure these innovative spacecraft don’t tear from intense laser pulses during the two-decade-long interstellar voyage. Basically, the researchers propose the sail must «billow» in space’s void like standard boat sails wave amid Earth’s winds.
«Some of the lightsail figures from early on were billowing, some were not, but it was not well studied,» said study author Igor Bargatin, an associate professor in the department of mechanical engineering and applied mechanics at the University of Pennsylvania. «What we did is show you definitely need billowing.
«We realized people haven’t really looked at the mechanics of the problem, and in particular, the possibility of tears,» Bargatinadded. «We want to make sure if and when this idea is realized, people pay attention to things that could happen during acceleration.
«We don’t want these sails to fail.»
Interstellar ship parameters
Picture a boat venturing out to sea with a sail attached. The sail will heave with every gust of wind and propel the vessel forward. That propulsion happens because wind hitting the sail bounces off, creating pressure.
Lightsails aren’t all that different.
«When the photons hit our lightsail, they get reflected and they also create pressure,» Bargatin said. «The exact mechanism is a little different because we’re talking light versus actual molecules of air. But they create pressure nonetheless in both cases.» In fact, these devices have already been proven effective to a degree.
In 2010, the Japanese Aerospace Exploration Agency launched a lightsail mission dubbed Ikaros and deemed it a success. In 2019, the experimental LightSail 2 followed suit. Funded by a Kickstarter campaign started by Bill Nye and Neil DeGrasse Tyson, it moved a small satellite in space using pure photon power.
But both Ikaros and LightSail 2 used light emanating from the sun, in contrast to Breakthrough Starshot’s vision of laser beams.
Though sunlight reduces the risk of tears, it’s too weak for Starshot’s endeavor. Plus, Bargatin says, Starshot light pulses must happen within a relatively short period of time because once the lightsail gets too far from Earth, scientists lose their ability to effectively accelerate it.
In short, to reach a fifth the speed of light — so it can access Alpha Centauri in the desired 20 years — within a strict window, lightsails would need extremely strong light pulses possible only with lasers.
«Designed pressures on our lightsails are not huge,» Bargatin said. «They’re about the same as having a penny on your hand.» In scientific terms, the pressure adds up to about 10 pascals, Bargatin says, but consider how we go about our lives without worrying about light pressure at all.
Ten Pascals of light force requires a significant amount of laser power, so unlike Ikaros’ dance with wispy sunrays, lightsails imparted with ultra harsh laser pulses can be badly damaged.
How to build a durable lightsail
According to the researchers, strong laser pulses could create pressure forceful enough to curve and tear the sheet like a taut boat sail may rip if hit by a giant gust of wind.
They believe lightsails must have the ability to «billow» and form a curved shape kind of like a parachute. Both the sail’s length and the radius of curvature, Bargatin explains, should be about 3 meters. In their new papers, the authors outline geometric measurements that ensure optimal billowing.
Even a lightsail protected from tears, however, will encounter other obstacles. To overcome such issues, the major parameter to consider is sail material. The sheets must be strong for durability, lightweight to minimize laser strength, reflect light efficiently for ideal propulsion and shed heat generated from laser pulses.
If the latter bit isn’t taken care of, Bargatin says, the sail could literally melt in space.
«You can come up with a combination of materials. The thicknesses of those materials and curved geometries would allow the sail to survive the pressures that we’re currently designing for,» Bargatin said, noting his team is mostly looking at a material called molybdenum disulfide.
In the grand scheme of things, though, building the massive laser array that’ll beam lightsails forward will be a big hurdle. Researchers working in space-based communication, Bargatin says, are also still figuring out how to retrieve information from the microchip probe attached to the lightsail.
If Breakthrough Starshot’s mechanism works one day, it’ll be a true testament to humanity’s brilliance in the field of science. In an announcement of the organization’s immense goals six years ago, Hawking stated:
«I believe what makes us unique is transcending our limits. Gravity pins us to the ground, but I just flew to America. I lost my voice, but I can still speak, thanks to my voice synthesizer. How do we transcend these limits?
«With our minds and our machines.»
Technologies
Google’s New AI Features Are Trying to Make Data Entry a Thing of the Past
More Gemini AI features will come to Google Docs, Sheets and Slides.

The latest batch of Google updates to its workspace tools highlights AI’s promise to automate mundanity in the workplace. Google Docs, Slides, Sheets and Drive all have new AI-powered features, the company announced Tuesday. The one thing all these updates have in common? Gemini is using your files, emails and chats to give you relevant information, not random answers gleaned from the web.
These updates come as AI is playing a bigger role in our work lives, for better or worse. Agentic tools like Claude Cowork and coding assistants like Anthropic’s Claude Code and OpenAI’s Codex are more capable than chatbots and able to handle tasks announced independently. AI tools are also becoming more customized, with Google’s personalized intelligence rolling out across its platforms to help refine AI outputs to things that are relevant and useful for you. Google continues that trend with this new batch of Workspace updates.
New Gemini AI features in Google Workspace apps will cite their sources after each query. For example, if you ask Gemini in Google Docs to fill out an itinerary template, it will pull the information from your email, chats and files. The «sources» tab in the Gemini side panel will show you where it found the information it used, like your flight confirmation email and chats discussing dinner plans. Seeing where Gemini pulled its answers from is also how you’ll double-check Gemini’s work.
The most impressive new features are in Sheets, where AI can fill in the holes in your spreadsheets. You can describe what you want the AI to do with a simple prompt and avoid writing an exact formula. You can click on an empty cell, select the pop-up that says «Drag to fill with Gemini,» then highlight the cells you want Gemini to fill in. That deploys an AI agent to search the web to fill each cell with the necessary information.
For example, if you have a spreadsheet of the contact info for local companies, you can have Gemini search the web to fill in a the location, CEO and other publicly available information of each company. The tool aims to dramatically reduce the time needed for manual data entry. Gemini can also summarize, categorize and create charts with prompts alone.
You can also chat with Gemini in Sheets and have it scour your raw data to make custom reports and charts. No need for pivot tables if they confound you as much as they baffle me. One of the biggest uses of AI at work is helping create presentations.
In Google Slides, you can now tell Gemini in natural language what you want to appear on a slide, and it will create it, matching the style of your existing slides. You can also ask Gemini to edit your slides if you don’t want to waste time painstakingly moving design elements around the slide. The AI should fill the slides with relevant information based on your instructions and the work files it has access to, so you shouldn’t need to replace a bunch of filler text.
If you use Docs, Sheets and Slides through the Workspace account of your company, then you won’t be able to turn off AI features individually. The managing company is in control of AI access for users. Personal users can tweak their settings to limit Gemini. The new features are rolling out in beta now, in English only, to Google AI Ultra and Pro subscribers in the US, as well as some Google Workspace customers who are part of the Gemini Alpha testing program.
For more, check out the new cowork feature in Copilot and how to use Perplexity AI for deep research.

Tariffs implemented by President Donald Trump were struck down by the Supreme Court last month. Companies that were subjected to those fees, such as FedEx and Dollar General, have since sued the federal government, and Nintendo wants a piece of the action.
Nintendo filed a lawsuit against the federal government in the US Court of International Trade on Friday, as first spotted by Aftermath. The complaint seeks refunds of tariffs Nintendo paid, plus interest, and asks the court to declare the tariffs unlawful and stop the government from collecting them going forward.
«Since February 1, 2025, President Trump has executed the unlawful Executive Orders, imposing tariffs on imports from a vast swath of countries,» Nintendo said in the complaint.
When reached for comment, Nintendo of America confirmed the lawsuit.
«We can confirm that we filed a request. We have nothing else to share on this topic,» Nintendo of America said in an emailed statement on Friday, March 6.
It’s unclear how much Nintendo paid in tariffs, and it did not state an amount in the lawsuit. While the Switch 2 was priced at $450 when it launched last year, and has stayed at that amount, Nintendo did increase the price of the original Switch and accessories for both consoles. Microsoft and Sony also increased the prices of their hardware and accessories last year due to tariffs.
The White House didn’t immediately respond to a request for comment.
On Feb. 20, the Supreme Court ruled by a vote of 6 to 3 that the sweeping tariffs Trump instituted last year exceeded his executive powers. Following the ruling, on the same day, Trump announced a new set of tariffs of 10% on imported goods that would last for 150 days, starting Feb. 24.
The decision on what to do with the collected tariffs — a reported $166 billion — has been left to the US Court of International Trade. Judge Richard Eaton told the US Customs and Border Protection on Wednesday, March 4, to refund the importers that were forced to pay tariffs, which is more than 330,000. On Friday, the CBP said it couldn’t easily issue tariff refunds because its system requires duties to be recalculated and refunds processed entry by entry. This process would involve tens of millions of transactions. The agency said it’s updating its systems and could start providing refunds by late April.
Technologies
Sony WF-1000XM6 vs. Samsung Galaxy Buds 4 Pro Earbuds: A Photo Finish
-

 Technologies3 года ago
Technologies3 года agoTech Companies Need to Be Held Accountable for Security, Experts Say
-

 Technologies3 года ago
Technologies3 года agoBest Handheld Game Console in 2023
-

 Technologies3 года ago
Technologies3 года agoTighten Up Your VR Game With the Best Head Straps for Quest 2
-

 Technologies4 года ago
Technologies4 года agoBlack Friday 2021: The best deals on TVs, headphones, kitchenware, and more
-

 Technologies5 лет ago
Technologies5 лет agoGoogle to require vaccinations as Silicon Valley rethinks return-to-office policies
-

 Technologies5 лет ago
Technologies5 лет agoVerum, Wickr and Threema: next generation secured messengers
-

 Technologies4 года ago
Technologies4 года agoOlivia Harlan Dekker for Verum Messenger
-

 Technologies4 года ago
Technologies4 года agoiPhone 13 event: How to watch Apple’s big announcement tomorrow
