Technologies
‘Phenomenal breakthrough’: Nuclear fusion test sparks high-energy hopes
A laser blast in California creates a miniature sun for a tiny fraction of a second and ignites a self-sustaining chain reaction.
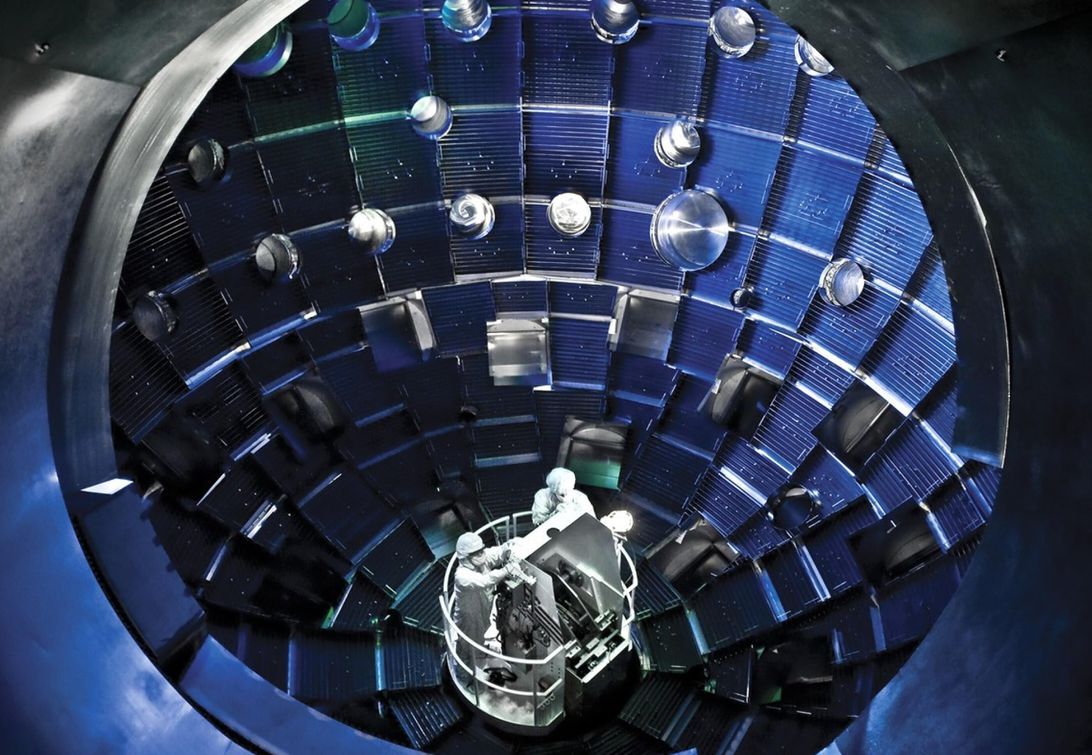
For an almost imperceptible fraction of a second on Aug. 8, massive lasers at a government facility in Northern California re-created the power of the sun in a tiny hot spot no wider than a human hair. The result is a significant step forward in the pursuit of nuclear fusion, a long-sought-after panacea for many energy and environmental challenges.
The experiment took place at the National Ignition Facility, which takes up the space of three football fields at the campus of the Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory on the eastern edge of the San Francisco Bay metroplex. Powerful lasers there were focused onto a target the size of a BB, resulting in a reaction that threw off over 10 quadrillion watts of power.
Remarkably, that’s about 6% of the total energy of all the sunshine striking Earth’s surface at any given moment, although the powerful burst only lasted for 100 trillionths of a second. Even in that minuscule timeframe, though, scientists observed a big breakthrough: The hotspot was able to ignite a self-sustaining chain reaction, fusing more hydrogen atoms together and continuing the process of energy generation, like an internal combustion engine burning through one molecule of fuel after another to keep going.
Achieving this ignition point is a key milestone in the roadmap to fusion power.
«This phenomenal breakthrough brings us tantalizingly closeto ademonstration of ‘net energy gain’ from fusion reactions — justwhenthe planet needs it,» said Arthur Turrell, physicist and author of The Star Builders: Nuclear Fusion and the Race to Power the Planet, in a statement.
Nuclear power plants today are fueled by thereaction from nuclear fission, the process of splitting atoms to createenergy. Fusion is just the opposite: merging hydrogen atomsinto helium the same way the sun does, releasing gobs of energy in theprocess. Fusion is a sort of holy grail, because theoretically it wouldprovide a limitless source of clean energy with fewer safety and wasteconcerns compared to fission reactors.
For decades now, dozens offacilities have been experimenting with different methods. The challenge isn’tjust to achieve fusion, but to do so in a way that doesn’t require moreenergy to create the reaction than is produced as a result.
This month’s experiment was still a net negative in terms of energy in versus energy out, but it puts the science on the threshold of breaking even.
Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory reports that while a final analysis still needs to be peer reviewed, the initial data showed that the results yielded eight times the energy output of experiments done earlier this year and 25 times that seen in 2018.
«For reference this [is] about 1000x more energy output than we were getting when I joined the project 10 years ago,» project physicist Jayson Luc Peterson added on Twitter.
Jeremy Chittenden, co-director of the Center for Inertial Fusion Studies at Imperial College London, said in a statement that improvement in fusion energy output has accelerated over the past year, «suggesting we may soonreach moreenergy milestones, such as exceeding the energy input fromthe lasersused to kick-start the process.»
Interestingly, the National Ignition Facility is not primarily meant as a tool for fusion energy development, but rather for nuclear weapons research. Chittenden says the result should spur on other efforts focused on creating clean power.
«We have now proven it is possible to reach ignition, givinginspiration to other laboratories and start-ups around the world workingon fusion energy production to try to realize the same conditionsusinga simpler, more robust and above all cheaper method.»
Technologies
Sony WF-1000XM6 vs. Samsung Galaxy Buds 4 Pro Earbuds: A Photo Finish
Technologies
The Apple Watch Series 12 Could Bring Back a Throwback iPhone Feature
Everything we’ve heard so far about the rumored Apple Watch Series 12.

We’re hot off a busy March Apple launch with seven new products, including an iPhone 17E, updated MacBook Pros and a colorful MacBook Neo that’s about to rattle the Chromebook market. As we set our sights on the next big hardware launch, the Apple Watch Series 12 is already on the horizon.
While there haven’t been any concrete leaks yet, there’s plenty we can infer based on Apple’s past launches and typical release patterns. There are also a few lingering rumors that could finally land this year, including a possible nod to a long-removed but not forgotten iPhone feature.
Apple Watch Series 12 launch date
If there’s one thing Apple tends to keep consistent, it’s the timing of its fall hardware event, where it typically unveils its newest flagship iPhones and Apple Watch models.
Apple typically holds this event on the second Tuesday of September (usually the week after Labor Day). By that logic, Sept. 15 seems like the most likely candidate for Apple’s 2026 fall event. Because it lands a bit later in the month than in previous years, there’s also a slim chance Apple moves it up to Sept. 9 (Labor Day week), as it has before.
As in previous years, preorders would likely open on the Friday after the event, with availability following a week or so later (assuming no production delays).
Pricing and availability
Expect pricing for the new watches to stay roughly in line with the current Series 11 lineup, which starts at about $400 (42mm Wi-Fi model). Though price hikes aren’t completely off the table, with lingering tariff increases and the potential for supply chain issues.
How many Apple Watch models will we get?
A Series 12 is all but guaranteed — we’ve had a new Apple Watch model arrive every year since its launch. What’s less certain is whether Apple will refresh the entire lineup again this year. The Apple Watch SE and Ultra models don’t follow the same annual update cycle, and because both the SE 3 and Ultra 3 were refreshed in 2025, it’s less likely that Apple will update both again this year.
If Apple does add another model alongside the Series 12, the Ultra would be the more plausible candidate. Apple isn’t one to hold out on new features for its high-end models when warranted. Or if it follows the pattern set with the Ultra 2, the company might just roll out a new color model for the Ultra 3.
Design upgrades on the Apple Watch Series 12
There are rumblings of a redesign in the works, but given how sparse the chatter has been, my guess is we won’t see a major design overhaul this year. Expect the same silhouette, similar colors and materials. What could change: screen technology. A more energy-efficient display — potentially an improved LTPO panel with better brightness, as seen on the Series 10 — could help claw back some battery life without adding bulk.
Battery life and processor
The Series 11 and Ultra 3 got a significant battery bump over their predecessors: at least 6 hours more by Apple’s numbers and roughly an extra half day (or more) in my real-world testing. And the Ultra 3 also got charging speed worthy of its name, like its newer siblings. But there’s still a lot of room for improvement on both battery life and charging speed.
With no major clues hinting at bigger batteries yet, I’d bet we see more incremental gains (if any) on the Series 12. Improvements could come from better screen technology, software optimizations, and more efficient processors.
In theory, the processor name usually matches the watch number, suggesting an S12 chip this year. But since the Series 11 and Ultra 3 are still running on the previous year’s S10 chip, the next upgrade could technically be an S11, making this year’s naming a bit awkward.
New health features on the horizon
Apple has already dipped its toes into blood pressure monitoring with hypertension notifications on the Apple Watch (Series 10, Series 11 and Ultra 3). The feature alerts owners when it detects signs of abnormally high blood pressure, but it stops short of providing an on-the-spot read. This could be on the table for the fall of 2026.
Other wearable health companies like Omron and Med-Watch have proven that wrist-based blood pressure measurement is possible, though it’s not as reliable as a traditional cuff and may require new (bulkier) hardware to bring to the Apple Watch.
According to Bloomberg’s Mark Gurman, Apple has been testing the feature internally but has encountered accuracy issues. And even if Apple pulls it off for this year, it might measure only baseline trends similar to Samsung’s blood pressure feature on the Galaxy Watch 7 and Ultra (not supported in the US).
Glucose monitoring is another long-running rumor that’s on the table, but according to Gurman, it’s even further from a finished product than blood pressure and realistically wouldn’t appear before 2027.
Biometric authentication: Touch ID or Face ID?
Rumors of a camera on the Apple Watch have been around for a few years — not for selfies, but potentially for Face ID or AI-based image recognition.
Apple Intelligence on the iPhone introduced a visual search tool that uses the camera to identify objects and places in real time, and it might be a matter of time before this feature eventually makes its way to the wrist. Meanwhile, wearable-focused processors like Qualcomm’s Snapdragon chips already support cameras and even livestreaming. Apple is known to use its proprietary chips, so it’s unlikely this would impact Apple’s timeline, but it shows the technology is there, and we may see it down the line on the Apple Watch. Just not this year, according to Bloomberg.
A more feasible near-term option could be Touch ID. Macworld recently spotted lines of internal code suggesting Apple has been experimenting with biometric authentication for the 2026 Apple Watch lineup. According to the report, the code references «AppleMesa,» which is Apple’s internal code name for a watch-based Touch ID. It’s still unclear whether the sensor would be integrated under the display, like we see on Android phones, or built into the side button or the Digital Crown.
Watch OS 27 wishlist
Now that Apple has standardized its operating system names to match the year ahead, you don’t need to be a rocket scientist to figure out that the next big update for the Apple Watch will be WatchOS 27.
With a major redesign already in the books (5 New Apple Watch Features Coming With WatchOS 26), we’re not expecting a dramatic visual change this time around, but there’s plenty on the wishlist, including better battery management tools and more customizable gesture controls. Apple could also expand Workout Buddy from metric-driven encouragement into more concrete training territory. This could bring it closer to what Samsung is trying with its AI-powered Running Coach.
Lastly, I’d welcome a more robust symptom tracker tied into the Vitals app similar to Oura Ring’s Symptom Radar that can flag early signs of illness.
Other Health app updates
The next version of WatchOS 27 could also bring changes to the Health app. According to a report from Mark Gurman at Bloomberg, Apple has been working on a top-secret initiative code-named Project Mulberry, aimed at revamping the Health app with an AI-powered health concierge that could unify your health, fitness, and medical data in one place.
However, the project has recently run into some obstacles. Bloomberg’s latest report suggests Apple has put the effort on hold (at least for this year). That still leaves room for improvement on the Health app front with a potential redesign to the main dashboard that would make spotting trends easier.
Technologies
Today’s NYT Connections: Sports Edition Hints and Answers for March 10, #533
Here are hints and the answers for the NYT Connections: Sports Edition puzzle for March 10, No. 533.

Looking for the most recent regular Connections answers? Click here for today’s Connections hints, as well as our daily answers and hints for The New York Times Mini Crossword, Wordle and Strands puzzles.
Today’s Connections: Sports Edition features a lot of team names, but that doesn’t mean it’s an easy one to solve. If you’re struggling with today’s puzzle but still want to solve it, read on for hints and the answers.
Connections: Sports Edition is published by The Athletic, the subscription-based sports journalism site owned by The Times. It doesn’t appear in the NYT Games app, but it does in The Athletic’s own app. Or you can play it for free online.
Read more: NYT Connections: Sports Edition Puzzle Comes Out of Beta
Hints for today’s Connections: Sports Edition groups
Here are four hints for the groupings in today’s Connections: Sports Edition puzzle, ranked from the easiest yellow group to the tough (and sometimes bizarre) purple group.
Yellow group hint: Play ball!
Green group hint: Not front.
Blue group hint: Certain NFL player.
Purple group hint: They play at Smoothie King Center.
Answers for today’s Connections: Sports Edition groups
Yellow group: An AL Central player.
Green group: Words appearing before «back,» in football.
Blue group: Associated with Derrick Henry.
Purple group: New Orleans Pelicans.
Read more: Wordle Cheat Sheet: Here Are the Most Popular Letters Used in English Words
What are today’s Connections: Sports Edition answers?
The yellow words in today’s Connections
The theme is an AL Central player. The four answers are Guardian, Royal, Tiger and Twin.
The green words in today’s Connections
The theme is words appearing before «back,» in football. The four answers are corner, defensive, full and running.
The blue words in today’s Connections
The theme is associated with Derrick Henry. The four answers are Heisman, King, Ravens and Titans.
The purple words in today’s Connections
The theme is New Orleans Pelicans. The four answers are Bey, Fears, Murphy and Queen.
-

 Technologies3 года ago
Technologies3 года agoTech Companies Need to Be Held Accountable for Security, Experts Say
-

 Technologies3 года ago
Technologies3 года agoBest Handheld Game Console in 2023
-

 Technologies3 года ago
Technologies3 года agoTighten Up Your VR Game With the Best Head Straps for Quest 2
-

 Technologies4 года ago
Technologies4 года agoBlack Friday 2021: The best deals on TVs, headphones, kitchenware, and more
-

 Technologies5 лет ago
Technologies5 лет agoGoogle to require vaccinations as Silicon Valley rethinks return-to-office policies
-

 Technologies5 лет ago
Technologies5 лет agoVerum, Wickr and Threema: next generation secured messengers
-

 Technologies4 года ago
Technologies4 года agoOlivia Harlan Dekker for Verum Messenger
-

 Technologies4 года ago
Technologies4 года agoiPhone 13 event: How to watch Apple’s big announcement tomorrow
