Technologies
Wild Weather Ahead: Summer 2024 Could Be a Scorcher After Hottest Year on Record
The climate crisis is causing more severe heatwaves and related events. Here’s what to know about dealing with extreme weather in 2024.
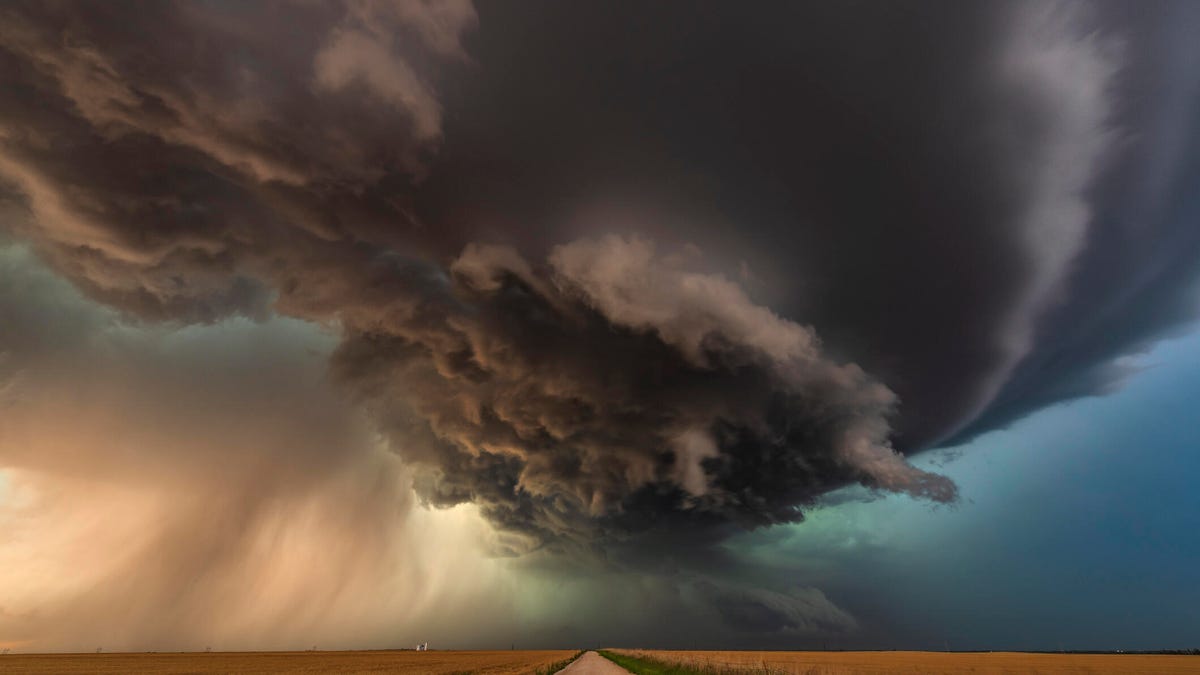

We just lived through the hottest year since recordkeeping began more than a century ago, but before too long, 2023 might not stand out as the pinnacle of extreme heat.
That’s because it’s unlikely to be the only hottest year that we experience. Our climate is changing, growing warmer due to the emissions from burning fossil fuels, and our weather is changing with it. It’s possible that this year may turn out to be hotter still.
In March, scientists from the EU’s Copernicus Climate Change Service said February 2024 was the hottest February according to records that stretch back to 1940. The news came on the heels of their report in early January that, as expected, 2023 was indeed the hottest year on record. Temperatures closed in on the critical 1.5-degree Celsius rise above preindustrial levels, after which we will see irreversible damage to the planet. These aren’t freak outliers: The extreme heat we’re experiencing is something we’ll need to be prepared to deal with on a much more regular basis, along with storms, floods and drought.
Later in March, the US National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration issued its spring outlook, predicting that most of the continental US and Alaska will see above-average temperatures from April through June. The risk of flooding, it said, will ease during the three-month period because of «historically low winter snow cover» in large parts of the country.
In April, a forecast from the Weather Company also predicted an «abnormally hot» summer in parts of the US. NOAA published a map this month showing where it expects the heat to be most extreme compared to normal. It highlighted a band stretching from the north west down through the south west and into Texas. The combination of heat and little rain could increase the risk of drought and wildfires in some regions.
A key trend highlighted by the US government’s Fifth National Climate Assessment, published in November, was that climate change is provoking extreme weather events across the country that are both more frequent and more severe. It pointed to an increase in heatwaves and wildfires in the West over the past few decades, the increased drought risk in the Southwest over the past century and more extreme rainfall east of the Rockies. Hurricanes have also been intensifying, as those who have found themselves in the path of a storm know all too well.
You’ll need to be prepared. Extreme weather is going to have a widespread impact on industry, society and individuals. Last year in the US there were 25 extreme weather events with losses amounting to over $1 billion that resulted in the deaths of 464 people. People lost their homes, saw personal property damaged or suffered mental and physical health issues.
Three months into 2024, we’re staring down the barrel of another potentially record-setting hot year. If there’s a silver lining, it’s that the US is now better prepared than ever, and we know what steps you can take to better deal with these unwelcome events. When it comes to weather, forewarned is forearmed.
The US has been taking active steps. The Biden administration has provided funding to build resilient communities, and a new (as of September 2023) National Climate Resilience Framework, which should provide the US with a whole range of protections. These include conserving water resources, modernizing and strengthening the electric grid against weather and disasters and building infrastructure to protect communities and ecosystems from sea level rise, tidal flooding, hurricanes and storm surges.
At home and in your community, you can take steps, too, including preparing your home for wildfires and flooding and recognizing signs of heat-related health issues. This way, when wild weather comes calling, its impact on our homes, health and livelihoods is minimized.
Forecast 2024
Last year’s heat was no anomaly. It’s part of a long-term trend: The last 10 years have been the 10 warmest on record, according to NASA, with most of the Earth’s warming taking place over the last 40 years. Most forecasters are anticipating yet another year of extreme heat ahead.
«If we look at the forecast for the next three months in the long range, it’s suggesting that the trend that we’re seeing in baseline warming could continue, and so 2024 could rival 2023 for being the hottest year on record, which is very scary,» says Chloe Brimicombe, a heatwave researcher at the University of Graz.
Some of the extreme weather we experienced in the latter half of last year and will continue to experience in the first half of this year is a result of El Niño, a cyclical climate event that sees unusually warm ocean waters that has a knock-on effect of warmer temperatures and increased rainfall across the southern part of the US. For instance, temperatures in Death Valley, California, peaked at 128 degrees Fahrenheit in July, while forecasters predicted warmer temperatures in northern parts of the US stretching into February and a colder, wetter winter for Southern states.

While meteorologists are able to make long-term predictions about El Niño, other climate-related predictions are trickier. «All things told, we’re going to see an increased prevalence of heat events across the globe, but we can’t tell right now exactly where that will be,» says Andy Hoell, a climate scientist at NOAA.
What we do know, he adds, is that the climate crisis can compound events such as extreme heat or extreme rainfall to make them more likely or more severe.
In the past, it wasn’t always easy to draw direct links between extreme weather events and climate change. But huge improvements in attribution science (the ability to specifically identify emissions as the cause for unusually dramatic weather) in recent years have changed the game. The World Weather Attribution program, based at Imperial College London, has now completed nine studies on droughts, heatwaves, wildfires and heavy rainfall in North America. «Every study found that climate change made the event more intense and more likely,» says Ben Clarke, a researcher at WWA.
The speed at which climate scientists are able to identify human-caused climate change as the culprit for extreme weather has also dramatically improved. Last year alone, Climate Central was able to attribute record-breaking spring heat in the western US, and ongoing extreme heat stretching through the summer in Texas and Florida, to climate change as it was happening. «It’s much more impactful as far as our understanding of what climate change really is if we can make that connection in real time,» says Andrew Pershing, vice president of science at Climate Central, a climate science analysis non-profit.
Thanks to attribution science, we can confidently point to a heatwave we’ve experienced and say whether climate change played a role in making it happen. But it also helps us to recognize that extreme weather events we’re experiencing are part of a pattern – one that can’t be broken without tackling the root causes of the climate crisis. «Until the world moves away from fossil fuels and reduces emissions to net zero,» says Clarke, «extreme weather events in North America will continue to become more intense, more dangerous and more deadly.»
Even if you live in a region that hasn’t yet directly been impacted by a climate-linked weather event, you’re not off the hook.
«As the climate continues to warm, most areas will be at an increased risk of some types of climate-linked extreme weather,» says Russell Vose, chief of the Monitoring and Assessment Branch at NOAA’ National Centers for Environmental Information and one of the NCA’s authors. «Perhaps the best example is extreme heat – it can occur anywhere.»
He points to the scorching heat dome that descended on the Pacific Northwest in June and July 2021, which was unprecedented in the historical record. The unpredictable nature of such extreme heat means no regions are marked as safe.
In fact, a region that’s been lucky enough to not yet experience an extreme heat event is more likely to experience one in the future and suffer more greatly due to lack of preparedness, according to a study published by scientists from Bristol University last April.
Scientists are more concerned about the ability of people in areas that don’t usually get intensely hot to cope when their turn comes. «What worries me would be something in the Upper Midwest or the Northeast that just hasn’t had a major heat event for a few years,» says Pershing. «I think we kind of lose a little bit of that muscle memory.»
Weather’s unequal impacts
The weather might not discriminate when it comes to who gets hit, but that doesn’t mean its impacts are experienced equally by all groups across American society.
«Certain groups are simply more vulnerable to extreme events due to geographic, socioeconomic or demographic factors,» says Vose. He points to the extreme rainfall brought by Hurricane Harvey in 2017, which led to a large number of homes being flooded in Harris County, Texas, with a disproportionate impact on low-income Hispanic neighborhoods.
When a heatwave hits, it will feel hotter in high-density urban environments that are more likely to be occupied by people of color or people living in poverty than in more spread-out neighborhoods or rural areas. Then some are homeless and can’t access health care. They have little ability to protect themselves, no matter how much warning they get about an incoming heatwave. This makes these groups much more vulnerable to the health risks of extreme heat.
Heat researchers are extremely concerned about people who live in housing not resistant to warm temperatures, says Brimicombe, who points out that those who rent are especially at risk. «If you’re a tenant, you have less ability to adapt your house to extreme heat than if you’re a homeowner,» she says. «And that also means young families, because babies are vulnerable to extreme heat.»
Not only are economically disadvantaged communities in the US more susceptible to feeling the worst impacts of extreme weather, but they have also done the least to contribute towards the climate crisis in the first place. A study published last August revealed that the wealthiest households in the US are historically responsible for 40% of the country’s climate emissions.
Meanwhile, these same households have more tools at their disposal to protect themselves from the impact of climate-related weather events. In 2019, The New York Times reported that wealthy California residents were banding together to hire private firefighters to protect them from the impacts of wildfires.
The Biden administration is well aware that marginalized and minority groups are hardest hit by climate change, including extreme weather. At the beginning of his term, the president set up the White House Environmental Justice Advisory Council, made up of leading experts from the US climate justice community.
Last September the group published its policy recommendations urging the government to ensure climate disasters do not further or exacerbate harm to vulnerable populations and communities.

«Disaster relief should never be the cause of deepening inequality in any neighborhood, region, or Tribal community,» the council wrote in its recommendations. «When disaster hits, the goal of government should be that the people hit the hardest should emerge stronger and more secure than before, not the opposite.»
It recommended a number of measures that would help protect people in case of extreme weather including the creation of a low-cost national flood insurance and the establishment of a «Just Relocation Fund» that would provide communities hit by climate impacts with a relocation process based on a dignity framework with respect for their human rights.
The White House has yet to respond to the recommendations, but if it does act on them this would hopefully prevent a repeat of the aftermath of Hurricane Katrina in 2005, in which Black communities were allocated less money to rebuild their housing, resulting in a lawsuit against the federal government.
Through the Bipartisan Infrastructure Law and other initiatives, the Biden administration is investing heavily in adaptation, mitigation and resilience measures designed to protect all Americans from the impacts of climate-linked extreme weather. As with all funding, people may have to wait some time to feel the full impact of that funding. In the meantime, there are a number of steps you can take to keep yourself safe in the months ahead.
How to weather the weather, whatever the weather
Summer’s not so far off, meaning sizzling days are on the horizon.
Intense heat poses some scary risks to our health, including heat cramps, heat exhaustion and heat stroke, which can be life-threatening. It’s important to familiarize yourself with the signs so that you’ll recognize them in yourself and others, and can therefore seek medical attention if necessary.
Remember that heat is more likely to adversely affect older people, children and babies, and those with preexisting health conditions. There may be cooling centers or other well-air-conditioned places in your community where you can take refuge – if you do, consider taking elderly or vulnerable neighbors with you. «Look out for friends and families,» said Brimicombe. «Don’t be complacent.»
The British writer and fellwalker Alfred Wainwright is widely credited as coining the phrase, «there’s no such thing as bad weather, only unsuitable clothing.» Wainwright, who died in 1991, didn’t live through the kind of consistently bad weather we’re experiencing in this era of extreme heat, but that doesn’t mean we have nothing to learn from him. In the midst of a heatwave, it’s best to wear loose-fitting clothes in light colors, rather than black, which absorbs the heat.
Make sure you stay hydrated and try to spend as little time as possible outside in the sun. Try to block sunlight from warming your house, and consider buying reflectors to place in your windows that can help keep the heat out. At nighttime, take note of when it might be cooler outside than in, and use this to your advantage by opening doors and windows to let the internal temperature of your house regulate. Fans can be effective, but at very high temperatures they’re likely to just start pushing the hot air around – in which case you should, sparingly and without putting too much pressure on the grid, resort to air conditioning, or moving to your local cooling center.
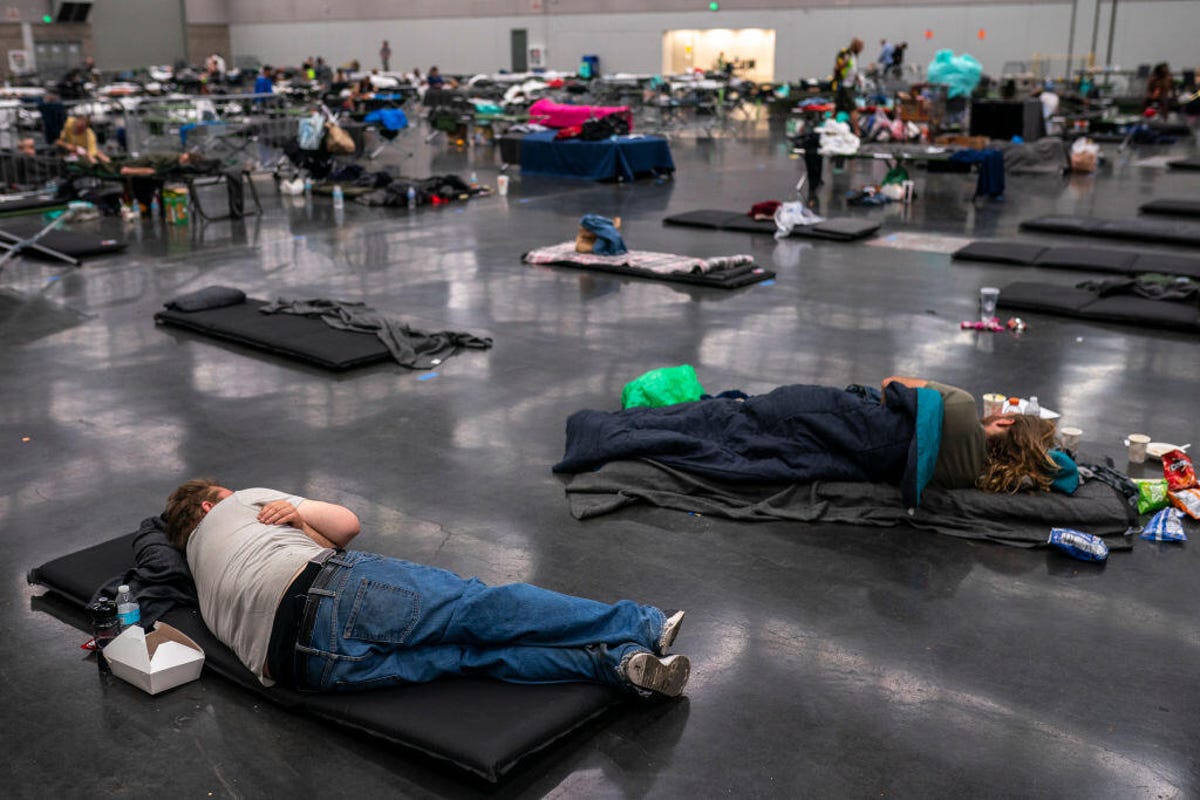

Remember that global warming is worldwide, so the same heat warnings apply even if you plan to travel to other parts of the world over the summer. The heat waves that hit the US in the summer of 2023 also impacted areas of Europe, including popular vacation spots in the Mediterranean. Countries including Greece, Spain and Italy were all affected by wildfires that resulted in the evacuation of locals and tourists alike from some areas and islands.
The surge in Europe-bound American tourists that occurred in 2023 is expected to continue this year, but if you’re planning to be among them it’s important not to travel without comprehensive insurance. Likewise, if you’re traveling in the peak months of July and August, be prepared to adjust your itinerary in case of extreme heat to ensure you’re not putting your health at risk. This may mean spending more time indoors than you’d planned for the sake of your health.
For other types of extreme weather that may hit your property such as wildfires, storms or floods, it may be useful to have an evacuation plan. You should prepare an emergency evacuation bag, also known as a go bag or a bug-out bag. Don’t forget to plan for your pets. The National Fire Protection Association has a handy guide on how to prepare your home for wildfires.
One of the easiest but most important things you can do is keep an eye on long- and short-term weather forecasts. The silver lining for people in the US, says Pershing, is that the country has great weather forecasting capabilities and the channels to communicate incoming events to people so you can prepare. «The gaps are really whether you take it seriously yourself,» he says.
So for anyone who does take it seriously, be sure to read our tips on how to prepare yourself and your home for wildfires, hurricanes, floods and storms.
Here are some additional resources:
- Natural Disaster Guide: How to Prep for Wildfires, Hurricanes, Storms and More
- Flood Insurance: What It Costs and What It Covers
- Pet Disaster Prep: Take These Steps to Keep Your Pets Safe
- Emergency Prep: 3 Tips to Recover Important Documents
- 16 Emergency Apps for Wildfires, Earthquakes and Other Disasters
- Wildfire Season Is Here: Prepare Your Emergency Evacuation Bag Now
- Climate Change Is Intensifying Severe Weather. Take These 4 Steps to Fortify Your Home
For even more details on natural disasters and how to prepare beforehand or respond after an event takes place, check out https://www.ready.gov/.
Correction, March 15: This story originally misstated the name of the National Fire Protection Association.
Technologies
How to Turn Off AI Features on Your Samsung Galaxy Smartphone
Too much AI on your Galaxy phone? Here’s how to disable it.
Samsung is known for throwing virtually every feature imaginable into its smartphones, whether or not you intend to use them. There are countless additional customizations and apps in Galaxy phones that make it a bit overwhelming to figure out what you actually need.
Every new generation of Galaxy phone seems to gain more and more AI features that you may not find useful. Luckily, you can remove nearly anything you don’t want on your Samsung phone.
Whether you just want to turn off some of the AI features on your Galaxy smartphone or you want to disable them completely, we’ll show you how to do that below.
Read more: The 8 Biggest Announcements from Samsung’s Galaxy Unpacked 2026 Event
How to turn off Galaxy AI services
Some of the features that smartphones can do using AI are undeniably cool. If you like some of them but don’t want AI everywhere, Samsung will allow you to pick and choose what to take advantage of.
To turn off AI for individual services:
- Go to Settings.
- Tap Galaxy AI.
- Select the service to disable.
- Tap the toggle to Off.
You’ll see a list of the services that form Galaxy AI. You can choose the apps for which you want to turn AI on or off from here.
If you’re more privacy-minded but still want to take advantage of Galaxy AI features, there’s a toggle at the bottom of this screen that will limit AI from sending anything to the cloud and keep data processing on your device only. Going for this option will disable some AI features altogether that require the internet to process, and the results may be less useful.
Goodbye, Bixby
Bixby, the Samsung digital assistant that you may not even realize is on your phone, is something that you’ll want to disable if you’re trying to tame the AI on your Galaxy device.
Luckily, Samsung has a way for you to replace Bixby with another voice assistant of your choosing. For all intents and purposes, Google Assistant will be your best bet, even if it will eventually be replaced by Google’s advanced AI assistant somewhere down the road.
It’s likely already installed on your phone, but you may need to redownload the Google app if you uninstalled it or never had it.
- Go to Settings.
- Tap Apps.
- Tap Default apps.
- Tap Digital assistant app.
- Tap Google.
That’s it. Now, when you trigger your voice assistant, you’ll be greeted by Google Assistant instead of the AI-powered Bixby.
Technologies
How to Watch the February 2026 Pokemon Presents Livestream
Celebrate Pokemon Day with the latest and greatest announcements from the world of pocket monsters.

We are just a day away from the annual celebration of all things Pokemon. The Pokemon Day event starts tomorrow morning and should be chock full of free goodies and exciting game reveals for creature-collecting fans across the world. Considering the juggernaut franchise is celebrating its 30th anniversary, it’s safe to assume there will be juicy information included in the next Pokemon Presents stream.
There’s plenty of excitement leading up to the main event. Pokemon TCG Pocket just released the Paldean Wonders card set expansion, and The Pokemon Company revealed that FireRed and LeafGreen are getting Switch ports with Pokemon Home compatibility. Now the stage is set for The Pokemon Company to reveal new mainline Pokemon games for the Switch and Switch 2.
Here’s when The Pokemon Company goes live with its first Pokemon Presents stream of the year, setting audience expectations for what we can expect to see from the world of pocket monsters in 2026.
What time is the Pokemon Presents stream on Pokemon Day?
The first Pokemon Presents livestream of the year takes place tomorrow, Friday, Feb. 27. The show begins bright and early for American audiences, so you’ll have to avoid sleeping in if you want to keep up with the latest announcements.
Here’s when Friday’s Pokemon Day livestream begins in your time zone:
ET: 9 a.m.
CT: 8 a.m.
MT: 7 a.m.
PT: 6 a.m.
How to watch the February Pokemon Presents livestream
The Pokemon Company is responsible for the Pokemon Presents livestreams, which means you can view the announcement through any of its social media channels.
While I recommend watching the stream on The Pokemon Company’s YouTube or Twitch channels, you can also keep up with the announcements on TikTok. Regular updates will also be posted to the company’s Instagram account throughout the event.
What will be announced on Pokemon Day 2026?
It’s safe to assume that the February Pokemon Presents livestream will feature some long-anticipated reveals, since 2026 is a big year for the Pokemon brand.
The livestream marks the 30th anniversary of Pokemon Red and Pokemon Green (the original Pokemon games for the Game Boy) releasing in Japan. We know the stream will be roughly 25 minutes long, making one of the longest Pokemon Presents showcases ever.
I suspect the livestream will serve as a victory lap celebrating Pokemon’s cultural impact before pivoting to the future and showing fans what’s coming next.
And what treats are in store for tomorrow’s event? I expect to see updates and freebies for Pokemon mobile games first, since these are some of the big moneymakers. If this Pokemon Day presentation mirrors the one from last year, we’ll be treated to some goodies in Pokemon Go, Pokemon Masters EX, Pokemon Cafe ReMix and Pokemon TCG Pocket. We might also see an announcement for a special Pokemon Scarlet and Violet raid event and Pokemon Legends: Z-A Mega stone distributions.
After celebrating the currently released games, it’s likely that the presentation will pivot to what’s coming next. We’ll almost certainly get a reminder that Nintendo Switch ports of Pokemon FireRed and Pokemon LeafGreen are available starting on Pokemon Day. I expect the biggest news will be a concrete release date for Pokemon’s big new competitive game, Pokemon Champions, which is slated to come out in time for the Pokemon World Championships 2026.
If we’re really lucky, we might even hear about the 10th generation of mainline Pokemon games. While Game Freak has unmoored itself from a consistent release schedule, we’re certainly due to see the rumored Pokemon Wind and Wave. While the infamous Teraleak hints toward what the development studio might show off next, it’s high time we get a glimpse of what the next big Pokemon games are really all about.
Technologies
Only Hours Remain to Grab the Skullcandy Push 720 Open Earbuds for 40% Off
That drops these earbuds to under $100, a hard-to-beat bargain.
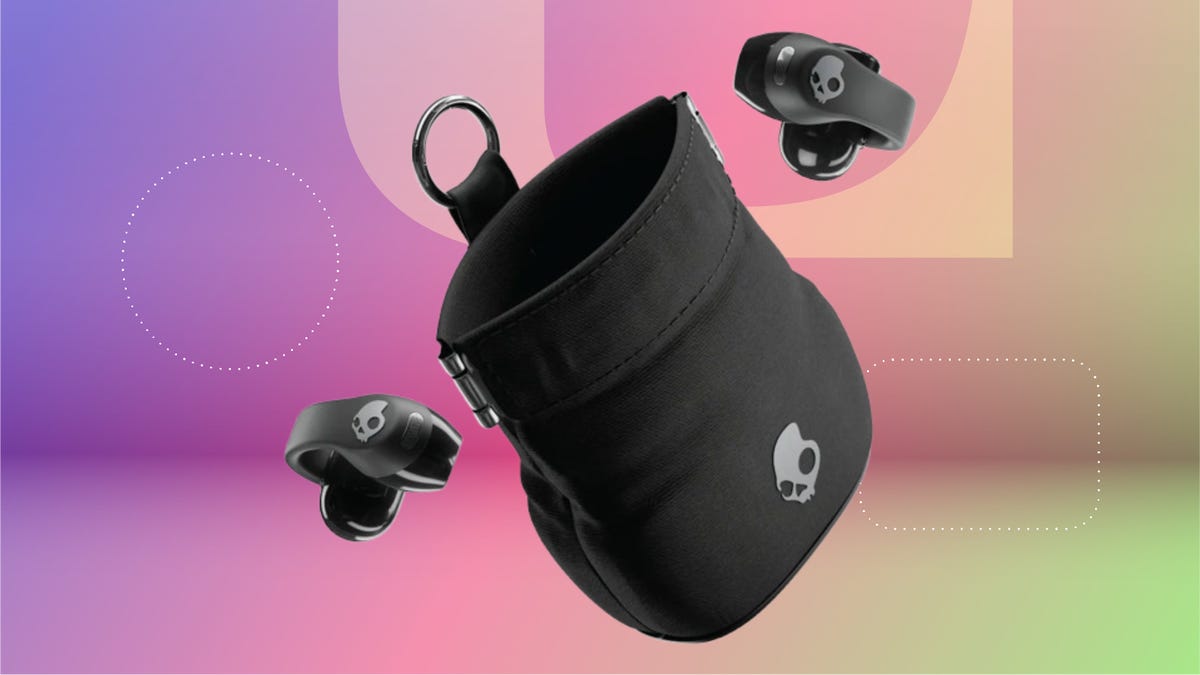

Until the end of the day, you can pick up a pair of the Skullcandy Push 720 open-earbuds for a nice $60 discount. That’s just $10 more than the previous record low, and this deal is available at both Best Buy and Amazon. Best Buy has labeled this deal as ending tonight and we except Amazon to follow suit. Grab yours now before the deal expires.
The Skullcandy Push 720 Open earbuds are designed to keep you connected to your audio and the world at the same time. The open-ear clip-on design delivers directional sound. But since they’re open, you’ll still be able to hear the outside world, making them great for commuting, workouts and more. The buds are lightweight and comfortable in your ear as they are built for all-day wear. They have an an IP67 rating for sweat- and water-resistance, so you can confidently take them on outdoor runs, gym sessions and through rainy weather.
The buds use precision directional speakers so your audio stays personal without disturbing people nearby. The over-the-ear fit is one-size-fits-all, and it’s made to stay secure through any kind of activity. They have a decent 30-hour battery life. But with rapid charging you’ll be back up and running in no time, and the carrying pouch has a built-in charger for on the go convenience.
HEADPHONE DEALS OF THE WEEK
-
$248 (save $152)
-
$170 (save $181)
-
$398 (save $62)
-
$200 (save $250)
Why this deal matters
These open-ear earbuds are great for anyone that’s active. Whether you’re running in the gym or playing sports, these headphones will comfortably clip onto your ears. Previously, we saw these buds come down to $80. Considering this is only $10 more, it’s not worth waiting to see if the price will drop back to $80. Best Buy says there’s only hours left for this deal. We think the Best Buy and Amazon deals will expire together, so act fast.
-

 Technologies3 года ago
Technologies3 года agoTech Companies Need to Be Held Accountable for Security, Experts Say
-

 Technologies3 года ago
Technologies3 года agoBest Handheld Game Console in 2023
-

 Technologies3 года ago
Technologies3 года agoTighten Up Your VR Game With the Best Head Straps for Quest 2
-

 Technologies4 года ago
Technologies4 года agoBlack Friday 2021: The best deals on TVs, headphones, kitchenware, and more
-

 Technologies5 лет ago
Technologies5 лет agoGoogle to require vaccinations as Silicon Valley rethinks return-to-office policies
-

 Technologies5 лет ago
Technologies5 лет agoVerum, Wickr and Threema: next generation secured messengers
-

 Technologies4 года ago
Technologies4 года agoOlivia Harlan Dekker for Verum Messenger
-

 Technologies4 года ago
Technologies4 года agoiPhone 13 event: How to watch Apple’s big announcement tomorrow
