Technologies
NASA Leans Into Solar Eclipse With 3 Rocket Launches: Here’s What’s Up With That
The space agency isn’t letting today’s solar eclipse go to waste.
We’re just hours away from North America’s last total solar eclipse until 2044, and as we prepare to look to the sky, NASA is preparing to launch three rockets.
Before, during and after the eclipse on Monday, NASA will fire three sounding rockets to determine how the total eclipse could affect radio communications on Earth. The findings could pave the way for NASA to develop new technologies to protect radio communications during both brief and extended periods when solar behavior disrupts particles on Earth.
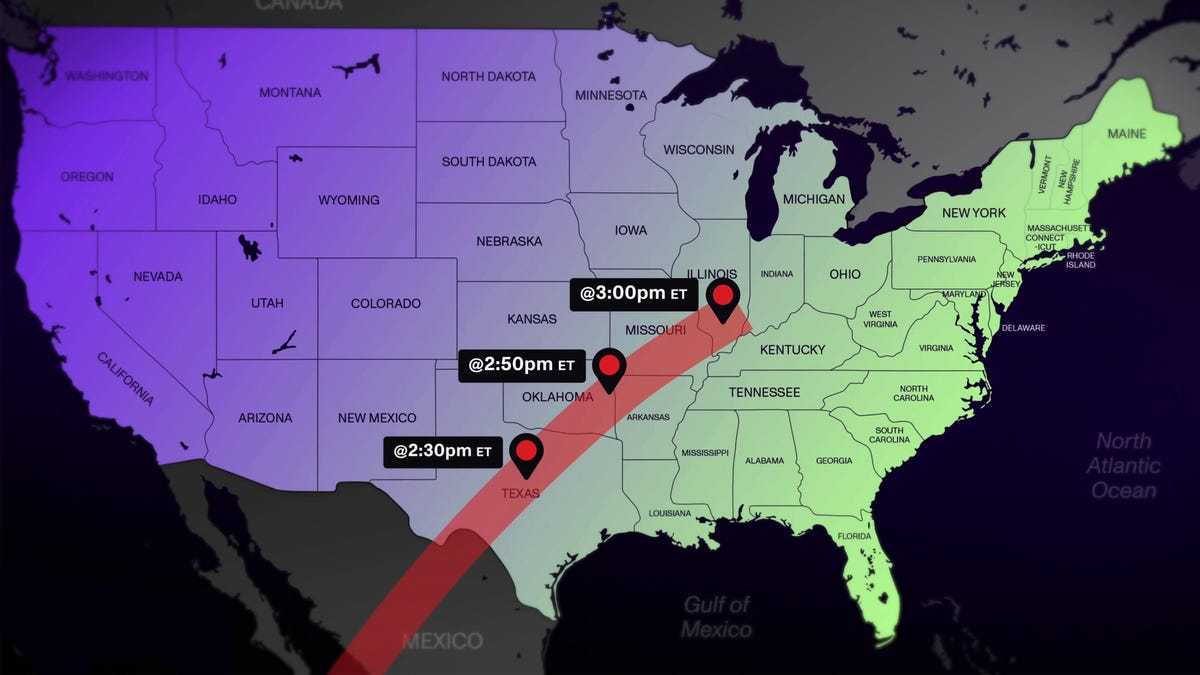
Stargazers from Mexico to the US and Canada are standing by for the last total solar eclipse to pass over the contiguous US for the next 20 years. The duration of totality, or the time during which the moon completely shrouds the sun from view, will last 4 minutes and 27 seconds. The eclipse will reach Texas at approximately 1:10 p.m. ET and Maine by 2:22 p.m. ET. By 4:17 p.m. ET, it will move beyond the eastern North American border.
Firing rockets during an eclipse may sound like it comes straight from a sci-fi movie, but it’s a technique that’s been used for years to measure scientific data and theories. Indeed, eclipses provide critical, if short-lived, opportunities for scientists to gather information on a variety of topic areas to test whether their concepts are accurate.
Arguably the most important finding during an eclipse occurred in May 1919, when scientists discovered during a total eclipse that some stars appeared to be in the wrong place, according to NASA. The finding provided critical evidence to support Albert Einstein’s theory of relativity and the idea that the sun or other large celestial objects have so much gravity that they can bend light and distort spacetime.
NASA’s rocket launches on Monday won’t necessarily have that same gravitas, but science works in increments. The launches will be streamed live, so you can see what happens. Here’s how.
Why is NASA firing rockets during the eclipse?
The space agency is firing three sounding rockets, or rockets carrying scientific instruments, into the ionosphere, the region of the Earth’s atmosphere between the lower atmosphere, where we live, and space.
The ionosphere is scientifically important because it’s made up of particles that become ionized, or electrically charged, when they interact with the sun’s radiation. According to NASA, the ionosphere thins at night and thickens when the sun’s rays are hitting it. The ionosphere can be unpredictable, since it’s highly sensitive to disruption.
«Earth’s terrestrial weather and space weather can impact these particles, making it a dynamic region and difficult to know what the ionosphere will be like at a given time,» NASA says.
Another thing: the ionosphere affects communication, and especially high-frequency communication like radio waves. That could, for instance, create disturbances in communications with pilots in the air or with government agencies doing research. But radio waves traveling to and from satellites aren’t just of concern to aviators and scientists. They’re also vital elements of daily life, from satellite internet services like SpaceX’s Starlink to the GPS signals that underlie all manner of financial transactions and that help you get where you’re going.
From a site in Virginia, NASA’s three rockets will be launched into the ionosphere 45 minutes apart: before the eclipse starts; when the eclipse is ongoing; and after the eclipse has reached its peak. The rockets will reach a maximum altitude of 260 miles, allowing them to spend plenty of time in the ionosphere, which spans 55 miles to 310 miles above the Earth’s surface.
Each of the rockets is carrying four two-liter soda bottle-sized instruments that will be ejected during flight to evaluate any ionosphere disturbances, or perturbations, during the eclipse.
«Gathering the data on these perturbations will help scientists validate and improve current models that help predict potential disturbances to our communications, especially high frequency communication,» NASA says.
Has NASA fired rockets at an eclipse before?
This isn’t the first time NASA has fired rockets during an eclipse. In October, NASA fired the same three rockets from its White Sands Test Facility in North Mexico during an annular solar eclipse. The agency said that it was able to recover the rockets and refurbish them, allowing them to be used in Monday’s mission.
Thanks to that mission, scientists were able to see ionosphere disturbances after it fired the second and third rockets, during and after the eclipse, respectively. NASA didn’t see any ionosphere disturbance during the first launch.
However, this time around, the rockets are equipped with additional instruments, allowing them to capture more information than they did last year, NASA says.
When is NASA firing its rockets?
NASA plans to launch all three rockets from its Wallops Island facility in Virginia. The first rocket will launch at approximately 2:40 p.m. ET, with the second rocket launching at approximately 3:25 p.m. ET. NASA plans to launch the final rocket by 4:05 p.m. ET.
As always, timing on the launches depends on a variety of factors, including on-the-ground conditions, and may be subject to change. But since the eclipse isn’t waiting for NASA to be ready to fire rockets, expect the space agency to try to keep a tight schedule to ensure it doesn’t miss its window to capture data.
How can I watch NASA fire rockets at the eclipse?
If you’re interested in watching NASA’s rocket-firing mission, the agency will livestream it from its official Wallops Island YouTube page. It’ll also be featured during NASA’s official solar eclipse broadcast
The rocket-only livestream will begin at 2:30 p.m. ET. NASA will start airing its solar eclipse coverage at 1 p.m. ET.
Technologies
Today’s NYT Mini Crossword Answers for Monday, March 9
Here are the answers for The New York Times Mini Crossword for March 9.

Looking for the most recent Mini Crossword answer? Click here for today’s Mini Crossword hints, as well as our daily answers and hints for The New York Times Wordle, Strands, Connections and Connections: Sports Edition puzzles.
Need some help with today’s Mini Crossword? Read on for all the answers. And if you could use some hints and guidance for daily solving, check out our Mini Crossword tips.
If you’re looking for today’s Wordle, Connections, Connections: Sports Edition and Strands answers, you can visit CNET’s NYT puzzle hints page.
Read more: Tips and Tricks for Solving The New York Times Mini Crossword
Let’s get to those Mini Crossword clues and answers.
Mini across clues and answers
1A clue: Talk ___ (boastfully banter)
Answer: SMACK
6A clue: What has legs, but never walks?
Answer: TABLE
7A clue: French for «love»
Answer: AMOUR
8A clue: What has a mouth, but never talks?
Answer: RIVER
9A clue: Run-down in appearance
Answer: SEEDY
Mini down clues and answers
1D clue: Milky Way bits
Answer: STARS
2D clue: ___ Eisenhower, 1950s first lady
Answer: MAMIE
3D clue: Overhead
Answer: ABOVE
4D clue: Given a crossword hint
Answer: CLUED
5D clue: Actress Washington of «Scandal»
Answer: KERRY
Technologies
Today’s NYT Connections: Sports Edition Hints and Answers for March 9, #532
Here are hints and the answers for the NYT Connections: Sports Edition puzzle for March 9, No. 532.

Looking for the most recent regular Connections answers? Click here for today’s Connections hints, as well as our daily answers and hints for The New York Times Mini Crossword, Wordle and Strands puzzles.
Today’s Connections: Sports Edition features a mix of topics. As a Minnesota Vikings fan, the green group came quickly to me. If you’re struggling with today’s puzzle but still want to solve it, read on for hints and the answers.
Connections: Sports Edition is published by The Athletic, the subscription-based sports journalism site owned by The Times. It doesn’t appear in the NYT Games app, but it does in The Athletic’s own app. Or you can play it for free online.
Read more: NYT Connections: Sports Edition Puzzle Comes Out of Beta
Hints for today’s Connections: Sports Edition groups
Here are four hints for the groupings in today’s Connections: Sports Edition puzzle, ranked from the easiest yellow group to the tough (and sometimes bizarre) purple group.
Yellow group hint: Rocky Mountain High.
Green group hint: Upper Midwest division.
Blue group hint: Speed demons.
Purple group hint: Leading the team.
Answers for today’s Connections: Sports Edition groups
Yellow group: A Colorado athlete.
Green group: NFC North cities.
Blue group: Types of racing.
Purple group: Coach ____.
Read more: Wordle Cheat Sheet: Here Are the Most Popular Letters Used in English Words
What are today’s Connections: Sports Edition answers?
The yellow words in today’s Connections
The theme is a Colorado athlete. The four answers are Bronco, Buffalo, Nugget and Rockie.
The green words in today’s Connections
The theme is NFC North cities. The four answers are Chicago, Detroit, Green Bay and Minneapolis.
The blue words in today’s Connections
The theme is types of racing. The four answers are BMX, drag, horse and stock car.
The purple words in today’s Connections
The theme is Coach ____. The four answers are Carter, K, Prime and speak.
Technologies
Today’s Wordle Hints, Answer and Help for March 9, #1724
Here are hints and the answer for today’s Wordle for March 9, No. 1,724.

Looking for the most recent Wordle answer? Click here for today’s Wordle hints, as well as our daily answers and hints for The New York Times Mini Crossword, Connections, Connections: Sports Edition and Strands puzzles.
Today’s Wordle puzzle is a bit tricky, thanks to some unusual letters. If you need a new starter word, check out our list of which letters show up the most in English words. If you need hints and the answer, read on.
Read more: New Study Reveals Wordle’s Top 10 Toughest Words of 2025
Today’s Wordle hints
Before we show you today’s Wordle answer, we’ll give you some hints. If you don’t want a spoiler, look away now.
Wordle hint No. 1: Repeats
Today’s Wordle answer has no repeated letters.
Wordle hint No. 2: Vowels
Today’s Wordle answer has one vowel and one sometimes vowel.
Wordle hint No. 3: First letter
Today’s Wordle answer begins with H.
Wordle hint No. 4: Last letter
Today’s Wordle answer ends with Y.
Wordle hint No. 5: Meaning
Today’s Wordle answer can refer to something done with excessive speed.
TODAY’S WORDLE ANSWER
Today’s Wordle answer is HASTY.
Yesterday’s Wordle answer
Yesterday’s Wordle answer, March 8, No. 1,723, was LOBBY.
Recent Wordle answers
March 4, No. 1,719: THEFT
March 5, No. 1,720: SHEEP
March 6, No. 1,721: GUNKY
March 7, No. 1,722: VOGUE
-

 Technologies3 года ago
Technologies3 года agoTech Companies Need to Be Held Accountable for Security, Experts Say
-

 Technologies3 года ago
Technologies3 года agoBest Handheld Game Console in 2023
-

 Technologies3 года ago
Technologies3 года agoTighten Up Your VR Game With the Best Head Straps for Quest 2
-

 Technologies4 года ago
Technologies4 года agoBlack Friday 2021: The best deals on TVs, headphones, kitchenware, and more
-

 Technologies5 лет ago
Technologies5 лет agoGoogle to require vaccinations as Silicon Valley rethinks return-to-office policies
-

 Technologies5 лет ago
Technologies5 лет agoVerum, Wickr and Threema: next generation secured messengers
-

 Technologies4 года ago
Technologies4 года agoOlivia Harlan Dekker for Verum Messenger
-

 Technologies4 года ago
Technologies4 года agoiPhone 13 event: How to watch Apple’s big announcement tomorrow
