Technologies
‘Free Solo’ Star Alex Honnold Climbs Unexplored Arctic Mountains to Track Climate Change
His new National Geographic miniseries, Arctic Ascent, follows Honnold and his team tracking ice formation in Greenland’s frigid fjords.
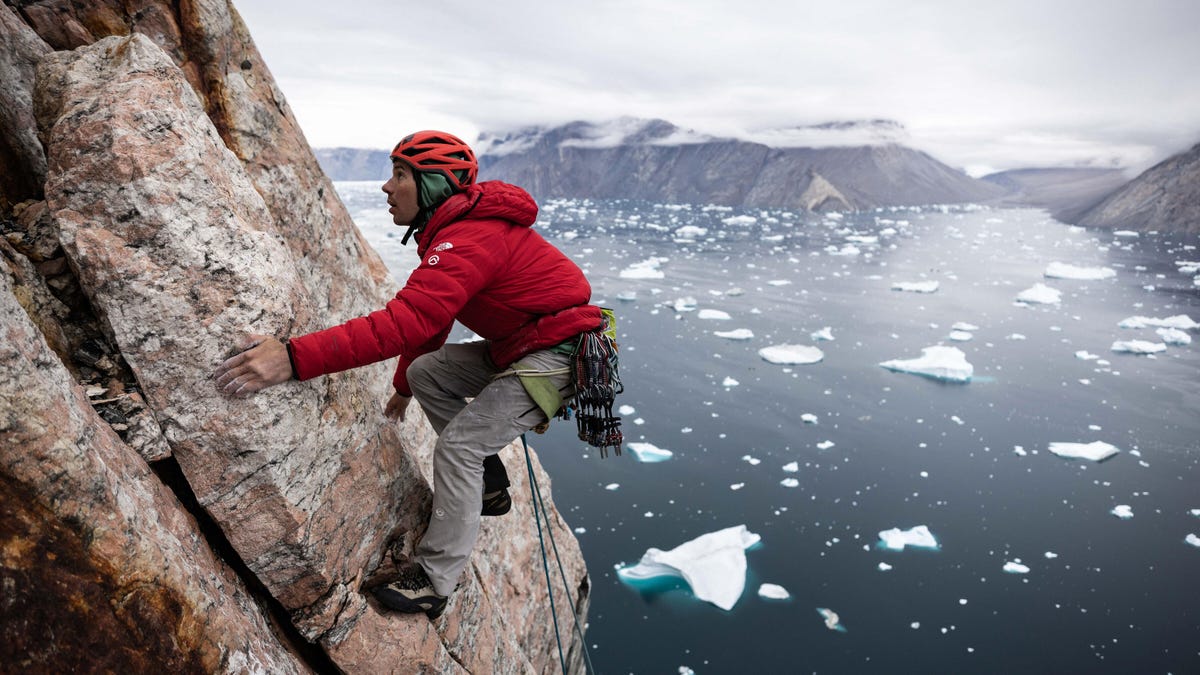

Alex Honnold ascended to fame making one of the most daring no-rope climbs of a rock face in history, as documented in the award-winning film Free Solo. Then he turned to climbing for causes — the latest of which took him to the Arctic Circle, where he traveled with a team to measure the impact of climate change on some of the most remote parts of planet Earth.
Honnold’s expedition to check on Greenland’s ice, performed in 2022, was documented for a National Geographic three-episode miniseries that will arrive on Disney Plus on Feb. 5, titled Arctic Ascent.
Much like Honnold’s prior journey to track down undiscovered frogs up the sides of yet-to-be-climbed jungle mesas in South America, his venture in Greenland’s frigid fjords is filled with firsts. He and the team ascended a rock wall that hadn’t previously been climbed to reach an iced-over plateau that nobody had crossed on foot before, made a boat trip across uncharted waters, and finally ascended Ingmikortilaq, a 3,750-foot previously unclimbed mountain that’s nearly a thousand feet taller than Yosemite’s El Capitan cliff face, which Honnold summited in Free Solo.
«When we were sailing up the fjord in boats to go up to Ingmikortilaq, we did actually literally cross a point where there was no more information on the depth chart,» Honnold said. «We crossed a line and it was just blank after that. Nowadays, it’s relatively rare to go somewhere where you’re kind of off the edge of the map.»
As remote as Honnold’s trek was, what they were investigating has implications for the whole world. Emissions from burning fossil fuels are causing our climate to change, warming up the planet and leading to more extreme weather. As scientists expand their study of climate change’s impact, they’re also looking farther afield to understand how it can upset natural processes — and in Greenland, the melting of vast ice sheets could lead to a rise in global water levels, which could put coastal settlements around the world underwater.
The expedition took the team nearly 100 miles through subzero temperatures and even colder winds, which is difficult enough to endure in the open ice plain but extra torturous when climbing. As Honnold pointed out, you can’t climb with gloves as your fingers need to be free to grip holes and cracks in the sheer rock wall, so they must be exposed to the elements. And unlike Honnold’s previous trips to Antarctica, which had been cold but largely sunny, Greenland’s rain and snow meant many grim overcast days for his adventuring team.
Instead of finding frogs, the pro-environmental angle for this trip was to forge a path across ice fields and up mountain faces for Heïdi Sevestre, a glaciologist with the Arctic Monitoring and Assessment Program, who came to measure how climate change is affecting the formations of ice layers in arctic Greenland. Over the course of the journey, Sevestre took readings and collected samples in areas humans have never walked or climbed — a rare opportunity to collect data that could better our understanding of our warming world.
To Honnold, that’s a worthy cause for adventure. His post-Free Solo fame led to work that he funneled into a new foundation that has hooked up disadvantaged communities to solar power around the world. The Arctic Ascent expedition fed the same urge for Honnold to tend to the planet.
«I think a project like this is just a way to help talk about the environment to a mainstream audience, in talking about the importance of climate change, basically,» Honnold said.
Sevestre and Honnold make up a third of the six-person crew that went on the expedition, which also included Hazel Findlay and Mikey Schafer, two other climbers well-known for their skill in so-called «first ascents» up rock faces; as well as safety specialist adventurer Aldo Kane and Greenland guide Adam Kjeldsen. The challenging conditions and pioneering opportunities in adventure and science attracted them all to help crucial research at the edge of the world.
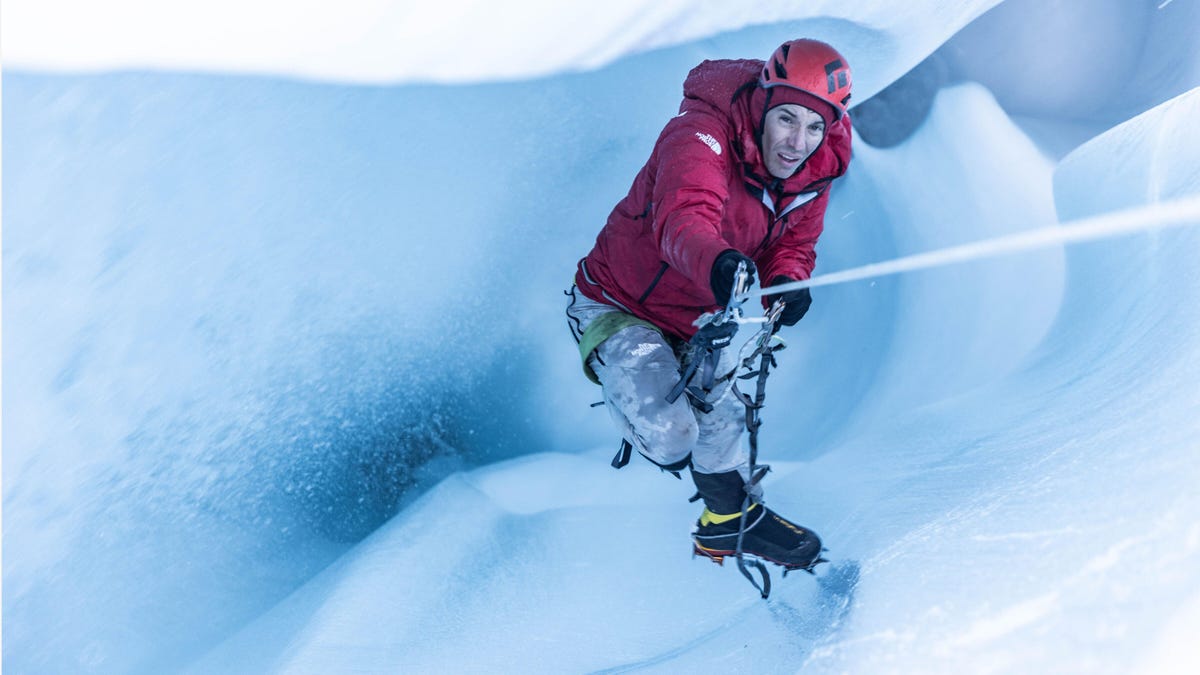

Forging through the arctic with research tech and iPhones
The three-episode miniseries documents the team’s arduous journey, which is peppered with interludes wherein Sevestre deploys scientific equipment to measure conditions and estimate their normalcy — or how much climate change has made them abnormal.
But the climbers sometimes need to court danger to get those instruments into the right position. One incident early in the series’ first episode has Honnold and others rappelling down a gaping hole carved by water rushing down to a glacier’s base, and dropping a piezometer into the flood to measure how much is flowing. Another data point to bring back to the scientific community from places it’s never accessed before.
Sevestre took a range of measurements over the course of the trip, including rock samples from the initial rock wall that could provide historical data to compare to modern climate progression. She took sonar measurements of the plateau to estimate how much water might flow into the world’s oceans if the ice sheets melt. And when they got past the ice field to the lake, she dropped a knee-high cylinder into the water — an actual aquatic probe for NASA (one of many in its Oceans Melting Greenland, or OMG, network of probes).
Honnold brought his iPhone.
While most of the miniseries is shot by National Geographic videographers with conventional cameras and drones for jaw-dropping ultrawide shots of gorgeous landscapes and sheer rock walls, it can be tough to get filmmakers into position in more extreme moments. So Honnold recorded a small portion of the footage himself in the fleeting triumph when he and his fellow climbers reached the top of an arctic wall that had never been climbed before. And he did it with an off-the-shelf iPhone.
«You’re almost required to do little video diaries [with phones] all the time because you just can’t capture it otherwise, those kinds of interactions where it’s just you and your partner at the anchor being like, ‘Here we are, we’re doing a thing, isn’t this exciting?'» said Honnold. He used either an iPhone 12 Mini or iPhone 13 Mini, he recalled.
Viewers won’t notice when the show seamlessly switches to his iPhone point-of-view, which is stunning proof that the smartphones in our pockets can produce documentary-quality footage, even at the edge of the world. Honnold kept the phone in an inner jacket pocket close to his warm chest for the most part so it wouldn’t die when exposed to Greenland’s subzero temperatures, but it still let him take part in contributing his own moments, from jokey chitchats with his team to euphoric cheers atop mountains, to the documentary.
Honnold has carried smartphones on climbs before, which he used to listen to music and take photos to send to family and friends. But phones have come a long way, and production companies now outfit him with the latest phones. His next trip, another National Geographic-recorded expedition to Alaska, has him using an iPhone 14 Pro Max so he can use its ProRes high-quality video format.
«The quality of phones now is good enough that you can put on a big screen,» Honnold said.
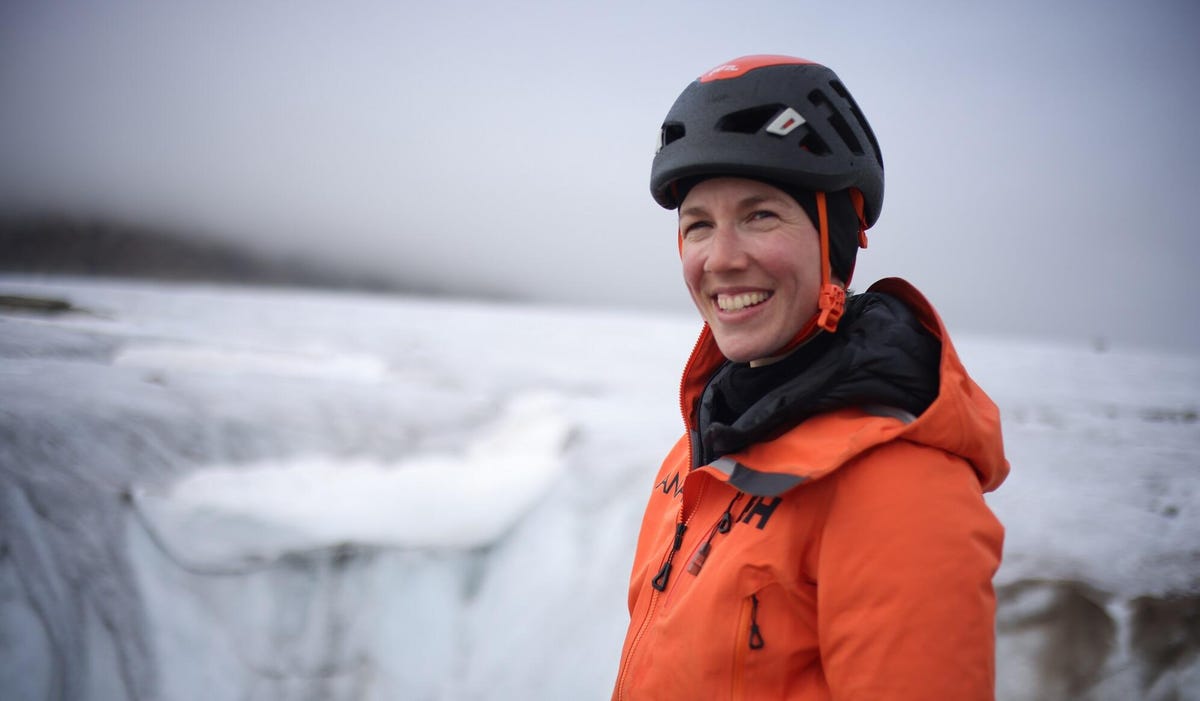

An expedition of science and adventure, the National Geographic way
The actual Arctic Ascent expedition happened in 2022, and Sevestre bundled her research into the trip to execute experiments for multiple universities. These myriad readings and measurements are, as Honnold described them, pieces of data that institutions around the world will use for different projects.
«Nothing we did is groundbreaking in and of itself, but that’s kind of the nature of science is that no individual piece of data determines any outcome. It’s always just part of this broader web of human knowledge,» Honnold said. «We’re hoping to fill in a gap in the map, for sure.»
That said, expeditions can be productive long after they’ve finished. The science expert from Honnold’s previous trip up the South American jungle mesas is still publishing research on the frogs discovered during the expedition, which occurred years ago. We won’t know the full impact of the Arctic Ascent expedition for some time, but there are other benefits to documenting such a tough adventure in some of the most wildly beautiful and unexplored parts of the world.
«I think showing the landscape is important, just showing people the wild beauty of Eastern Greenland. And I think that people can be inspired by nature in that way,» Honnold said. «But I think it’s nice to have an educational component, to have [Sevestre] along, to help people understand what’s at stake in Eastern Greenland.»
Technologies
Today’s NYT Connections: Sports Edition Hints and Answers for Feb. 4, #499
Here are hints and the answers for the NYT Connections: Sports Edition puzzle for Feb. 4, No. 499.

Looking for the most recent regular Connections answers? Click here for today’s Connections hints, as well as our daily answers and hints for The New York Times Mini Crossword, Wordle and Strands puzzles.
Today’s Connections: Sports Edition is a tough one. One of the words —«fronton» — might not be known to all the people who attempt the puzzle. There’s also a heavy focus on one specific team, which can be tough if you don’t know that roster well. If today’s puzzle has you stuck but you still want to crack it, keep reading for hints and answers.
Connections: Sports Edition is published by The Athletic, the subscription-based sports journalism site owned by The Times. It doesn’t appear in the NYT Games app, but it does in The Athletic’s own app. Or you can play it for free online.
Read more: NYT Connections: Sports Edition Puzzle Comes Out of Beta
Hints for today’s Connections: Sports Edition groups
Here are four hints for the groupings in today’s Connections: Sports Edition puzzle, ranked from the easiest yellow group to the tough (and sometimes bizarre) purple group.
Yellow group hint: Nice victory!
Green group hint: I’ll give you that guy for this guy.
Blue group hint: Where to play.
Purple group hint: Florida hoops.
Answers for today’s Connections: Sports Edition groups
Yellow group: Win smoothly.
Green group: Fantasy sports trade options.
Blue group: Areas of play, in different sports.
Purple group: Members of the Orlando Magic.
Read more: Wordle Cheat Sheet: Here Are the Most Popular Letters Used in English Words
What are today’s Connections: Sports Edition answers?
The yellow words in today’s Connections
The theme is win smoothly. The four answers are breeze, coast, cruise and waltz.
The green words in today’s Connections
The theme is fantasy sports trade options. The four answers are accept, counter, propose and reject.
The blue words in today’s Connections
The theme is areas of play, in different sports. The four answers are course, court, fronton and rink.
The purple words in today’s Connections
The theme is members of the Orlando Magic. The four answers are Banchero, Bane, Black and Suggs.
Toughest Connections: Sports Edition categories
The Connections: Sports Edition puzzle can be tough, but it really depends on which sports you know the most about. My husband aces anything having to do with Formula 1, my best friend is a hockey buff, and I can answer any question about Minnesota teams.
That said, it’s hard to pick the toughest Connections categories, but here are some I found exceptionally mind-blowing.
#1: Serie A Clubs. Answers: Atalanta, Juventus, Lazio, Roma.
#2: WNBA MVPs. Answers: Catchings, Delle Donne, Fowles and Stewart.
#3: Premier League team nicknames. Answers: Bees, Cherries, Foxes and Hammers.
#4: Homophones of NBA player names. Answers: Barns, Connect, Heart and Hero.
Technologies
Xbox Cloud Gaming Ad-Supported Tier: When Does It Start, How Much Will It Cost and More
Ads could remove the sting of Xbox Game Pass price hikes, but will it be worth it?
Xbox Cloud Gaming is one of the key selling points of Xbox Game Pass, and it generally works well. The service lets gamers stream Xbox titles to a wide range of devices, including phones, tablets, handhelds and select smart TVs from Samsung, LG and Hisense. However, following the Xbox Game Pass price increase from November, streaming alone may not be enough to keep some subscribers on board, which is where an ad-supported tier could come into play.
Microsoft confirmed the existence of an ad-supported tier last year but has not shared details on when it will launch or what it will include. New screenshots shared by players suggest the tier may be arriving soon, though questions remain about how it will work and what limitations it may have.
Don’t miss any of our unbiased tech content and lab-based reviews. Add CNET as a preferred Google source.
When will the Xbox Cloud Gaming ad-supported tier launch?
Microsoft hasn’t made an official announcement yet, but it’s expected to roll out sometime this year, according to Windows Central. Last month, some gamers saw a different loading screen for Xbox Cloud Gaming with a message saying «1 hour of ad-supported play time per session,» which would point to the ads coming soon.
looks like ad-supported Xbox Cloud Gaming is coming soon 👀 pic.twitter.com/c8hAERrVB9
— Tom Warren (@tomwarren) January 17, 2026
How much will the Xbox Cloud Gaming ad-supported tier cost?
In October, Microsoft confirmed it was internally testing the ad-supported tier, and at the time, said it would be free. Going by the load screen message I mentioned earlier, there will likely be a limit on how long people can play on the tier and during internal testing, players would have to watch a 2-minute ad.
What games will be available on the ad-supported tier?
Rumors about the internal testing suggested players would only have access to certain games for free, but the question is, which ones? Microsoft has a significant number of games available to stream, whether it’s purchased digital games or those available with an Xbox Game Pass subscription. Microsoft may allow all the digital games in a player’s library to be streamed and might make a few games available for free on a weekly or monthly basis, similar to the Free Play Days games.
Technologies
My Experience With United’s Starlink Service: How All In-Flight Wi-Fi Should Be
No need to load up devices with movies on long flights. You can stream them — and even live events — on Starlink-equipped United flights.

If I weren’t buckled into a seat, I might not have noticed that I was using in-flight Wi-Fi. When it came to working on my laptop and streaming movies on my phone and tablet, I could have been on my broadband at home.
But instead I was 30,000 feet up connected to Starlink Wi-Fi, on a United Airlines flight between Chicago and Minneapolis and thinking back to all the times I’d fought with expensive, slow, annoying internet access on planes. The ginger ale offered by a friendly attendant was a nice addition, too.
This experience was a demonstration flight on United’s first mainline Boeing 737-800 aircraft to be outfitted with the new satellite hardware. United now offers Starlink Wi-Fi service on 25% of its fleet, which includes 300 regional aircraft and dozens of mainline planes during 2025. It’s aiming to install the low-profile technology on up to 500 aircraft by the end of 2026.
At a time when our phones and smartwatches have satellite connectivity options — helping us reach emergency responders or send text messages when we’re out of range of a cell signal — Starlink and United are providing travelers with an upgraded convenience. What’s more, we’re getting in-flight Wi-Fi with speeds and connectivity that rival what we experience at home or the office.
Air travel presents a conundrum: If you need Wi-Fi in the air and it’s not working, you’re cooked. There’s no stepping out to a coffee shop hotspot or rebooting your home router. In-flight Wi-Fi has improved over the years, but it still feels risky whether it will work well or at all. And you don’t discover that until you’re already in the air.
The plane I traveled on isn’t the first United aircraft carrying Starlink’s satellite Wi-Fi equipment. United began outfitting many of its regional Embraer E175 jets in March after signing a deal with Starlink’s parent company, SpaceX, last year. Although it’s the inaugural United mainline aircraft, Hawaiian Airlines got the jump late last year when it outfitted its Airbus planes with the technology.
The Boeing 737-800 I flew on went into active service the next day, starting with a leg from Houston to Fort Lauderdale. Over the coming months, United expects to outfit approximately 15 mainline Boeing 737-800 planes per month with Starlink antennas.
United is offering Starlink Wi-Fi access free to United MileagePlus members. The Standard Wi-Fi option costs $8 or 1,600 miles for MileagePlus members, or $10 for everybody else. Subscriptions for frequent travelers start at $49 a month (or 7,500 miles).
In-flight Wi-Fi is all about the experience
Believe me, I want to talk about speeds and bandwidth and what a Starlink connection could mean for getting work done or being entertained in the air. But it all starts with getting connected, and too often, that experience sucks.
On my flight from Seattle to Chicago the day before my demo, United’s Standard Wi-Fi took nearly an hour to connect to any of my devices. (United uses different internet providers depending on the aircraft and operating area, and this flight was connected by satellite internet provider ViaSat.) Once the main menu page loaded, selecting most options, including «sign in» and «free messaging,» timed out with an error that there was no network connection.
That cut into my work time, but more importantly, it was incredibly frustrating. Many of us look forward to focused time on a flight to get things done without interruptions, and more frustration is the last thing we want to add to our air travel experience.
Two experiences stood out when I was on the Starlink-equipped plane. First, it operates gate-to-gate, so you can connect on your phone or tablet (laptops still need to be put away during takeoff) as soon as you get settled in your seat. After we’d landed and were taxiing back to the gate, I forgot that I was still connected through Starlink.
For almost as long as I’ve owned a cellphone, wheels-down meant it’s time to switch off Airplane mode and embrace the familiar connection of local cellular.
Second, the few sign-on steps I had to go through weren’t any more onerous than getting on a public cafe or hotel Wi-Fi network. After connecting to the United Wi-FI network, a portal window opened with a trio of screens explaining how great the new service is (you can skip them) and a field to enter my United MileagePlus account and password.
Oh, and then there’s a video ad, which is 15 seconds or less. (If you’ve been reading so far and thinking, «Wait, it can’t really be free, can it?» there’s your answer.) That ad turns out to be important: You aren’t connected until the video completes.
I was impatient and dismissed the ad on my laptop, which led to some trouble getting connected. Another journalist on the flight mentioned that he encountered the same situation, and the friendly United tech staff on the flight were curious whether the ad had played when they helped me diagnose the issue. I also emptied my browser caches and told the computer to forget the Wi-Fi network, essentially starting me from scratch.
As far as I can tell, no one else on the flight experienced this problem, but it’s safe to say there could have been some prelaunch bugs being worked out. United’s tech support won’t be on hand for regular flights, which is why one of them mentioned they were trying to iron out any points where flyers might run into difficulty.
Once connected, I could concentrate on trying to use as much bandwidth as possible and look outside occasionally since United scheduled this flight on a beautiful autumn day (instead of bringing everyone to Chicago in the dead of winter).
How Starlink Wi-Fi performed
The hardware that makes this happen is a pair of low-profile 500Mbps antennas mounted on the top of the fuselage. Unlike current units on planes offering standard Wi-Fi, the antennas are essentially exposed to communicate with the network of nearly 8,000 Starlink satellites operating in low Earth orbit (LEO), or about 350 miles in altitude.
To compare, the antenna module on a non-Starlink-equipped United plane parked at the next gate was much larger to shield its antennas, which need to adjust their angles during flight to talk to high-altitude satellites about 22,000 miles up.
In the time it takes a signal to go from a plane to high-altitude satellites, the signal can round-trip the distance between an aircraft and the Starlink satellites 70 times, according to Mara Palcisco, United Airlines vice president of engineering and reliability.
(This is also different from T-Satellite, the Starlink-powered satellite technology offered by T-Mobile. T-Satellite uses a separate collection of satellites to work with phones using a portion of the cellular spectrum.)
What does that mean in terms of the internet experience? Honestly, I’d think I was at home on my high-speed fiber internet if not for the cabin noise and the occasional tight banking turn. I streamed the (underrated, in my opinion) movie Cowboys & Aliens over Netflix on my iPad, played one of United’s available videos in a window on my MacBook Pro and watched YouTube videos on my iPhone.
Also, because this was a special flight for the press and several United employees, I initiated a video call with two colleagues. Usually, video and voice calls are not allowed — in fact, they’re illegal — and United makes a point of telling customers that they shouldn’t engage in any behavior that disturbs the people around them, including calls, listening to audio without headphones or watching media that would make others uncomfortable. You can watch a live call, but technically not talk on one, and that’s behavior flight attendants will have to enforce.
In this instance, we were encouraged to go ahead, so I had a hard-to-hear video conference with CNET managing editor Patrick Holland and senior reporter David Lumb (maybe it’s time to invest in a pair of AirPods Pro 3). The video quality was stellar — no, I’m not making a Starlink pun, I promise — even better than a few recent calls we’ve had in our respective offices. A FaceTime call with a friend was similar: clear, sharp video with no telltale streaming artifacts.
But let’s get to numbers. It’s always a nerd joy to go to Speedtest.net or run the Speedtest app and be surprised at the numbers it sends back. I consistently got around 250Mbps of download speed and anywhere from 25Mbps to 65Mbps upload speed. I saw that on all of my devices: iPhone 17 Pro, M1 iPad Pro and a 2021 MacBook Pro with an M1 Pro chip.
To put that into perspective, SpaceX says that Starlink residential internet gets up to 350Mbps download speeds, depending on location. According to an Ookla report, Starlink’s median performance is 105Mbps download, 15Mbps upload and 45ms latency. CNET senior writer Joe Supan saw similar performance when recently testing the Starlink Mini in Washington’s North Cascades mountains. (Disclosure: CNET’s parent company, Ziff Davis, also owns Ookla.)
To make what now looks like an unfair comparison, when I did get United’s standard Wi-Fi access the night before (which I paid $8 for), my speeds were 9.65Mbps down and 1.03Mbps up. Yes, those decimal points are in the correct places.
Streaming video, whether watching in-flight movies, catching up on a series on Netflix or Apple TV or watching live sports, will undoubtedly become more prevalent on flights when this level of bandwidth is available. In fact, when I chatted during the flight with Grant Milstead, United vice president of digital technology, I asked whether the in-flight videos available via United’s portal were cached on a server aboard the plane. (On my flight the previous night, I could view those even when an internet connection was elusive.)
He said that for mainline flights, which carry roughly 170 passengers, the company would still maintain those local servers for redundancy. But the regional Embraer E175 jets, the first of United’s fleet to be outfitted with the Starlink technology, rely on streamed content with no local backup. Given that the video and audio quality, from my perspective, was indistinguishable from broadband at home, that doesn’t come as a surprise.
While waiting for my trip back home (on a plane not equipped with Starlink Wi-Fi), I pondered my lasting impression of this assignment, which had me fly to Chicago, circle above Wisconsin for a couple of hours and then fly back to Seattle.
On my flight with Starlink Wi-Fi, I had uncompromised internet access. I wasn’t thinking about latency, artifacts or whether I was getting my $8 worth. I could work, watch videos, play live video games and just be bothered with any of the usual complications. And that was the best experience.
-

 Technologies3 года ago
Technologies3 года agoTech Companies Need to Be Held Accountable for Security, Experts Say
-

 Technologies3 года ago
Technologies3 года agoBest Handheld Game Console in 2023
-

 Technologies3 года ago
Technologies3 года agoTighten Up Your VR Game With the Best Head Straps for Quest 2
-

 Technologies4 года ago
Technologies4 года agoBlack Friday 2021: The best deals on TVs, headphones, kitchenware, and more
-

 Technologies5 лет ago
Technologies5 лет agoGoogle to require vaccinations as Silicon Valley rethinks return-to-office policies
-

 Technologies5 лет ago
Technologies5 лет agoVerum, Wickr and Threema: next generation secured messengers
-

 Technologies4 года ago
Technologies4 года agoOlivia Harlan Dekker for Verum Messenger
-

 Technologies4 года ago
Technologies4 года agoiPhone 13 event: How to watch Apple’s big announcement tomorrow
