Technologies
Gen Z Prevailed in a Climate Lawsuit. More Youth Trials Are on the Way
Young people fighting for a better future for the planet are beginning to discover that the law is on their side.
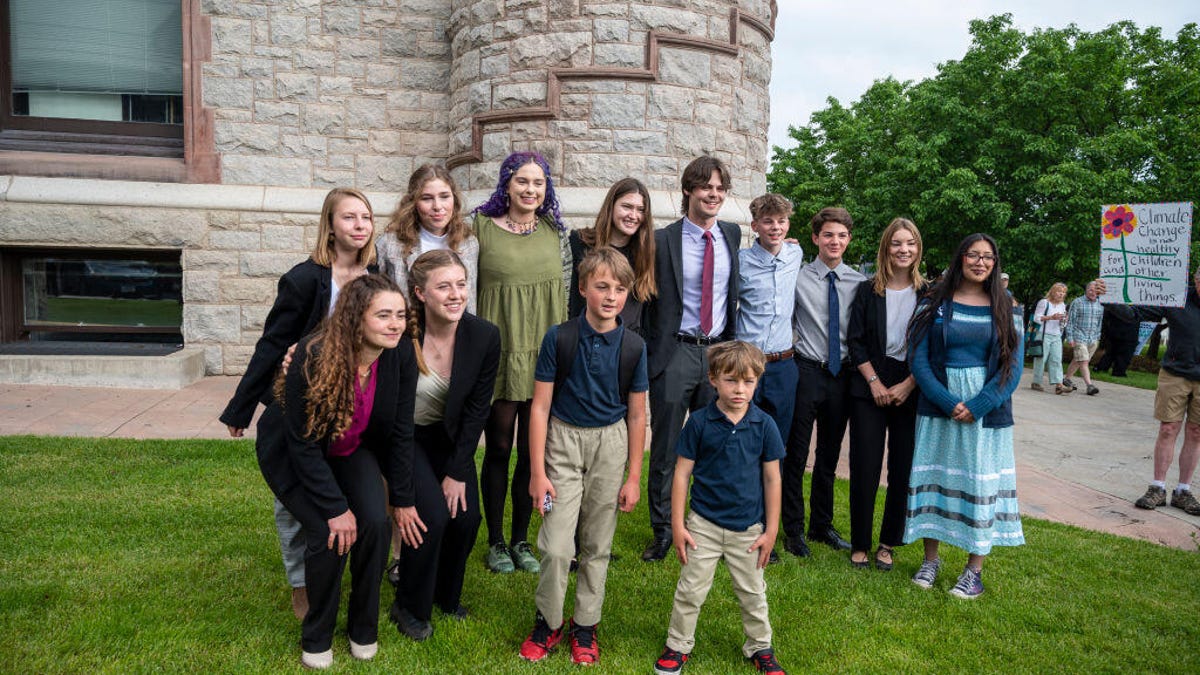
For two weeks in June, a Montana court heard from young people – 16 in total, ages 5 to 22 – and their families about the toll of extreme weather events caused by climate change on their health and other aspects of their lives.
They argued that the state of Montana had violated their constitutional rights to, among other things, a clean and healthful environment, by supporting a fossil fuel energy system and by failing to take action that would protect them against the harmful effects of climate change.
On Monday, after a two-month wait, they learned that they’d won.
In a landmark victory, Judge Kathy Seeley ruled in their favor, concluding in a 103-page decision that they’d proved significant injuries had occurred. Not only that, the decision in Held v. Montana said the case, launched in 2020, had shown that the Montana state government had been instrumental in causing these injuries and would be required to make changes to its conduct.
It’s a ruling that will likely have repercussions well beyond Montana’s state lines.
«We set the precedent not only for the United States, but for the world,» said 18-year-old Kian Tanner from Bigfork, Montana, in a statement.
It’s also another sign that Generation Z is finding new and forceful ways to make itself heard on climate issues. Gen Zers are using legal systems in the US and other countries to try to stem the damage being done by the burning of fossil fuels and the resulting greenhouse gases and to hold the responsible parties accountable.
Most young people are encouraged to avoid brushes with the legal system, but the plaintiffs in Montana, underpinned by legal team Our Children’s Trust, join a growing number of youth from around the world who are wielding the law to pressure governments into taking more radical action on climate.
Now that we’re regularly facing the impacts of human-caused climate change in our daily lives in the form of extreme weather events or breathing in smoke from forest fires, it’s easy to feel overwhelmed or powerless. But there are things we can do: recycle, cut down on car use, install solar panels and heat pumps, vote eco-friendly and support environmental campaigns. And litigate.
The Montana plaintiffs didn’t seek financial damages for the harms they’ve suffered due to climate change. Instead they wanted to change the current system – they sued over a law that prohibited the state from considering greenhouse gas emissions or climate change impacts when greenlighting fossil fuel projects.
«Young people are turning to court because they know that this isn’t about just the consumer choices that people make,» said Andrea Rodgers, senior litigation attorney at Our Children’s Trust, in an interview ahead of the verdict being issued. «This is about how we get energy, how we transfer goods, those kinds of systemic issues that governments really control.»
Monday’s decision is a game-changer, said Julia Olson, chief legal counsel and executive director with Our Children’s Trust, in a statement. «More rulings like this will certainly come.»
Here’s a look at some other prominent climate cases being driven by young people.
Kids vs. climate change
Way back in 2015, 21 young people filed a constitutional climate lawsuit against the federal government. They asserted that through government actions that cause climate change, it has violated the youngest generation’s constitutional rights to life, liberty and property.
Known as Juliana v. The United States, the federal case (also backed by Our Children’s Trust) was delayed by opposition from the Department of Justice under the Trump administration. Then, in June of this year, US District Court Judge Ann Aiken ruled that it can proceed to trial. Now the organizations supporting the young plaintiffs are asking the Biden administration not to delay the trial further.
«It’s long past time for the Department of Justice to end its opposition to the Juliana plaintiffs and youth climate justice,» said Zanagee Artis, founder and executive director of youth activist nonprofit Zero Hour. «Young Americans have the right to be heard by our nation’s courts, the branch of our government that has a duty to protect our constitutional right to a livable planet.»
For many years, courts were reluctant to hear and decide the merits of climate cases, said Rodgers. Just getting the Montana case to trial was a victory that signified «a real moment of change,» she added, that’s paved the way for trials to proceed both in the Juliana case and in another case that Our Children’s Trust is pursuing, in Hawaii.
Rodgers says the courts are now opening their doors to American youth because of the increasingly real and visceral impacts of climate change. «That does make a difference,» she said, «because it takes the injuries that the youth are experiencing … from being hypothetical to being real and tangible.»
Youth victories in and out of court
In the climate justice movement, young activists are key players in moving the needle on key issues, through protests, direct action and dialogues with politicians. But the combination of youth activism and legal action can be an especially potent mix.
In 2018, Indigenous climate activist and environmental engineer Yurshell Rodriguez, now 28, was one of 25 young people who successfully sued the government of Colombia for failing to reduce deforestation of the Amazon rainforest, thereby threatening their fundamental rights to a healthy environment, life, health, food and water. The lawsuit resulted in an intergenerational pact that meant the government had to consult with the plaintiffs, the affected communities and scientists to reduce deforestation in the Amazon.
«Activism sends a powerful message that the younger generation refuses to inherit a world plagued by environmental degradation and the consequences of inaction,» Rodriguez said in an interview. «But through lawsuits, we are raising awareness, mobilizing public support and challenging the status quo, compelling governments to prioritize sustainable policies, reduce carbon emissions and protect the planet for future generations.»

Young plaintiffs shouldn’t get discouraged if a judge rules against them, Rodriguez says – the awareness and public support a legal case can drive is also a positive result, which can in turn force the government’s hand.
In Europe in 2021, the People’s Climate Case, brought by 10 families including their children, was ultimately ruled inadmissible on a technicality by the Court of Justice of the European Union, but it spurred the EU to ramp up its fossil fuel reduction targets. «It’s all about kind of embarrassing the government into action,» said British human rights barrister Marc Willers.
There are always benefits to having young people tell their stories in open court alongside expert evidence and see states fail to defend their inaction, says Rodgers. «Even though there have been defeats and decisions that we consider to be unfavorable, it is still moving the ball forward.»
How to sue your government
No matter your age, it can be a «daunting prospect» to take on the state, even more so a fossil fuel giant that will throw everything it has at fighting your claim and attempting to discredit you, said Willers, who’s worked on a number of high-profile international environmental cases.
To bring a legal case, you’re going to need the support of sympathetic lawyers and an NGO or grassroots climate organization that knows the system and provides the necessary support, Willers said. He also advises forming a group, as the young people in the Montana and Juliana cases did, rather than going it alone, and finding a legal team that’s willing to spend time getting to understand your perspective.
In his work, Willers said, he’s found there are «real benefits to having young people involved in the litigation.» Children and youth can bring energy, positivity and unique viewpoints into the courtroom as representations of the future generations inheriting the Earth. They’re also often more knowledgeable about the issues than people give them credit for.

Young people often have a sophisticated understanding of the science combined with a sense of frustration and impatience, said Rodgers. She cited the example of a climate activist who achieved worldwide renown in her teens. «Greta Thunberg probably expresses that most prominently, but she’s simply expressing the feelings of youth universally, in my experience.»
Mounting global pressure
There’s no sign of youth-led climate litigation slowing down, what with legal wins in Colombia and Montana; the first lawsuit involving individuals versus the federal government underway in the US; and a major trial due to kick off in France this September based on six children and young adults suing 32 European countries.
As in the Montana case, the plaintiffs in that European case, all from Portugal, aren’t seeking financial damages – even though they’re entitled to. Instead, they’re pursuing a legally binding decision from the European Court of Human Rights that would require the countries to take action against climate change.
The more these cases occur around the world, the more they build momentum and make the voices of youth harder to ignore, said Rodgers. «What’s really cool is seeing these young people inspiring one another and building off of one another’s work.»
Such cases are strengthened by the fast-evolving field of attribution science, which can increasingly draw direct lines between specific emissions and the harms they’re causing. Lawsuits lodged by individuals against companies or institutions will only continue to get stronger and more frequent as our understanding of the science of climate change improves, Willers predicts.
When taking the legal route, progress can be painfully slow, as the young people in the now 8-year-old Juliana case have discovered. Some of them are no longer the kids they were at the time the suit was filed. But with children more aware than ever of growing up in a world threatened by climate change, there will be no shortage of young people willing to fight for their rights.
Rodriguez, who’s been there herself, is supportive of other young people considering demanding accountability and pushing for new measures through legal action. She encourages them to see themselves as «custodians of the future» who can leverage their voices and rights to hold those in power responsible for safeguarding the environment.
«To all the young people I will just say: Our actions inspire hope and serve as a reminder that collective efforts are essential in tackling the complex challenges of this climate crisis,» she says. «Be the change you want to see.»
Technologies
Today’s NYT Strands Hints, Answers and Help for Feb. 7 #706
Here are hints and answers for the NYT Strands puzzle for Feb. 7, No. 706.

Looking for the most recent Strands answer? Click here for our daily Strands hints, as well as our daily answers and hints for The New York Times Mini Crossword, Wordle, Connections and Connections: Sports Edition puzzles.
Today’s NYT Strands puzzle is especially tricky, as a variety of words could fit the theme. Some of the answers are difficult to unscramble, so if you need hints and answers, read on.
I go into depth about the rules for Strands in this story.
If you’re looking for today’s Wordle, Connections and Mini Crossword answers, you can visit CNET’s NYT puzzle hints page.
Read more: NYT Connections Turns 1: These Are the 5 Toughest Puzzles So Far
Hint for today’s Strands puzzle
Today’s Strands theme is: Boo-o-o-o-ring
If that doesn’t help you, here’s a clue: Zzzz… not very exciting.
Clue words to unlock in-game hints
Your goal is to find hidden words that fit the puzzle’s theme. If you’re stuck, find any words you can. Every time you find three words of four letters or more, Strands will reveal one of the theme words. These are the words I used to get those hints but any words of four or more letters that you find will work:
- HIND, DATE, DRUM, MOST, CHIN, PAIN, RAIN, NOSE, TOME, TOMES
Answers for today’s Strands puzzle
These are the answers that tie into the theme. The goal of the puzzle is to find them all, including the spangram, a theme word that reaches from one side of the puzzle to the other. When you have all of them (I originally thought there were always eight but learned that the number can vary), every letter on the board will be used. Here are the nonspangram answers:
- DULL, DREARY, HUMDRUM, MUNDANE, TIRESOME
Today’s Strands spangram
Today’s Strands spangram is WATCHINGPAINTDRY. To find it, start with the W that’s three letters up from the bottom on the far-left row, and wind up, across and down.
Toughest Strands puzzles
Here are some of the Strands topics I’ve found to be the toughest.
#1: Dated slang. Maybe you didn’t even use this lingo when it was cool. Toughest word: PHAT.
#2: Thar she blows! I guess marine biologists might ace this one. Toughest word: BALEEN or RIGHT.
#3: Off the hook. Again, it helps to know a lot about sea creatures. Sorry, Charlie. Toughest word: BIGEYE or SKIPJACK.
Technologies
Spotify Launches ‘About the Song’ Beta to Reveal Stories Behind the Music
The stories are told on swipeable cards as you listen to the song.
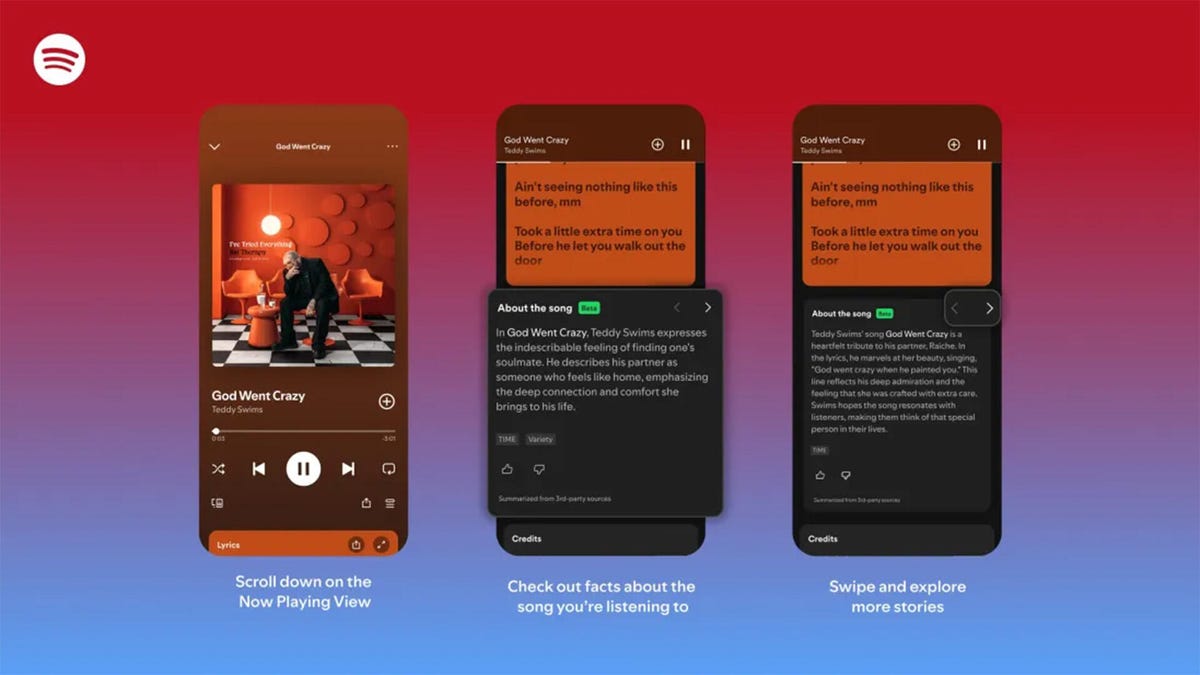
Did you know Chappell Roan drew inspiration for her hit song Pink Pony Club from The Pink Cadillac, the name of a hot-pink strip club in her Missouri hometown? Or that Fountains of Wayne’s song Stacy’s Mom was inspired by a confessed crush a friend had on the late co-founder Adam Schlesinger’s grandmother?
If you’re a fan of knowing juicy little tidbits about popular songs, you might find more trivia in About the Song, a new feature from streaming giant Spotify that’s kind of like the old VH1 show Pop-Up Video.
About the Song is available in the US, UK, New Zealand and Australia, initially for Spotify Premium members only. It’s only on certain songs, but it will likely keep rolling out to more music. Music facts are sourced from a variety of websites and summarized by AI, and appear below the song’s lyrics when you’re playing a particular song.
«Music fans know the feeling: A song stops you in your tracks, and you immediately want to know more. What inspired it, and what’s the meaning behind it? We believe that understanding the craft and context behind a song can deepen your connection to the music you love,» Spotify wrote in a blog post.
While this version of the feature is new, it’s not the first time Spotify has featured fun facts about the music it plays. The streaming giant partnered with Genius a decade ago for Behind the Lyrics, which included themed playlists with factoids and trivia about each song. Spotify kept this up for a few years before canceling due to multiple controversies, including Paramore’s Hayley Williams blasting Genius for using inaccurate and outdated information.
Spotify soon started testing its Storyline feature, which featured fun facts about songs in a limited capacity for some users, but was never released as a central feature.
About the Song is the latest in a long string of announcements from Spotify, including a Page Match feature that lets you seamlessly switch to an audiobook from a physical book, and an AI tool that creates playlists for you. Spotify also recently announced that it’ll start selling physical books.
How to use About the Song
If you’re a Spotify Premium user, the feature should be available the next time you listen to music on the app.
- Start listening to any supported song.
- Scroll down past the lyrics preview box to the About the Song box.
- Swipe left and right to see more facts about the song.
I tried this with a few tracks, and was pleased to learn that it doesn’t just work for the most recent hits. Spotify’s card for Metallica’s 1986 song Master of Puppets notes the song’s surge in popularity after its cameo in a 2022 episode of Stranger Things. The second card discusses the band’s album art for Master of Puppets and how it was conceptualized.
To see how far support for the feature really went, I looked up a few tracks from off the beaten path, like NoFX’s The Decline and Ice Nine Kills’ Thank God It’s Friday. Spotify supported every track I personally checked.
There does appear to be a limit to the depth of the fun facts, which makes sense since not every song has a complicated story. For those songs, Spotify defaults to trivia about the album that features the music or an AI summary of the lyrics and what they might mean.
Technologies
Today’s NYT Connections: Sports Edition Hints and Answers for Feb. 7, #502
Here are hints and the answers for the NYT Connections: Sports Edition puzzle for Feb. 7, No. 502.

Looking for the most recent regular Connections answers? Click here for today’s Connections hints, as well as our daily answers and hints for The New York Times Mini Crossword, Wordle and Strands puzzles.
Today’s Connections: Sports Edition features a fun batch of categories. The purple one requires you to find hidden words inside some of the grid words, but they’re not too obscure. If you’re struggling with today’s puzzle but still want to solve it, read on for hints and the answers.
Connections: Sports Edition is published by The Athletic, the subscription-based sports journalism site owned by The Times. It doesn’t appear in the NYT Games app, but it does in The Athletic’s own app. Or you can play it for free online.
Read more: NYT Connections: Sports Edition Puzzle Comes Out of Beta
Hints for today’s Connections: Sports Edition groups
Here are four hints for the groupings in today’s Connections: Sports Edition puzzle, ranked from the easiest yellow group to the tough (and sometimes bizarre) purple group.
Yellow group hint: Golden Gate.
Green group hint: It’s «Shotime!»
Blue group hint: Same first name.
Purple group hint: Tweak a team name.
Answers for today’s Connections: Sports Edition groups
Yellow group: Bay Area teams.
Green group: Associated with Shohei Ohtani.
Blue group: Coaching Mikes.
Purple group: MLB teams, with the last letter changed.
Read more: Wordle Cheat Sheet: Here Are the Most Popular Letters Used in English Words
What are today’s Connections: Sports Edition answers?
The yellow words in today’s Connections
The theme is Bay Area teams. The four answers are 49ers, Giants, Sharks and Valkyries.
The green words in today’s Connections
The theme is associated with Shohei Ohtani. The four answers are Decoy, Dodgers, Japan and two-way.
The blue words in today’s Connections
The theme is coaching Mikes. The four answers are Macdonald, McCarthy, Tomlin and Vrabel.
The purple words in today’s Connections
The theme is MLB teams, with the last letter changed. The four answers are Angelo (Angels), Cuba (Cubs), redo (Reds) and twine (Twins).
-

 Technologies3 года ago
Technologies3 года agoTech Companies Need to Be Held Accountable for Security, Experts Say
-

 Technologies3 года ago
Technologies3 года agoBest Handheld Game Console in 2023
-

 Technologies3 года ago
Technologies3 года agoTighten Up Your VR Game With the Best Head Straps for Quest 2
-

 Technologies4 года ago
Technologies4 года agoBlack Friday 2021: The best deals on TVs, headphones, kitchenware, and more
-

 Technologies5 лет ago
Technologies5 лет agoGoogle to require vaccinations as Silicon Valley rethinks return-to-office policies
-

 Technologies5 лет ago
Technologies5 лет agoVerum, Wickr and Threema: next generation secured messengers
-

 Technologies4 года ago
Technologies4 года agoOlivia Harlan Dekker for Verum Messenger
-

 Technologies4 года ago
Technologies4 года agoiPhone 13 event: How to watch Apple’s big announcement tomorrow
