Technologies
Intel Enters the Quantum Computing Horse Race With 12-Qubit Chip
But before quantum physics revolutionizes computing, Intel and rivals will have to learn how to make vastly more powerful machines.
Intel has built a quantum processor called Tunnel Falls that it will offer to research labs hoping to make the revolutionary computing technology practical.
The Tunnel Falls processor, announced Thursday, houses 12 of the fundamental data processing elements called qubits. It’s a major step in the chipmaker’s attempt to develop quantum computing hardware it hopes will eventually surpass rivals.
Intel, unlike most of its rivals, makes its qubits from individual electrons housed in computer chips that are cousins to those that power millions of PCs. The company is lagging behind. Rivals like IBM, Google, Quantinuum and IonQ have been offering quantum computers for years, but Intel believes tying its fortunes to conventional chip technology will ultimately enable faster progress.
«To me, it’s natural to use the tools already developed rather than having to develop new tools,» said Jim Clarke, director of quantum computing hardware at Intel Labs. Intel makes its own quantum computing chips at its D1 fab in Oregon.
You won’t buy your own quantum computer, but they could affect your life very directly. Among those investing in the technology are financial services companies seeking more profitable investments, materials science researchers hoping for better batteries, pharmaceutical companies trying to design better drugs and governments trying to crack adversaries’ encrypted communications.
Those challenges are out of reach of conventional computers, but quantum computing has the potential to tackle them by taking advantage of the weird physics of the ultrasmall. Today’s quantum computers aren’t generally practical, and the full promise of the technology remains years away, but physicists and engineers have made steady progress year after year.
Intel, an expert in large-scale manufacturing, hopes to help speed things along by building many quantum chips, which it calls quantum processing units, or QPUs. The University of Maryland, one of the centers benefiting from a US government program to accelerate quantum computing progress, will use Intel machines.
The quantum computing race
One notable feature of quantum computing is the tremendous variety of approaches. Intel is using electrons, storing data with a quantum mechanical property called spin that’s analogous to the two directions a top can spin. IBM and Google are using small electrical circuits of superconducting materials. IonQ and Quantinuum manipulate charged atoms stored in a trap. Other approaches involve neutral atoms and even that most fleeting of particles, the photon.
At a sufficiently small scale, quantum mechanics dominates physics and anything can become a qubit, quantum computing pioneer and MIT researcher Seth Lloyd said in an earlier interview. «It’s a question of whether you can massage them in the right way to convince them to compute.»
In other words, quantum computing isn’t a horse race like in the traditional computer chip market. It’s more like a horse pitted against a falcon, a motorcycle and an Olympic sprinter.
Intel likes its approach. Tunnel Falls is in manufacturing today, but the company very soon will «tape out» its successor, meaning the design is finished, and it’s begun designing the model after that, Clarke said. Twelve qubits is a tiny fraction of what’s needed for useful quantum computers, but Intel started with a simple approach designed for fast improvement and sustained progress over the years required to make serious quantum computers.
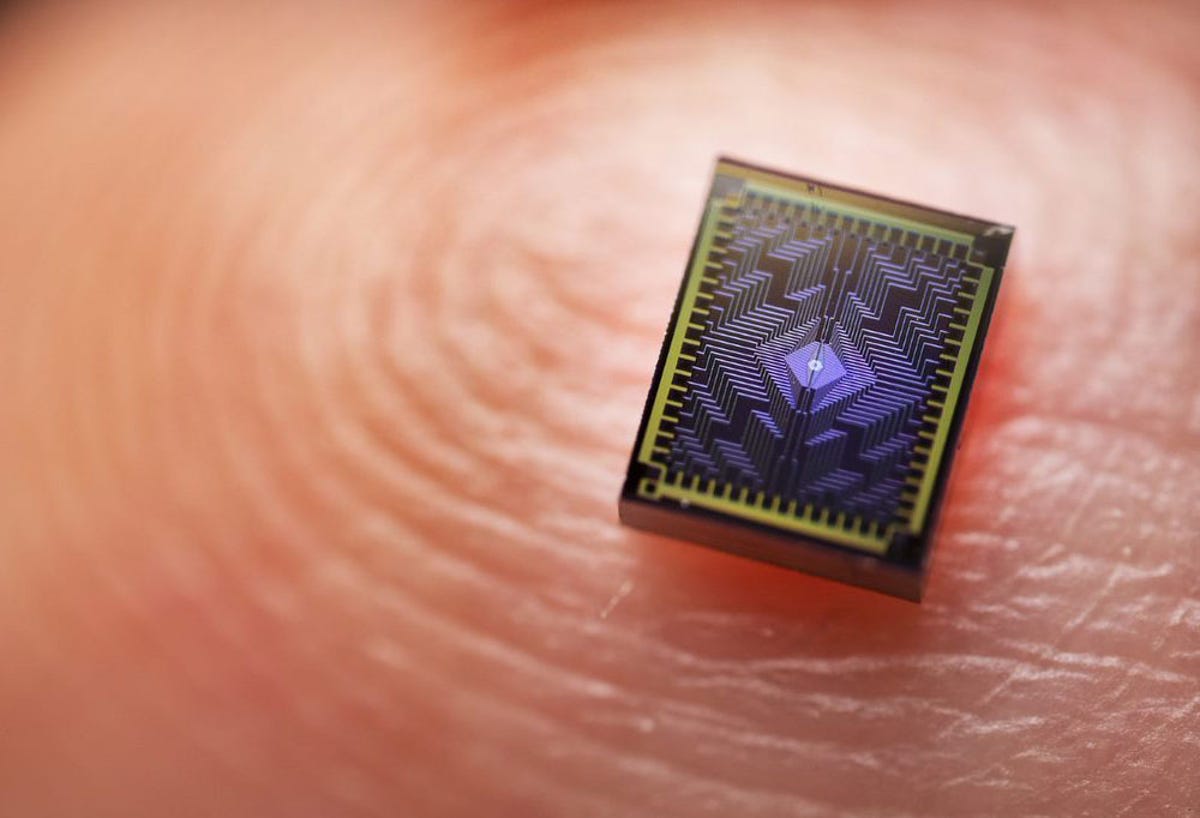

Intel’s Tunnel Falls quantum computer test chip perched on a fingertip
«The next big milestone is when we have a few thousand qubits,» a quantity that will let quantum computer engineers correct the frequent errors that plague qubit operations, Clarke said. «That’s probably three, four years, maybe five years away,» Clarke said. «And it’s probably the early 2030s or mid-2030s before we have a million cubits that are going to change the world.»
And Intel is engineering not just the QPUs, but the crucial data links that link each qubit to the outside world. Today’s quantum computers often look like high-tech chandeliers, with gleaming metal communication conduits looping down toward the processor, but that bulky design won’t work with thousands or millions of qubits, and Intel believes its control chips and chip interconnect technology will be necessary parts of an overall system.
Plenty of competitors
Intel is unusual in selecting photons housed in computer circuits for its quantum computing foundation. One of its biggest rivals, IBM, already offers multiple 127-qubit quantum computers for research and commercial use, with a 433-qubit machine up and running.
«We have a plan to get this out to hundreds of thousands of qubits using superconducting qubits,» said Jerry Chow, leader of IBM’s quantum computing hardware effort. IBM is working on quantum computer chips with a flock of code names — Egret, Heron, Condor, Crossbill — that are designed to prove out new technologies to reduce errors and improve the qubit-to-qubit connections that are central to the machines.
And it’s making progress. On Wednesday, it secured a coveted spot on the cover of the journal Nature for research showing its 127-qubit Eagle quantum computing chip can surpass conventional machines in simulating the materials physics that produce effects like magnetism.
Intel tried and rejected the supercomputing qubit approach, Clarke said. Its spin qubits are a million times smaller than a superconducting circuit, letting the company fit 25,000 of them on each 300mm silicon wafer that transits through its chip fabrication plant, called a fab. When Intel finds a problem building quantum chips, it figures out how to adapt the qubit to traditional chip manufacturing, not vice versa.
Disagreement with Intel’s approach
Such arguments haven’t persuaded others. Google is sticking with superconducting qubits.
«Superconducting qubits lead in critical metrics. We are confident they are the leading technology for the future of quantum supercomputers,» Google said in a statement, pointing to their processing speed and progress toward error correction to keep calculations on track longer. «We see a clear path to scale our technology to large-scale, error-corrected machines of general use.»
And IonQ Chief Executive Peter Chapman believes Intel’s approach is too inflexible for practical, large-scale quantum computers. His company is developing ion trap machines that scoot charged atoms around, letting different qubits interact with each other for computation. Fixing qubits onto the surface of a chip drastically complicates computations, he said.
«What worked in computing in the past — silicon-based processors — is not the right solution for the age of quantum,» Chapman said.
The deep disagreements about the best approach will perhaps be resolved as the machines evolve and grow larger. Intel’s plans rely on its manufacturing advantage, tapping into its experience building some of the most complicated electronics devices on the planet.
«Not everybody has a fab like this in their back pocket,» Clarke said.
Technologies
You Can’t Trust Your Car’s Driving Assistance System Yet, AAA Report Finds
Both hands-on and hands-off systems required human intervention to avoid accidents in this study.
Technologies
Google’s AI Mode Is Getting New Agentic Features for Restaurant Reservations and More
AI Mode can now do most of the work to find dinner reservations for you.

Google’s AI Mode is getting new agentic capabilities and expanding to 180 new countries and territories around the world, Google announced Thursday. AI Mode allows you to ask questions directly to Google and it’ll kick off a series of searches on your behalf. From there, it will surface relevant information to your query without the need to do any of the deep research yourself. It changes the way you search for things online, and it’s getting even smarter with this latest rollout.
Powered by DeepMind’s Project Mariner, the latest additions bring us further into the agentic AI future we’ve been promised for some time, directly from a search box. Instead of just finding things for you, AI Mode can now do things for you, like finding dinner reservations, flights or concert tickets. The update also brings personalized recommendations and link-sharing capabilities for easier collaboration with friends and family.
Most of the new features are either limited to premium AI subscribers and tucked behind an experiment in Google Labs, but it might not take long before they’re a standard part of your future search experience.
Google did not immediately respond to CNET’s request for further comment.
Restaurant recommendations
Instead of searching for restaurant reservations and then clicking on a specific website to make a reservation, AI Mode surfaces everything you need to complete the action right there. Since it’s contextually aware, you can add specificities to your query that a typical Google search wouldn’t handle well.
You can add the type of cuisine, number of people, time and location to a single query, and AI Mode will get to work and display real-time restaurant reservation time slots to choose from.
Google says it’s partnered with OpenTable, Resy, Tock, Ticketmaster and several other companies to make finding and doing what you want easier, since you won’t have to put in the legwork yourself.
This feature is currently rolling out to Google AI Ultra subscribers in the US who have enabled the specific experiment in Labs.
Personalized recommendations
Another experiment that’s currently available in the US (that also needs to be enabled in Labs) is personalized recommendations. Google says it’s starting with dining-related recommendations, which implies more options will be on the way in the future.
The experiment will use your past conversations with AI Mode, places you’ve interacted with on Search and Maps to provide suggestions tailored specifically to you.
Share AI Mode links with others for collaboration
If you’re planning a vacation or a party, you can now share your research directly with others with a new link-sharing feature built into AI Mode. People who interact with the link will be sent to the last response sent by AI Mode and can continue the conversation on their own to do more exploration on the topic. The original sender of the links can manage them and delete them at any time.
For more, don’t miss everything Google announced at its Pixel 10 event.
Technologies
IPhone or Android, Here’s How to Finally Escape That Endless Group Chat
Done with a group chat? Here’s how to ghost it on any service.

One reason people prefer group chats in Apple’s iMessage or RCS texting is the extra control and security these platforms provide. If everyone in your group is using iPhones, or if you’re on Android chatting through RCS, you’ll get features like typing indicators, high-quality media sharing, and the option to mute or leave a conversation when you need fewer notifications.
The biggest advantage is privacy. Both iMessage and RCS group chats offer end-to-end encryption, so your conversations stay secure. The only time that doesn’t apply is when a thread includes a mix of iPhone and Android users, which limits encryption support.
Knowing these differences can help you manage your chats more effectively, whether you’re keeping up with friends, planning events, or just looking for a little more control over your notifications.
And with RCS support with iOS 18, group chats that include a mix of iPhone and Android participants have more features than ever — but it’s not at the level you’ll experience when a conversation is fully on iMessage or Google Messages. «Green bubble chats» from an iPhone to an Android phone can now include typing indicators, higher-quality media and easier group chats.
However, RCS conversations between the iPhone and Android phones don’t include encryption now, but it should be added in a future update. This will hopefully give these conversations a similar level of privacy that we expect when using chat services like iMessage, WhatsApp or Signal.
Regardless of how you’re in a group chat with others, you can leave a chat. Here are the steps to leave any conversation from your phone’s texting app, regardless of whether it’s happening on iMessage, RCS or as a mixed MMS chat.
Leaving group chats on an iPhone
You can leave group conversations on your iPhone in two ways. You can either mute a chat,which keeps you in a conversation but you no longer receive notifications about it, or you can outright leave and no longer have access to the chat.
On an iPhone, open Messages and go to the chat thread you want to leave. At the top of the screen are conversation controls, a group of icons with the participants. Tap this to open a pop-up menu. As long as your conversation has four or more participants, iOS gives you the ability to tap Leave this Conversation with red text. If your chat has three or fewer participants, though, the option is grayed out, but you can tap Hide Alerts to prevent the conversation from notifying you further. Tapping Hide Alerts also allows you to mute a conversation, letting you keep access to a chat without necessarily leaving it. These steps apply to both iMessage conversations and to those over RCS.
Hide and block MMS chats on an iPhone
Although you can’t officially leave MMS group chats, you can hide or block the conversation. It’s not as good as outright leaving a conversation (other participants will still see you as in it), but you at least have no personal evidence of the conversation continuing.
On an iPhone, visit the group chat and tap the conversation controls. Instead of seeing Leave this conversation, you will see the option to Delete and Block this conversation. If you’d rather just mute the conversation instead of deleting and blocking it, you can hit Hide Alerts to mute it.
Leave group chats on an Android phone
On an Android phone using Google Messages, visit the chat thread you want to leave. Tap the conversation’s name to bring up the Group Details menu. Within this menu is the Leave Group button. Unlike with iMessage, you can leave chats with as few as three participants.
If you want to just mute notifications, tap Notifications on the Group Details screen to bring up a window with notifications controls. This includes options to make the conversation stay Silent to prevent it from ringing your chat, and if you tap Lock Screen, a pop-up menu will give you the option to prevent notifications. Tap Don’t show notifications at all to enable.
Hide and block MMS chats on an Android phone
On an Android phone with Google Messages, follow the same steps to access options for controlling notifications. This includes visiting the MMS chat thread and then tapping either the name of the conversation or the names of the participants at the top to bring up the Group Details menu. You won’t see a Leave Group option like you did with an RCS thread, but you do get the same ability to tap Notifications to access controls for hiding the conversation. This includes the same options for turning the conversation to Silent and to select Don’t show notifications at all.
SMS vs. MMS vs. RCS
SMS stands for Short Message Service and debuted in 1992. Text messages are limited to 160 characters. MMS stands for Multimedia Messaging Service and supports sending photos, videos or other files and messages longer than 160 characters. MMS supports a group of people chatting in a single conversation thread, while SMS can text multiple people at once but is sent as individual messages to each person. RCS, which launched 15 years ago, is short for Rich Communication Services and can show typing indicators, read receipts and has end-to-end encryption.
While cross-platform chat apps like WhatsApp, Signal and Telegram have better controls for conversations, encryption and privacy, regardless of the type of phone participants are using, they don’t support SMS, MMS or RCS. That’s why the default messaging app on most phones is still widely used, even if it means that a group chat is on a less feature-filled, unsecured standard like MMS.
-

 Technologies3 года ago
Technologies3 года agoTech Companies Need to Be Held Accountable for Security, Experts Say
-

 Technologies2 года ago
Technologies2 года agoBest Handheld Game Console in 2023
-

 Technologies2 года ago
Technologies2 года agoTighten Up Your VR Game With the Best Head Straps for Quest 2
-

 Technologies4 года ago
Technologies4 года agoVerum, Wickr and Threema: next generation secured messengers
-

 Technologies4 года ago
Technologies4 года agoGoogle to require vaccinations as Silicon Valley rethinks return-to-office policies
-

 Technologies4 года ago
Technologies4 года agoBlack Friday 2021: The best deals on TVs, headphones, kitchenware, and more
-

 Technologies4 года ago
Technologies4 года agoOlivia Harlan Dekker for Verum Messenger
-

 Technologies4 года ago
Technologies4 года agoiPhone 13 event: How to watch Apple’s big announcement tomorrow

