Technologies
US Tariffs Could Be Triggering New Inflation Woes. Everything You Need to Know
The pause on many tariffs was supposed to end this week, but it didn’t. Get the inside scoop on tariffs and what they mean for your budget.

The One Big Beautiful Bill may have been signed into law, but the economic plan of the second Trump administration is still uncertain due to the confusion around tariffs. President Donald Trump unleashed chaos on April 2 («Liberation Day») when he unveiled a laundry list of heavy tariffs for countries around the world. He then paused them for 90 days after the stock market dramatically tumbled.
That 90-day pause was supposed to end this week, but the tariffs have been been extended again through Aug. 1. More recently, the administration hiked tariffs against Canada to 35% and threatened Brazil with a 50% rate, while the US Labor Department announced on Tuesday that consumer prices rose 2.7% in June, the highest spike since February.
Amid the uncertainties and upheavals, Trump has barreled forward with his plans, including doubling the tariffs on steel and aluminum imports and announcing a new plan to increase the rate for China to 55%. He also hyped up a trade deal on July 2 that leaves Vietnam’s import tax rate at a historically high 20%. The sweeping tariff initiative will likely impact your cost of living, which we know from our surveys is something you’re worried about.
That all came after Trump’s push hit its biggest roadblock yet, when the US Court of International Trade ruled late last month that Trump had overstepped his authority when he imposed tariffs. That ruling was stayed, but the fight is likely to head to the Supreme Court. All the while, major US companies like Apple and Walmart have butted heads with the administration over the tariffs and their bluntness about how tariffs will make affording things harder for consumers.
Amid all this noise, you might still be wondering: What exactly are tariffs, and what will they mean for me?
The short answer: Expect to pay more for at least some goods and services. For the long answer, keep reading, and for more, check out CNET’s price tracker for 11 popular and tariff-vulnerable products.
What are tariffs?
Put simply, a tariff is a tax on the cost of importing or exporting goods by a particular country. So, for example, a 60% tariff on Chinese imports would be a 60% tax on the price of importing, say, computer components from China.
Trump has been fixated on imports as the centerpiece of his economic plans, often claiming that the money collected from taxes on imported goods would help finance other parts of his agenda. The US imports $3 trillion worth of goods from other countries annually.
The president has also shown a fixation on trade deficits, claiming that the US having a trade deficit with any country means that country is ripping the US off. This is a flawed understanding of the matter, many economists have said, since deficits are often a simple case of resource realities: Wealthy nations like the US buy specific things from nations that have them, while those nations in turn may not be wealthy enough to buy much of anything from the US.
While Trump deployed tariffs in his first term, notably against China, he ramped up his plans more significantly for the 2024 campaign, promising 60% tariffs against China and a universal 20% tariff on all imports into the US.
«Tariffs are the greatest thing ever invented,» Trump said at a campaign stop in Michigan last year. At one point, he called himself «Tariff Man» in a post on Truth Social.
Who pays the cost of tariffs?
Trump repeatedly claimed, before and immediately after returning to the White House, that the country of origin for an imported good pays the cost of the tariffs and that Americans would not see any price increases from them. However, as economists and fact-checkers stressed, this is not the case.
The companies importing the tariffed goods — American companies or organizations in this case — pay the higher costs. To compensate, companies can raise their prices or absorb the additional costs themselves.
So, who ends up paying the price for tariffs? In the end, usually you, the consumer. For instance, a universal tariff on goods from Canada would increase Canadian lumber prices, which would have the knock-on effect of making construction and home renovations more expensive for US consumers. While it is possible for a company to absorb the costs of tariffs without increasing prices, this is not at all likely, at least for now.
Speaking with CNET, Ryan Reith, vice president of International Data Corporation’s worldwide mobile device tracking programs, explained that price hikes from tariffs, especially on technology and hardware, are inevitable in the short term. He estimated that the full amount imposed on imports by Trump’s tariffs would be passed on to consumers, which he called the «cost pass-through.» Any potential efforts for companies to absorb the new costs themselves would come in the future, once they have a better understanding of the tariffs, if at all.
Which Trump tariffs have gone into effect?
Following Trump’s «Liberation Day» announcements on April 2 and subsequent shifting by the president, the following tariffs are in effect:
- A 50% tariff on all steel and aluminum imports, doubled from 25% as of June 4.
- A 30% tariff on all Chinese imports until the new deal touted by Trump takes effect, after which it will purportedly go up to 55%. China being a major focus of Trump’s trade agenda, it has faced a rate notably higher than other countries, peaking at 145% before trade talks commenced.
- 25% tariffs on imports from Mexico and 35% on those from Canada. This applies only to goods from each country that are not covered under the 2018 USMCA trade agreement brokered during Trump’s first term. The deal covers roughly half of all imports from Canada and about a third of those from Mexico, so the rest are subject to the new tariffs. Energy imports not covered by USMCA will be taxed at only 10%.
- A 25% tariff on all foreign-made cars and auto parts.
- A sweeping overall 10% tariff on all imported goods.
For certain countries that Trump said were more responsible for the US trade deficit, Trump imposed what he called «reciprocal» tariffs that exceed the 10% level: 20% for the 27 nations that make up the European Union, 26% for India, 24% for Japan and so on. These were meant to take effect on April 9 but were delayed by 90 days due to historic stock market volatility, and then delayed again to Aug. 1. These rates are subject to change until that new effective date, and some have already been altered: the rate against Japan was upped to 25%, the same as the rate against South Korea; Trump has also threatened a 50% rate against Brazil.
— Rapid Response 47 (@RapidResponse47) April 2, 2025
Trump’s claim that these reciprocal tariffs are based on high tariffs imposed against the US by the targeted countries has drawn intense pushback from experts and economists, who have argued that some of these numbers are false or potentially inflated. For example, the above chart says a 39% tariff from the EU, despite its average tariff for US goods being around 3%. Some of the tariffs are against places that are not countries but tiny territories of other nations. The Heard and McDonald Islands, for example, are uninhabited. We’ll dig into the confusion around these calculations below.
Notably, that minimum 10% tariff will not be on top of those steel, aluminum and auto tariffs. Canada and Mexico were also spared from the 10% minimum additional tariff imposed on all countries the US trades with.
On April 11, the administration said smartphones, laptops and other consumer electronics, along with flat panel displays, memory chips and semiconductors, were exempt from reciprocal tariffs. But it wasn’t clear whether that would remain the case or whether such products might face different fees later.
How were the Trump reciprocal tariffs calculated?
The numbers released by the Trump administration for its barrage of «reciprocal» tariffs led to widespread confusion among experts. Trump’s own claim that these new rates were derived by halving the tariffs already imposed against the US by certain countries was widely disputed, with critics noting that some of the numbers listed for certain countries were much higher than the actual rates and some countries had tariff rates listed despite not specifically having tariffs against the US at all.
In a post to X that spread fast across social media, finance journalist James Surowiecki said that the new reciprocal rates appeared to have been reached by taking the trade deficit the US has with each country and dividing it by the amount the country exports to the US. This, he explained, consistently produced the reciprocal tariff percentages revealed by the White House across the board.
Just figured out where these fake tariff rates come from. They didn’t actually calculate tariff rates + non-tariff barriers, as they say they did. Instead, for every country, they just took our trade deficit with that country and divided it by the country’s exports to us.
So we… https://t.co/PBjF8xmcuv— James Surowiecki (@JamesSurowiecki) April 2, 2025
«What extraordinary nonsense this is,» Surowiecki wrote about the finding.
The White House later attempted to debunk this idea, releasing what it claimed was the real formula, though it was quickly determined that this formula was arguably just a more complex version of the one Surowiecki deduced.
What will the Trump tariffs do to prices?
In short: Prices are almost certainly going up, if not now, then eventually. That is, if the products even make it to US shelves at all, as some tariffs will simply be too high for companies to bother dealing with.
While the effects of a lot of tariffs might not be felt straight away, some potential real-world examples have already emerged. Microsoft has increased prices across the board for its Xbox gaming brand, with its flagship Xbox Series X console jumping 20% from $500 to $600. Kent International, one of the main suppliers of bicycles to Walmart, announced that it would be stopping imports from China, which account for 90% of its stock.
Speaking about Trump’s tariff plans just before they were announced, White House trade adviser Peter Navarro said that they would generate $6 trillion in revenue over the next decade. Given that tariffs are most often paid by consumers, CNN characterized this as potentially «the largest tax hike in US history.» Estimates from the Yale Budget Lab, cited by Axios, predict that Trump’s new tariffs will cause a 2.3% increase in inflation throughout 2025. This translates to about a $3,800 increase in expenses for the average American household.
Reith, the IDC analyst, told CNET that Chinese-based tech companies, like PC makers Acer, Asus and Lenovo, have «100% exposure» to these import taxes, with products like phones and computers the most likely to take a hit. He also said that the companies best positioned to weather the tariff impacts are those that have moved some of their operations out of China to places like India, Thailand and Vietnam, singling out the likes of Apple, Dell and HP. Samsung, based in South Korea, is also likely to avoid the full force of Trump’s tariffs.
In an effort to minimize its tariff vulnerability, Apple has begun to move the production of goods for the US market from China to India.
Will tariffs impact prices immediately?
In the short term — the first days or weeks after a tariff takes effect — maybe not. There are still a lot of products in the US imported pre-tariffs and on store shelves, meaning the businesses don’t need a price hike to recoup import taxes. Once new products need to be brought in from overseas, that’s when you’ll see prices start to climb because of tariffs or you’ll see them become unavailable.
That uncertainty has made consumers anxious. CNET’s survey revealed that about 38% of shoppers feel pressured to make certain purchases before tariffs make them more expensive. About 10% say they have already made certain purchases in hopes of getting them in before the price hikes, while 27% said they have delayed purchases for products that cost more than $500. Generally, this worry is the most acute concerning smartphones, laptops and home appliances.
Mark Cuban, the billionaire businessman and Trump critic, voiced concerns about when to buy certain things in a post on Bluesky just after Trump’s «Liberation Day» announcements. In it, he suggested that consumers might want to stock up on certain items before tariff inflation hits.
«It’s not a bad idea to go to the local Walmart or big box retailer and buy lots of consumables now,» Cuban wrote. «From toothpaste to soap, anything you can find storage space for, buy before they have to replenish inventory. Even if it’s made in the USA, they will jack up the price and blame it on tariffs.»
CNET’s Money team recommends that before you make any purchase, especially a high-ticket item, be sure that the expenditure fits within your budget and your spending plans. Buying something you can’t afford now because it might be less affordable later can be burdensome, to say the least.
What is the goal of the White House tariff plan?
The typical goal behind tariffs is to discourage consumers and businesses from buying the tariffed, foreign-sourced goods and encourage them to buy domestically produced goods instead. When implemented in the right way, tariffs are generally seen as a useful way to protect domestic industries.
One of the stated intentions for Trump’s tariffs is along those lines: to restore American manufacturing and production. However, the White House also says it’s negotiating with numerous countries looking for tariff exemptions, and some officials have also floated the idea that the tariffs will help finance Trump’s tax cuts.
Those things are often contradictory: If manufacturing moves to the US or if a bunch of countries are exempt from tariffs, then tariffs aren’t actually being collected and can’t be used to finance anything. This and many other points have led a lot of economists to allege that Trump’s plans are misguided.
As for returning — or «reshoring» — manufacturing in the US, tariffs are a better tool for protecting industries that already exist because importers can fall back on them right away. Building up the factories and plants needed for this in the US could take years, leaving Americans to suffer under higher prices in the interim.
That problem is worsened by the fact that the materials needed to build those factories will also be tariffed, making the costs of «reshoring» production in the US too heavy for companies to stomach. These issues, and the general instability of American economic policies under Trump, are part of why experts warn that Trump’s tariffs could have the opposite effect: keeping manufacturing out of the US and leaving consumers stuck with inflated prices. Any factories that do get built in the US because of tariffs also have a high chance of being automated, canceling out a lot of job creation potential. To give you one real-world example of this: When warning customers of future price hikes, toy maker Mattel also noted that it had no plans to move manufacturing to the US.
Trump has reportedly been fixated on the notion that Apple’s iPhone — the most popular smartphone in the US market — can be manufactured entirely in the US. This has been broadly dismissed by experts, for a lot of the same reasons mentioned above, but also because an American-made iPhone could cost upward of $3,500. One report from 404 Media dubbed the idea «a pure fantasy.» The overall sophistication and breadth of China’s manufacturing sector have also been cited, with CEO Tim Cook stating in 2017 that the US lacks the number of tooling engineers to make its products.
For more, see how tariffs might raise the prices of Apple products and find some expert tips for saving money.
Technologies
AI Slop Is Destroying the Internet. These Are the People Fighting to Save It
Technologies
The Sun’s Temper Tantrums: What You Should Know About Solar Storms
Solar storms are associated with the lovely aurora borealis, but they can have negative impacts, too.
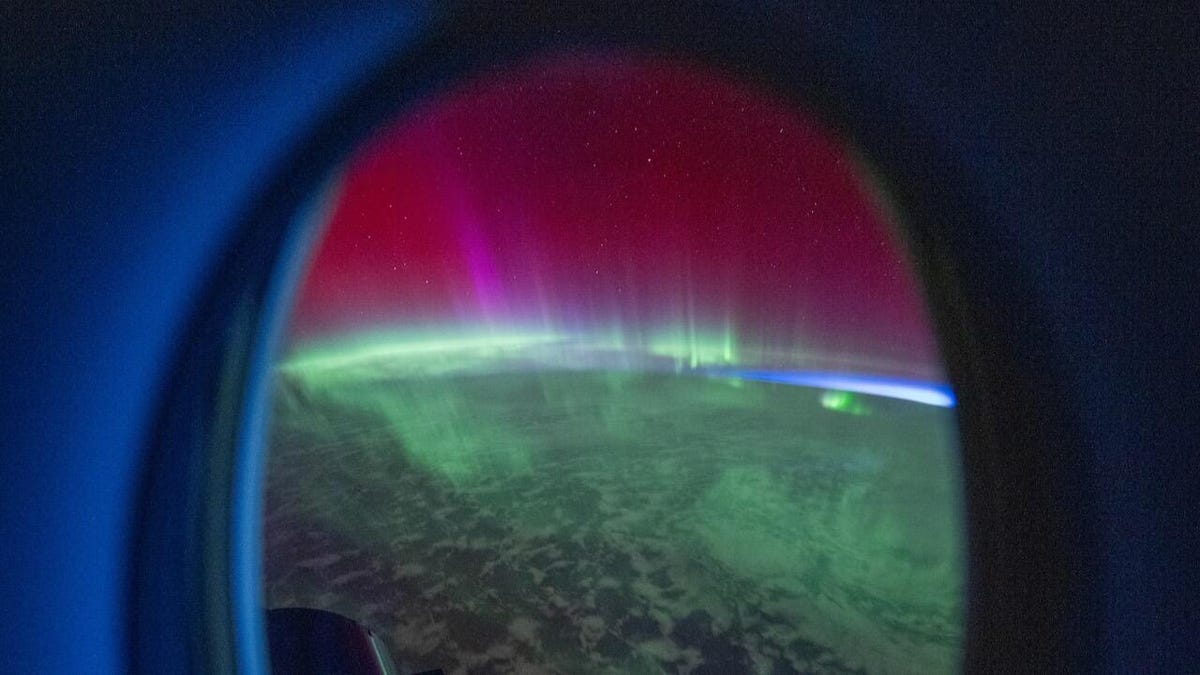

Last month, Earth was treated to a massive aurora borealis that reached as far south as Texas. The event was attributed to a solar storm that lasted nearly a full day and will likely contend for the strongest of 2026. Such solar storms are usually fun for people on Earth, as we are protected from solar radiation by our planet’s atmosphere, so we can just enjoy the gorgeous greens and pretty purples in the night sky.
But solar storms are a lot more than just the aurora borealis we see, and sometimes they can cause real damage. There are several examples of this in recorded history, with the earliest being the Carrington Event, a solar storm that took place on Sept. 1, 1859. It remains the strongest solar storm ever recorded, where the world’s telegraph machines became overloaded with energy from it, causing them to shock their operators, send ghost messages and even catch on fire.
Things have changed a lot since the mid-1800s, and while today’s technology is a lot more resistant to solar radiation than it once was, a solar storm of that magnitude could still cause a lot of damage.
What is a solar storm?
A solar storm is a catchall term that describes any disturbance in the sun that involves the violent ejection of solar material into space. This can come in the form of coronal mass ejections, where clouds of plasma are ejected from the sun, or solar flares, which are concentrated bursts of electromagnetic radiation (aka light).
A sizable percentage of solar storms don’t hit Earth, and the sun is always belching material into space, so minor solar storms are quite common. The only ones humans tend to talk about are the bigger ones that do hit the Earth. When this happens, it causes geomagnetic storms, where solar material interacts with the Earth’s magnetic fields, and the excitations can cause issues in everything from the power grid to satellite functionality. It’s not unusual to hear «solar storm» and «geomagnetic storm» used interchangeably, since solar storms cause geomagnetic storms.
Solar storms ebb and flow on an 11-year cycle known as the solar cycle. NASA scientists announced that the sun was at the peak of its most recent 11-year cycle in 2024, and, as such, solar storms have been more frequent. The sun will metaphorically chill out over time, and fewer solar storms will happen until the cycle repeats.
This cycle has been stable for hundreds of millions of years and was first observed in the 18th century by astronomer Christian Horrebow.
How strong can a solar storm get?
The Carrington Event is a standout example of just how strong a solar storm can be, and such events are exceedingly rare. A rating system didn’t exist back then, but it would have certainly maxed out on every chart that science has today.
We currently gauge solar storm strength on four different scales.
The first rating that a solar storm gets is for the material belched out of the sun. Solar flares are graded using the Solar Flare Classification System, a logarithmic intensity scale that starts with B-class at the lowest end, and then increases to C, M and finally X-class at the strongest. According to NASA, the scale goes up indefinitely and tends to get finicky at higher levels. The strongest solar flare measured was in 2003, and it overloaded the sensors at X17 and was eventually estimated to be an X45-class flare.
CMEs don’t have a named measuring system, but are monitored by satellites and measured based on the impact they have on the Earth’s geomagnetic field.
Once the material hits Earth, NOAA uses three other scales to determine how strong the storm was and which systems it may impact. They include:
- Geomagnetic storm (G1-G5): This scale measures how much of an impact the solar material is having on Earth’s geomagnetic field. Stronger storms can impact the power grid, electronics and voltage systems.
- Solar radiation storm (S1-S5): This measures the amount of solar radiation present, with stronger storms increasing exposure to astronauts in space and to people in high-flying aircraft. It also describes the storm’s impact on satellite functionality and radio communications.
- Radio blackouts (R1-R5): Less commonly used but still very important. A higher R-rating means a greater impact on GPS satellites and high-frequency radios, with the worst case being communication and navigation blackouts.
Solar storms also cause auroras by exciting the molecules in Earth’s atmosphere, which then light up as they «calm down,» per NASA. The strength and reach of the aurora generally correlate with the strength of the storm. G1 storms rarely cause an aurora to reach further south than Canada, while a G5 storm may be visible as far south as Texas and Florida. The next time you see a forecast calling for a big aurora, you can assume a big solar storm is on the way.
How dangerous is a solar storm?
The overwhelming majority of solar storms are harmless. Science has protections against the effects of solar storms that it did not have back when telegraphs were catching on fire, and most solar storms are small and don’t pose any threat to people on the surface since the Earth’s magnetic field protects us from the worst of it.
That isn’t to say that they pose no threats. Humans may be exposed to ionizing radiation (the bad kind of radiation) if flying at high altitudes, which includes astronauts in space. NOAA says that this can happen with an S2 or higher storm, although location is really important here. Flights that go over the polar caps during solar storms are far more susceptible than your standard trip from Chicago to Houston, and airliners have a whole host of rules to monitor space weather, reroute flights and monitor long-term radiation exposure for flight crews to minimize potential cancer risks.
Larger solar storms can knock quite a few systems out of whack. NASA says that powerful storms can impact satellites, cause radio blackouts, shut down communications, disrupt GPS and cause damaging power fluctuations in the power grid. That means everything from high-frequency radio to cellphone reception could be affected, depending on the severity.
A good example of this is the Halloween solar storms of 2003. A series of powerful solar flares hit Earth on Oct. 28-31, causing a solar storm so massive that loads of things went wrong. Most notably, airplane pilots had to change course and lower their altitudes due to the radiation wreaking havoc on their instruments, and roughly half of the world’s satellites were entirely lost for a few days.
A paper titled Flying Through Uncertainty was published about the Halloween storms and the troubles they caused. Researchers note that 59% of all satellites orbiting Earth at the time suffered some sort of malfunction, like random thrusters going offline and some shutting down entirely. Over half of the Earth’s satellites were lost for days, requiring around-the-clock work from NASA and other space agencies to get everything back online and located.
Earth hasn’t experienced a solar storm on the level of the Carrington Event since it occurred in 1859, so the maximum damage it could cause in modern times is unknown. The European Space Agency has run simulations, and spoiler alert, the results weren’t promising. A solar storm of that caliber has a high chance of causing damage to almost every satellite in orbit, which would cause a lot of problems here on Earth as well. There were also significant risks of electrical blackouts and damage. It would make one heck of an aurora, but you might have to wait to post it on social media until things came back online.
Do we have anything to worry about?
We’ve mentioned two massive solar storms with the Halloween storms and the Carrington Event. Such large storms tend to occur very infrequently. In fact, those two storms took place nearly 150 years apart. Those aren’t the strongest storms yet, though. The very worst that Earth has ever seen were what are known as Miyake events.
Miyake events are times throughout history when massive solar storms were thought to have occurred. These are measured by massive spikes in carbon-14 that were preserved in tree rings. Miyake events are few and far between, but science believes at least 15 such events have occurred over the past 15,000 years. That includes one in 12350 BCE, which may have been twice as large as any other known Miyake event.
They currently hold the title of the largest solar storms that we know of, and are thought to be caused by superflares and extreme solar events. If one of these happened today, especially one as large as the one in 12350 BCE, it would likely cause widespread, catastrophic damage and potentially threaten human life.
Those only appear to happen about once every several hundred to a couple thousand years, so it’s exceedingly unlikely that one is coming anytime soon. But solar storms on the level of the Halloween storms and the Carrington Event have happened in modern history, and humans have managed to survive them, so for the time being, there isn’t too much to worry about.
Technologies
TMR vs. Hall Effect Controllers: Battle of the Magnetic Sensing Tech
The magic of magnets tucked into your joysticks can put an end to drift. But which technology is superior?
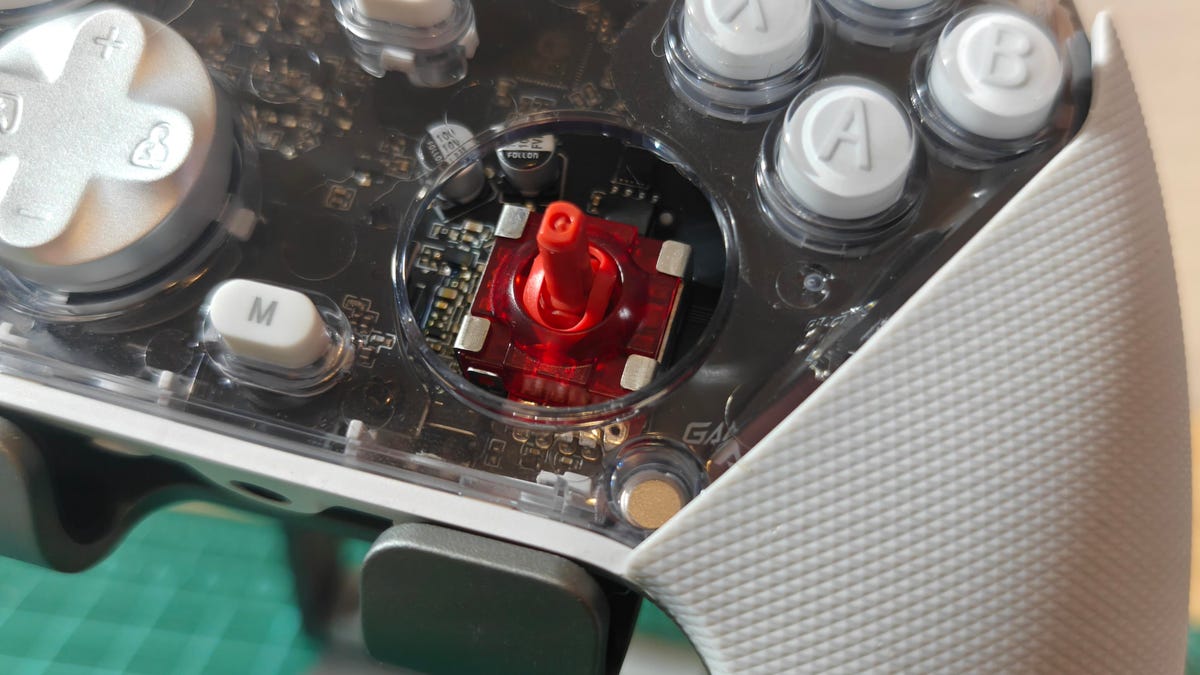
Competitive gamers look for every advantage they can get, and that drive has spawned some of the zaniest gaming peripherals under the sun. There are plenty of hardware components that actually offer meaningful edges when implemented properly. Hall effect and TMR (tunnel magnetoresistance or tunneling magnetoresistance) sensors are two such technologies. Hall effect sensors have found their way into a wide variety of devices, including keyboards and gaming controllers, including some of our favorites like the GameSir Super Nova.
More recently, TMR sensors have started to appear in these devices as well. Is it a better technology for gaming? With multiple options vying for your lunch money, it’s worth understanding the differences to decide which is more worthy of living inside your next game controller or keyboard.
How Hall effect joysticks work
We’ve previously broken down the difference between Hall effect tech and traditional potentiometers in controller joysticks, but here’s a quick rundown on how Hall effect sensors work. A Hall effect joystick moves a magnet over a sensor circuit, and the magnetic field affects the circuit’s voltage. The sensor in the circuit measures these voltage shifts and maps them to controller inputs. Element14 has a lovely visual explanation of this effect here.
The advantage this tech has over potentiometer-based joysticks used in controllers for decades is that the magnet and sensor don’t need to make physical contact. There’s no rubbing action to slowly wear away and degrade the sensor. So, in theory, Hall effect joysticks should remain accurate for the long haul.
How TMR joysticks work
While TMR works differently, it’s a similar concept to Hall effect devices. When you move a TMR joystick, it moves a magnet in the vicinity of the sensor. So far, it’s the same, right? Except with TMR, this shifting magnetic field changes the resistance in the sensor instead of the voltage.
There’s a useful demonstration of a sensor in action here. Just like Hall effect joysticks, TMR joysticks don’t rely on physical contact to register inputs and therefore won’t suffer the wear and drift that affects potentiometer-based joysticks.
Which is better, Hall effect or TMR?
There’s no hard and fast answer to which technology is better. After all, the actual implementation of the technology and the hardware it’s built into can be just as important, if not more so. Both technologies can provide accurate sensing, and neither requires physical contact with the sensing chip, so both can be used for precise controls that won’t encounter stick drift. That said, there are some potential advantages to TMR.
According to Coto Technology, who, in fairness, make TMR sensors, they can be more sensitive, allowing for either greater precision or the use of smaller magnets. Since the Hall effect is subtler, it relies on amplification and ultimately requires extra power. While power requirements vary from sensor to sensor, GameSir claims its TMR joysticks use about one-tenth the power of mainstream Hall effect joysticks. Cherry is another brand highlighting the lower power consumption of TMR sensors, albeit in the brand’s keyboard switches.
The greater precision is an opportunity for TMR joysticks to come out ahead, but that will depend more on the controller itself than the technology. Strange response curves, a big dead zone (which shouldn’t be needed), or low polling rates could prevent a perfectly good TMR sensor from beating a comparable Hall effect sensor in a better optimized controller.
The power savings will likely be the advantage most of us really feel. While it won’t matter for wired controllers, power savings can go a long way for wireless ones. Take the Razer Wolverine V3 Pro, for instance, a Hall effect controller offering 20 hours of battery life from a 4.5-watt-hour battery with support for a 1,000Hz polling rate on a wireless connection. Razer also offers the Wolverine V3 Pro 8K PC, a near-identical controller with the same battery offering TMR sensors. They claim the TMR version can go for 36 hours on a charge, though that’s presumably before cranking it up to an 8,000Hz polling rate — something Razer possibly left off the Hall effect model because of power usage.
The disadvantage of the TMR sensor would be its cost, but it appears that it’s negligible when factored into the entire price of a controller. Both versions of the aforementioned Razer controller are $199. Both 8BitDo and GameSir have managed to stick them into reasonably priced controllers like the 8BitDo Ultimate 2, GameSir G7 Pro and GameSir Cyclone 2.
So which wins?
It seems TMR joysticks have all the advantages of Hall effect joysticks and then some, bringing better power efficiency that can help in wireless applications. The one big downside might be price, but from what we’ve seen right now, that doesn’t seem to be much of an issue. You can even find both technologies in controllers that cost less than some potentiometer models, like the Xbox Elite Series 2 controller.
Caveats to consider
For all the hype, neither Hall effect nor TMR joysticks are perfect. One of their key selling points is that they won’t experience stick drift, but there are still elements of the joystick that can wear down. The ring around the joystick can lose its smoothness. The stick material can wear down (ever tried to use a controller with the rubber worn off its joystick? It’s not pleasant). The linkages that hold the joystick upright and the springs that keep it stiff can loosen, degrade and fill with dust. All of these can impact the continued use of the joystick, even if the Hall effect or TMR sensor itself is in perfect operating order.
So you might not get stick drift from a bad sensor, but you could get stick drift from a stick that simply doesn’t return to its original resting position. That’s when having a controller that’s serviceable or has swappable parts, like the PDP Victrix Pro BFG, could matter just as much as having one with Hall effect or TMR joysticks.
-

 Technologies3 года ago
Technologies3 года agoTech Companies Need to Be Held Accountable for Security, Experts Say
-

 Technologies3 года ago
Technologies3 года agoBest Handheld Game Console in 2023
-

 Technologies3 года ago
Technologies3 года agoTighten Up Your VR Game With the Best Head Straps for Quest 2
-

 Technologies4 года ago
Technologies4 года agoBlack Friday 2021: The best deals on TVs, headphones, kitchenware, and more
-

 Technologies5 лет ago
Technologies5 лет agoGoogle to require vaccinations as Silicon Valley rethinks return-to-office policies
-

 Technologies5 лет ago
Technologies5 лет agoVerum, Wickr and Threema: next generation secured messengers
-

 Technologies4 года ago
Technologies4 года agoOlivia Harlan Dekker for Verum Messenger
-

 Technologies4 года ago
Technologies4 года agoiPhone 13 event: How to watch Apple’s big announcement tomorrow
