Technologies
Spotify, Apple Music and more: What’s the best music app for you?
We compare the big streaming music services.
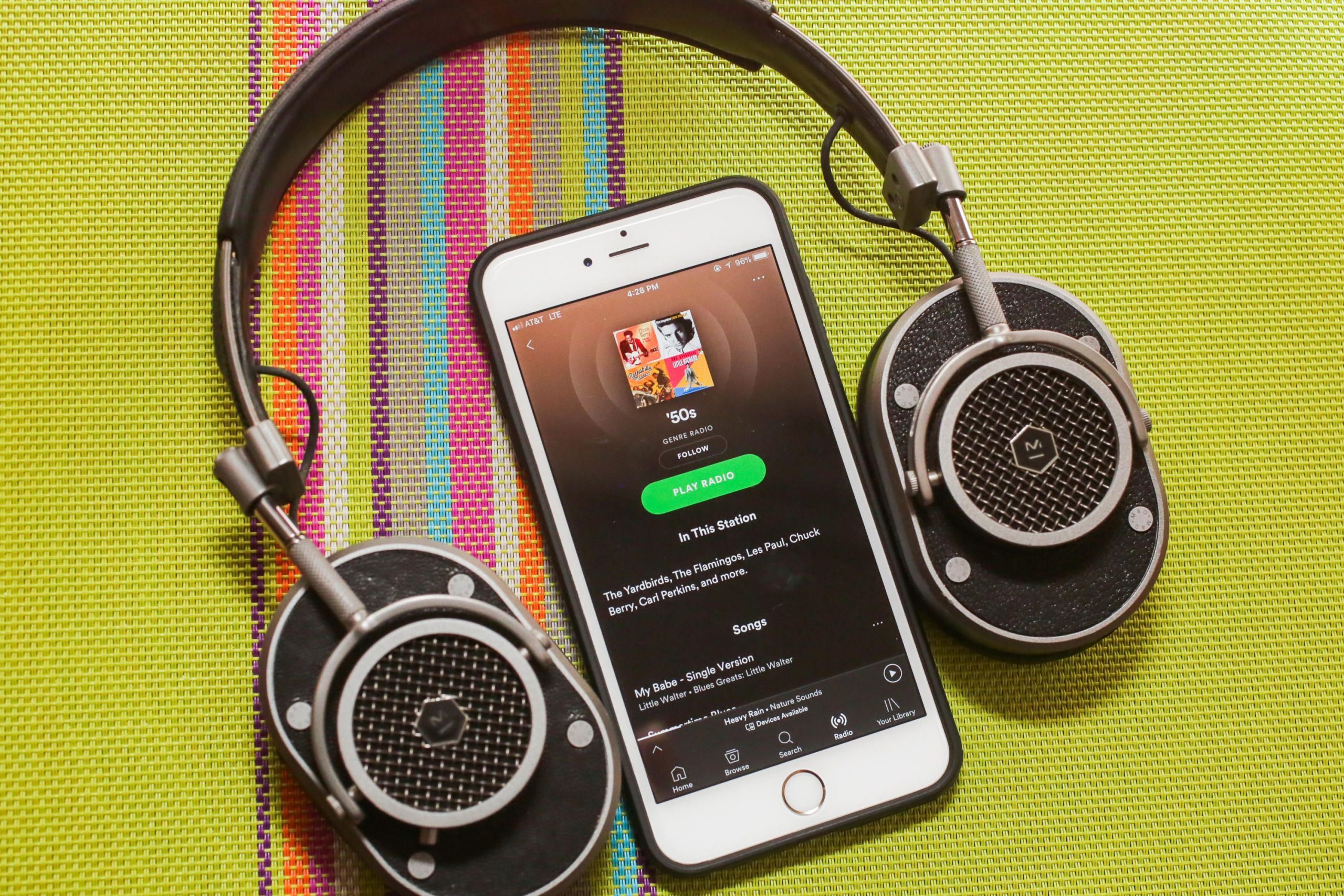
Sure, all the audiophiles and cool kids are talking about a vinyl resurgence and squabbling over the best turntables. But admit it, streaming music still is the most convenient way to listen to your favorite songs. While streaming used to mean sacrificing sound quality, that’s no longer the case. In fact, streaming music can sound indistinguishable from, or even superior to, an old-fashioned CD.
The question is, which streaming music service is best for you? We checked out Spotify, Amazon Music, Apple Music, YouTube Music, Tidal, Qobuz, Deezer and Pandora Premium to see how each platform stacks up for your subscription buck. While most offer music catalogs of over 50 million songs, each has its own unique pros and cons. We’ve also left out services that only play music in a radio format and don’t offer a la carte listening to allow you to select your own songs.
Services typically charge $10 a month and don’t have a contract, but swapping between them isn’t as straightforward as TV streaming. If you don’t want to rebuild your playlists and library from scratch when you switch, you have two main options — a music locker service such as YouTube Music, or the library import tool Soundiiz. The latter option can read the library from each of your music services and transfer them, and while there’s a $4.50 monthly charge, you can always cancel once you’ve converted your library.
So which music streaming services offer the best combination of price, sound quality and library size? Read on to find an in-depth look at each of the services and a feature comparison, along with a full price breakdown in the chart at the bottom of the page. We’ll update this list periodically. And if you want the TL;DR, these are the top three.
The best of the rest
Amazon Music Unlimited
Amazon Music Unlimited is the «grownup» (a.k.a. paid) version of Amazon Prime Music, which any Prime subscriber gets for «free.» It offers a greatly expanded catalog for an extra outlay per month: $8 for Prime members and $10 if you don’t have Prime. Rather than focusing on the cutting edge of music as some others here do, the Amazon music service features recommended playlists and radio stations that are grouped around artists you’ve already listened to.
The Good
- Cheaper than the top three if you’re an Amazon Prime member
- Lyrics automatically pop up on the «now playing» screen
- Offers free music stations for Amazon Echo, Echo Dot ($17 at Amazon) and Amazon Tap (includes ads)
- Step-up Amazon Prime Music HD service ($12.99 for Prime members) includes high-res and surround music from Sony 360 Reality Audio and Dolby Atmos
The Bad
- Artist profiles don’t have biographies
- Officially advertised as «tens of millions» of tracks strong, it’s unclear if the catalog is quite as large as its competitors
- The service no longer includes a music locker
Best for: Amazon Prime members who want to save a few bucks on a decent music catalog
YouTube Music
YouTube Music is the successor to Google Play Music, and if you sign up for the ad-free YouTube Premium you get YouTube Music thrown in for free. The good news is that YouTube Music is a mostly impressive service, and Google has retained the predecessor’s music locker system. If you have a legacy Google Play Music account you may be able to still transfer your library over to YouTube Music. And it’s not just legacy content: YouTube Music allows users to upload new tracks to its online music locker, too.
In even better news, YouTube Music offers a cleaner interface than Google Play Music. Instead of playlists, YouTube Music offers well-curated radio stations, which are the standout features. Unlike playlists, which are finite and contain specific tracks, radio stations play endlessly and are updated often.
The Good
- Monthly fee includes subscription to YouTube Music: commercial-free streaming on YouTube and YouTube Music
- Over 40 million tracks
- Retains Google Play Music’s music locker system: You can transfer existing songs from the old service, plus upload new ones in YouTube Music
The Bad
- The continued existence of Google Play Music is confusing for existing users
Best for: Heavy YouTube users and Android device users.
Pandora Premium
One of the most popular streaming radio services in the US, Pandora also offers the a la carte Premium ($10 a month)and no-ads Plus ($5 a month). The result is more flexibility than most competitors, and Premium has gained plenty more subscribers in recent years, even if the service is behind in terms of overall catalog size.
The Good
- One of the largest user bases, thanks to its free version
- Pandora’s Music Genome Project analyzes each track according to 450 different attributes in order to give better suggestions
The Bad
- Its audio quality is among the lowest available, even on the Premium subscription (192Kbps)
- It doesn’t really offer enough of an incentive for an upgrade from the free tier compared to the others here
- Not available outside the US
Best for: Pandora Premium is of most interest to people who already use Pandora and want to be able to pick exactly what they listen to. We’d recommend it to almost no one else.
Qobuz
Qobuz launched in the US in February 2019 with a clean interface, hi-res audio streams (which unlike Tidal’s don’t need an MQA decoder) and the ability to buy lossless music. It offers two plans — the hi-res Studio Premier for $15 a month and the $249 annual Sublime Plus, which offers discounts on the store. At 50 million tracks, Qobuz’s streaming catalog isn’t quite at the level of Tidal or Spotify, but it should be sufficient for everything but the more obscure artists.
The Good
- The app is really clean and fun to use
- Ability to listen to 24-bit music without needing a specialized decoder
- One of the most affordable hi-res services
- First 24-bit streaming service on Sonos
The Bad
- Some gaps in the catalog
Best for: Audiophiles who want hi-res music for a decent price plus the ability to buy and download albums
Deezer
French stalwart Deezer has been operating in the States since 2016, and it has a lot to offer, including a free tier (mobile only) and 56 million tracks. It has more than subscribers than some others on this list thanks, in part, to its previous affiliation with Cricket Wireless. The main Premium plan is $10 a month but users are also able to upgrade to a lossless version (CD quality) for $15 a month. While it reportedly boasts more users than Tidal, the service doesn’t offer enough to differentiate it from its similarly priced competitors.
What else do you need to know?
Streaming radio vs. on-demand
This guide covers on-demand music streaming services, and for that reason, we’ve purposely left out services that only play music in a radio format. Until recently this list excluded Pandora, but now that the company also offers a Premium tier we’ve included it here. Slacker Radio, TuneIn and iHeartRadio are other radio-style services that play music stations based around a theme or artist, without you explicitly picking tracks.
Music lockers: Your MP3s in the cloud
Amazon was one of the first services to offer uploading your MP3 collection into the cloud, but this was officially discontinued in 2018. Meanwhile, the Apple and Google services listed either allow you to combine your personal music collection with the streaming catalog, though tagging and organization can be a time-consuming challenge (your myriad live Phish tracks won’t organize themselves). Still, if you’ve invested money in digital music over the years, those two services offer a patch to continue enjoying that music online.
Music catalog sizes compared
The number of songs offered by a music service used to be one of the main differentiators, but most now have between 50 million and 70 million songs or more. However, depending on your favored genre, some of them have a more robust catalog that include many under-the-radar, indie or hip-hop artists. If you’re musically inclined, constantly on the hunt for your favorite new band, a streaming service like Spotify or Tidal may be more up your alley. Users who are less ambitious about expanding their musical taste will be satisfied with the smaller catalogs Amazon Music Unlimited or Pandora offer. Apple Music is somewhere in the middle, offering a healthy mix of mainstream tunes and underground unknowns.
Technologies
November Nights Will Dazzle with Three Meteor Showers. Here’s How to Watch Like a Pro
You won’t need binoculars or a telescope, but you will need to get away from urban and suburban lights.
Get ready for an active November, skygazers. The month features three annual meteor showers — the Northern Taurids, the Southern Taurids, and the Leonids — two of which are already active. Northern Taurids started on Oct. 20, and Southern Taurids — one of the longest meteor showers of the year — began on Sept. 20. Leonids are expected to start on Nov. 6.
Even though two of these meteor showers are already in progress, the best parts of each are still to come. All three showers peak during November. And while these showers aren’t as prolific as the biggest ones, including August’s Perseids and January’s Quadrantids, you can still marvel at meteors with a bit of luck and some tips we’ll provide.
Not everyone understands what a meteor shower actually is, but it’s fairly simple. Shooting stars are a common occurrence in space around planet Earth. According to NASA, 48.5 tons of meteoritic material hit Earth’s atmosphere every year. Sometimes, enough of that material comes from the same spot, and we humans refer to those as meteor showers.
Don’t miss any of our unbiased tech content and lab-based reviews. Add CNET as a preferred Google source.
Southern Taurids: The longest one
The Southern Taurids shower lasts for two months, making it one of the longest meteor showers of the year.
Southern Taurids is scheduled to peak on the evening of Nov. 4 into Nov. 5, and should spawn upwards of five meteors per hour during that peak. Southern Taurids is known for its increased chance of fireballs, which are meteors that are brighter than most. According to some reports, these fireballs can be brighter than the planet Venus when they streak across the night sky.
All meteor showers are named for the constellations where they appear to originate, a spot known as the radiant. For the Southern Taurids, the radiant is in the Taurus constellation near the Pleiades star cluster, so that is where you’ll want to look for them. Taurus will be visible in the eastern sky shortly after sunset and end its evening in the western sky as the sun rises.
Northern Taurids: Peaks later than its sibling
The Northern Taurids meteor shower is set to peak on Nov. 11 and 12. It’s identical to the Southern Taurids, only with a later peak date. The origin point will be the Taurus constellation, producing an average of five meteors per hour with an increased chance of fireballs.
Leonids: The most active
Of the three November meteor showers, Leonids should be the most active. It is fed by the Tempel-Tuttle Comet, which can produce some dense debris clouds, resulting in very strong showers. Leonids is set to peak on Nov. 16-17.
Some sources say as many as 15 visible meteors per hour is possible, while NASA estimates a more conservative three per hour under dark skies. It’s impossible to know for sure how active this shower will be until the peak occurs..
As the name implies, Leonids will appear out of the Leo constellation. Leo is visible in the eastern sky between midnight and 1 a.m. local time.
Per the American Meteor Society, Leonids has produced some intense meteor showers as recently as 2002, but isn’t scheduled to do so again until 2031, 2064, and 2099 as the comet returns to the solar system. During these rare meteor storms, NASA says that it’s possible to see upwards of 1,000 meteors per hour.
Tips for watching meteor showers
Here are some tips and tricks that will help increase your odds of spotting a meteor in November.
Get away from light pollution
This is the most important guideline to follow. Simply put, city lights make meteors harder to see.
«Light pollution will definitely hamper your viewing of meteors,» Michelle Nichols, director of public observing at the Adler Planetarium in Chicago, told CNET. «The more light pollution you are under, the fewer meteors you’ll see.»
Nichols says that unfavorable conditions can reduce the number of meteors you see by upwards of 75%.
Head to the countryside and find a spot that is as dark as possible. (There are other sources of light pollution that humans can’t do anything about, like the moon.)
The Southern Taurids peaks during November’s full moon, which is also a supermoon, meaning it shares the maximum amount of light pollution you can get from the moon. If you’re going to skip any of these showers, the Southern Taurids is probably the best choice. The other two showers will have much more favorable celestial conditions.
Don’t take any equipment
Meteor showers typically have an origin point, but you won’t need binoculars or telescopes.
«You want to just use your eyes,» said Nichols. «Binoculars or telescopes both look at ever-smaller pieces of sky, and you want to be able to look around at the entire sky.»
Meteors are very fast, and a magnification device may obstruct your ability to see the whole path. Nichols says that Taurids meteors tend to travel at 17 to 18 miles per second while Orionids may travel as fast as 41 miles per second.
Also, meteors don’t last for a long time.
«Look for short-lived, quick streaks of light,» Nichols says. «Meteors tend to last a fraction of a second to maybe a few seconds for the longer-lived ones.»
Nichols also notes that much of the material falling to Earth’s surface is «only about the size of a grain of sand.» As such, the streak humans often see isn’t the meteor itself, but rather the «glowing, superheated air that surrounds that bit of comet material» as it plummets toward Earth.
Dress for the occasion
Unless you live in the Deep South, it’s likely to be cold outside in November. Dressing for the occasion means you’ll be able to stay out longer, even if it’s chilly.
«When you go outside, dress warmly in layers, even if it’s not terribly cold where you are,» says Nichols. «You’ll be out there for a while, and at night, you may easily get chilled, especially if it’s damp out.»
Nichols recommends bringing an extra chair to put your feet on to keep them off the cold ground, especially if it’s wet, and also recommends against drinking alcohol, which causes blood vessels to dilate, causing the body to lose heat faster.
Patience is a virtue
The phrase «it’s a marathon, not a sprint» is about as apropos as it gets for meteor watching. Showers are unpredictable, and every number you’ve seen in this article or elsewhere online is essentially an estimate. You’ll want to make sure to give yourself as much time as you can to get settled.
«Give your eyes at least 20-30 minutes to adjust to the darkness,» Nichols advises. «You may not see meteors right away. And when you do, they’ll be sporadic.»
If it were easy to spot meteors, then it wouldn’t be special. You can help yourself by reducing your phone screen brightness to its lowest setting to preserve your night vision, and by using flashlights, not big camping lanterns.
Technologies
Today’s NYT Mini Crossword Answers for Sunday, Nov. 2
Here are the answers for The New York Times Mini Crossword for Nov. 2.
Looking for the most recent Mini Crossword answer? Click here for today’s Mini Crossword hints, as well as our daily answers and hints for The New York Times Wordle, Strands, Connections and Connections: Sports Edition puzzles.
Need some help with today’s Mini Crossword? A few clues are tricky. Read on for the answers. And if you could use some hints and guidance for daily solving, check out our Mini Crossword tips.
If you’re looking for today’s Wordle, Connections, Connections: Sports Edition and Strands answers, you can visit CNET’s NYT puzzle hints page.
Read more: Tips and Tricks for Solving The New York Times Mini Crossword
Let’s get to those Mini Crossword clues and answers.
Mini across clues and answers
1A clue: State with more pigs than people
Answer: IOWA
5A clue: Sporcle offering
Answer: QUIZ
6A clue: Facial cavity that can become congested
Answer: SINUS
7A clue: Jamaican style of preparing chicken
Answer: JERK
9A clue: On the ocean
Answer: ASEA
Mini down clues and answers
1D clue: Geniuses have high ones
Answer: IQS
2D clue: Kind of board whose name is trademarked by Hasbro
Answer: OUIJA
3D clue: Drinks kept in a cellar
Answer: WINES
4D clue: Sky-blue
Answer: AZURE
7D clue: Reggae relative
Answer: SKA
Technologies
Today’s NYT Connections: Sports Edition Hints and Answers for Nov. 2, #405
Here are hints and the answers for the NYT Connections: Sports Edition puzzle for Nov. 2, No. 405.
Looking for the most recent regular Connections answers? Click here for today’s Connections hints, as well as our daily answers and hints for The New York Times Mini Crossword, Wordle and Strands puzzles.
Today’s Connections: Sports Edition is a tricky one. If you’re struggling but still want to solve it, read on for hints and the answers.
Connections: Sports Edition is published by The Athletic, the subscription-based sports journalism site owned by the Times. It doesn’t show up in the NYT Games app but appears in The Athletic’s own app. Or you can play it for free online.
Read more: NYT Connections: Sports Edition Puzzle Comes Out of Beta
Hints for today’s Connections: Sports Edition groups
Here are four hints for the groupings in today’s Connections: Sports Edition puzzle, ranked from the easiest yellow group to the tough (and sometimes bizarre) purple group.
Yellow group hint: Sports where you need a certain piece of equipment.
Green group hint: Do very well.
Blue group hint: Football position.
Purple group hint: Fore!
Answers for today’s Connections: Sports Edition groups
Yellow group: Racket sports.
Green group: Prosper.
Blue group: Current NFL running backs.
Purple group: ____ golf.
Read more: Wordle Cheat Sheet: Here Are the Most Popular Letters Used in English Words
What are today’s Connections: Sports Edition answers?
The yellow words in today’s Connections
The theme is racket sports. The four answers are badminton, racquetball, squash and tennis.
The green words in today’s Connections
The theme is prosper. The four answers are blossom, develop, flourish and grow.
The blue words in today’s Connections
The theme is current NFL running backs. The four answers are Cook, Hall, Swift and Walker.
The purple words in today’s Connections
The theme is ____ golf. The four answers are disc, links, mini and Top.
-
Technologies3 года ago
Tech Companies Need to Be Held Accountable for Security, Experts Say
-
Technologies3 года ago
Best Handheld Game Console in 2023
-
Technologies3 года ago
Tighten Up Your VR Game With the Best Head Straps for Quest 2
-
Technologies4 года ago
Verum, Wickr and Threema: next generation secured messengers
-
Technologies4 года ago
Black Friday 2021: The best deals on TVs, headphones, kitchenware, and more
-
Technologies4 года ago
Google to require vaccinations as Silicon Valley rethinks return-to-office policies
-
Technologies4 года ago
Olivia Harlan Dekker for Verum Messenger
-
Technologies4 года ago
iPhone 13 event: How to watch Apple’s big announcement tomorrow